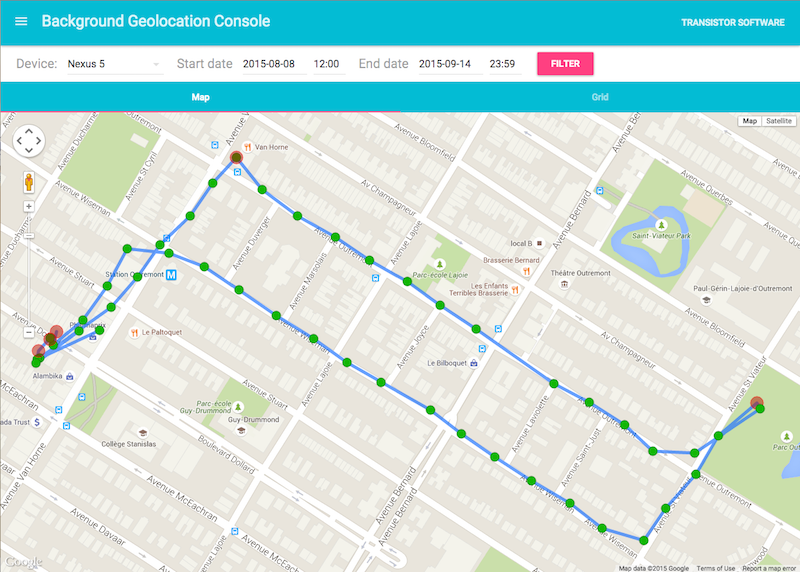
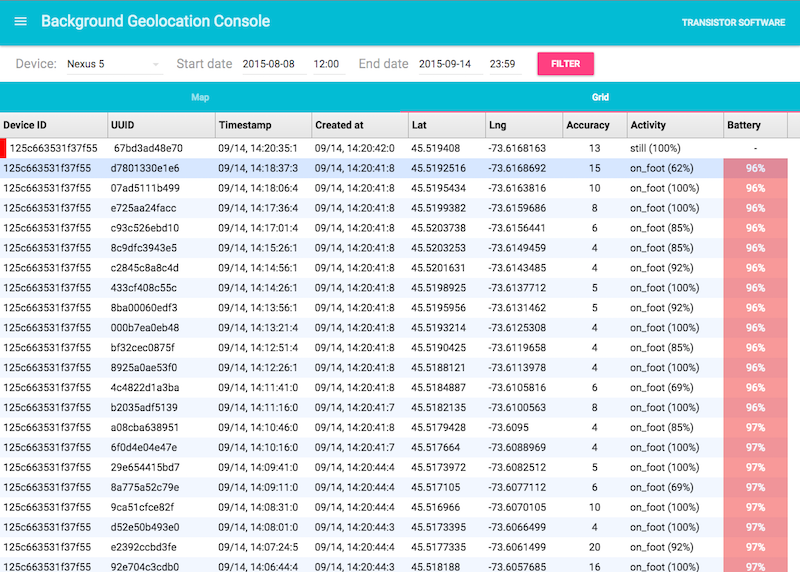
Background Geolocation for React Native · [Premium Version]

The most sophisticated background location-tracking & geofencing module with battery-conscious motion-detection intelligence for iOS and Android.
The plugin's Philosophy of Operation is to use motion-detection APIs (using accelerometer, gyroscope and magnetometer) to detect when the device is moving and stationary.
-
When the device is detected to be moving, the plugin will automatically start recording a location according to the configured distanceFilter (meters).
-
When the device is detected be stationary, the plugin will automatically turn off location-services to conserve energy.
Also available for Cordova, NativeScript and pure native apps.

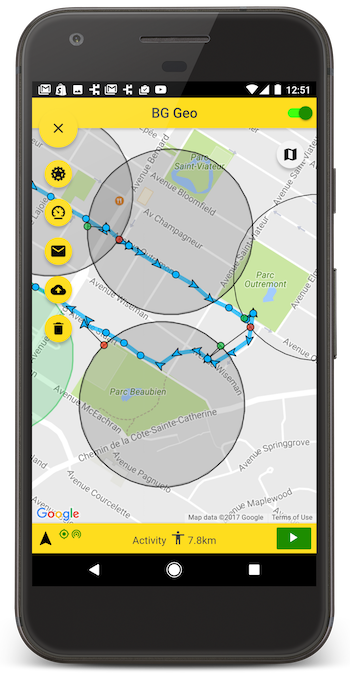
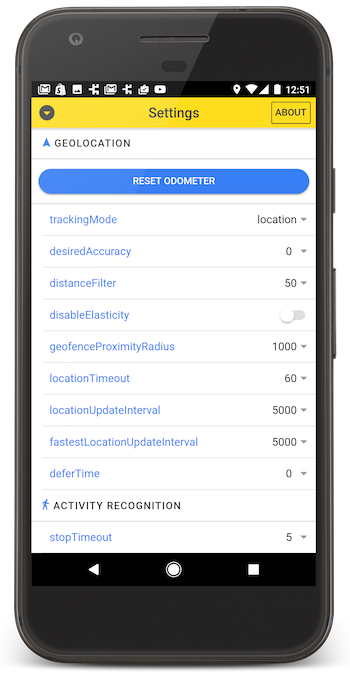
Contents
:large_blue_diamond: Installing the Plugin
[!WARNING]
Customers should uninstall react-native-background-geolocation and re-install from this private repo. See wiki Migrating from public package to private repo
But why install from the Private Repo? What's the difference?
