
Company News
Connect with Socket at RSA and BSidesSF 2024
Come meet the Socket team at BSidesSF and RSA! We're sponsoring several fun networking events and we would love to see you there.
@carlosvpi/flux
Advanced tools
Weekly downloads
Readme
Reactive programming made easy
A flux is an asynchronous stream if values. A flux is created open. While a flux is open, new values can be pushed to it. The flux can be terminated.
yarn add @carlosvpi/flux
const { Flux } = require('@carlosvpi/flux')
The constructor of the class Flux accepts two parameters:
(push: (value) => any, end: () => any, value: () => any) => any: the builder calls push whenever a value is to be pushed into the flux. To terminate the flux, the method end is called. The method value returns the value of the flux at any given moment. The value returned by the builder will be passed as a parameter to the second parameter in the constructor, the cleaner. Functions push and end return the created flux.(cleanData: any) => any: the cleaner takes as an argument the value returned by the builder. The cleaner is called when the flux is terminated. It can perform a last operation to clean memory or other processes (like clearing intervales).const flux = new Flux(push => push(42))
The above code creates a flux with value 42.
const flux = new Flux((push, end, value) => push(0) && setInterval(() => value() > 10 ? end() : push(value()+1), 1000), clearInterval)
The above code creates a flux that increments its value, starting from 0, every second, and clears the interval one second after reaching 10.
flux.push pushes a value into the flux.
flux.push(1)
The above call changes the internal value of the flux to 1.
A call to push triggers all the flux's subscriptions. If the flux is terminated, flux.push wont have any effect. The call to push returns the flux itself.
flux.end terminates flux.
flux.end()
The above call terminates the flux.
A call to end triggers all the flux's subscriptions. If the flux is terminated, flux.end wont have any effect. The call to end returns the flux itself.
flux.subscribe subscribes a method, called subscription, to the flux. A subscription is a function that receives parameters value and done, and is called every time a value is pushed to the flux, or it is terminated. When the flux is updated via push, value is given the current value of the flux, and done = false. When the flux is terminated, value has the last value of the flux and done = true.
flux.subscribe(console.log)
The above code logs each value of the flux, and whether it is terminated or not.
This call returns the flux.
flux.unsubscribe(subscription) removes a subscription from the flux, so it won't be triggered on push or end.
This call returns the flux.
flux.pop(...subscriptions) both call the subscriptions and subscribe them to the flux.
This call returns the flux.
flux.map(f) returns a flux whose values are those of flux operated by f. It ends at the same time as flux.
flux.reduce((acc, value) => f(acc, value), initial) returns a flux reductor whose values are the result of operating f with the current value of the reductor and the current value of the flux. The initial value of the reductor is initial. It ends at the same time as flux.
flux.filter(p) returns a flux whose values are those of flux that return true when operated by p. It ends at the same time as flux.
flux.reject(p) returns a flux whose values are those of flux that return false when operated by p. It ends at the same time as flux.
flux.compact(p) returns a flux whose values are those of flux that are truthy. It ends at the same time as flux.
flux.last(n: number) returns a flux whose values are an array of the n last values produced by flux. It ends at the same time as flux.
flux.toPromise() returns a promise that is resolved with the next value pushed to the flux. If the flux is terminated before getting a new value, the promise is rejected.
flux.mergeRace(...fluxes) returns a flux whose value is the value of the last of the fluxes (from its parameters and also flux) that was updated. It ends at the same time as the first flux ends.
flux.mergeAll(...fluxes) returns a flux whose value is the value of the last of the fluxes (from its parameters and also flux) that was updated. It ends at the same time as the last flux ends.
flux.debounce(ms) returns a flux whose value is the debounced (by ms milliseconds) value of flux. This is, upon a value is pushed to flux, that value is pushed to the debounced flux after ms milliseconds unless another value is pushed to flux in the meantime. It ends at the same time as the last flux ends.
flux.throttle(ms) returns a flux whose value is the throttled (by ms milliseconds) value of flux. This is, upon a value is pushed to flux, throttled pushes said value and sets a timer for ms milliseconds. While the timer is running no new pushes to flux are pushed to throttled. It ends at the same time as the last flux ends.
Flux.fromTimeout(ms) creates a flux. After ms milliseconds an undefined value is pushed, and then the flux is terminated. It is possible to terminate the flux before the timeout with flux.end().
Flux.fromInterval(ms) creates a flux. It sets an internval of ms milliseconds, and on each interval an undefined value is pushed. It is possible to terminate the flux with flux.end().
Flux.fromPromiseFactory(getPromise) creates a flux fromPromise. The parameter getPromise is a function that takes a {clear:()=>any} object and returns a promise. When getPromise is resolved when a value, that value is pushed to fromPromise and a new promise from getPromise is awaited. It is possible to terminate the flux with flux.end().
Flux.fromEvent(DOMNode, eventName, useCapture) creates a fromEvent flux and attaches an eventListener to a DOM node. Every time the specified event type is triggered in the DOM node, the event is pushed to fromEvent. It is possible to detach the eventListener from the DOM node by terminating fromEvent.
FAQs
Reactive programming made easy
The npm package @carlosvpi/flux receives a total of 0 weekly downloads. As such, @carlosvpi/flux popularity was classified as not popular.
We found that @carlosvpi/flux demonstrated a not healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Company News
Come meet the Socket team at BSidesSF and RSA! We're sponsoring several fun networking events and we would love to see you there.

Security News
OSI is starting a conversation aimed at removing the excuse of the SaaS loophole for companies navigating licensing and the complexities of doing business with open source.
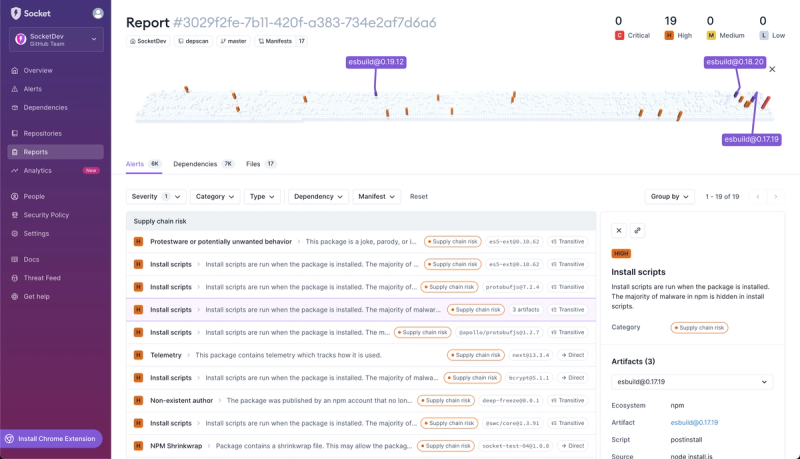
Product
We're introducing dependency visualization for reports - get a quick impression of the state of your dependencies without getting lost in the details.