- Latest updates (new features, bug-fixes) arrive first here at the private repo.
- The public version
react-native-background-geolocation is updated only about every 3 months.
With yarn
yarn add https://github.com/transistorsoft/react-native-background-geolocation-android.git
If you have problems installing with yarn, add the following to your ~/.ssh/config file:
Host github.com
User git
With npm
npm install git+https://git@github.com:transistorsoft/react-native-background-geolocation-android.git --save
- Note: For both
yarn add and npm install, you should append a #version to the url (eg: #4.0.2). See Releases for a list of all available versions.
- Authentication problems? See here
With Expo
[!WARNING]
The private repo cannot be used with Expo due to problems with Expo modules installed from private Github repos. Continue using the version installed from npm as documented in the public github repo.
:large_blue_diamond: Setup Guides
[!WARNING]
If you're upgrading from the public react-native-background-geolocation version, you need to completely remove that version.
iOS
Android
Expo
[!WARNING]
The private repo cannot be used with Expo due to problems with Expo modules installed from private Github repos. Continue using the version installed from npm as documented in the public github repo.
:large_blue_diamond: Configure your license
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.transistorsoft.backgroundgeolocation.react">
<application
android:name=".MainApplication"
android:allowBackup="true"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme">
<!-- react-native-background-geolocation licence -->
+ <meta-data android:name="com.transistorsoft.locationmanager.license" android:value="YOUR_LICENCE_KEY_HERE" />
.
.
.
</application>
</manifest>
:large_blue_diamond: Using the plugin
import BackgroundGeolocation from 'react-native-background-geolocation-android';
For those using Typescript (recommended), you can also import the interfaces:
import BackgroundGeolocation, {
State,
Config,
Location,
LocationError,
Geofence,
GeofenceEvent,
GeofencesChangeEvent,
HeartbeatEvent,
HttpEvent,
MotionActivityEvent,
MotionChangeEvent,
ProviderChangeEvent,
ConnectivityChangeEvent
} from "react-native-background-geolocation-android";
:large_blue_diamond: Example
There are three main steps to using BackgroundGeolocation
- Wire up event-listeners.
.ready(config) the plugin..start() the plugin.
[!WARNING]
Do not execute any API method which will require accessing location-services until the .ready(config) method resolves (Read its API docs), For example:
.getCurrentPosition.start
BackgroundGeolocation.getCurrentPosition(options);
BackgroundGeolocation.start();
BackgroundGeolocation.ready(config).then((state) => {
BackgroundGeolocation.getCurrentPosition(options);
BackgroundGeolocation.start();
});
BackgroundGeolocation.getCurrentPosition(options);
BackgroundGeolocation.start();
Example 1. — React Functional Component
Show Source
import React from 'react';
import {
Switch,
Text,
View,
} from 'react-native';
import BackgroundGeolocation, {
Location,
Subscription
} from "react-native-background-geolocation-android";
const HelloWorld = () => {
const [enabled, setEnabled] = React.useState(false);
const [location, setLocation] = React.useState('');
React.useEffect(() => {
const onLocation:Subscription = BackgroundGeolocation.onLocation((location) => {
console.log('[onLocation]', location);
setLocation(JSON.stringify(location, null, 2));
})
const onMotionChange:Subscription = BackgroundGeolocation.onMotionChange((event) => {
console.log('[onMotionChange]', event);
});
const onActivityChange:Subscription = BackgroundGeolocation.onActivityChange((event) => {
console.log('[onMotionChange]', event);
})
const onProviderChange:Subscription = BackgroundGeolocation.onProviderChange((event) => {
console.log('[onProviderChange]', event);
})
BackgroundGeolocation.ready({
desiredAccuracy: BackgroundGeolocation.DESIRED_ACCURACY_HIGH,
distanceFilter: 10,
stopTimeout: 5,
debug: true,
logLevel: BackgroundGeolocation.LOG_LEVEL_VERBOSE,
stopOnTerminate: false,
startOnBoot: true,
url: 'http://yourserver.com/locations',
batchSync: false,
autoSync: true,
headers: {
"X-FOO": "bar"
},
params: {
"auth_token": "maybe_your_server_authenticates_via_token_YES?"
}
}).then((state) => {
setEnabled(state.enabled)
console.log("- BackgroundGeolocation is configured and ready: ", state.enabled);
});
return () => {
onLocation.remove();
onMotionChange.remove();
onActivityChange.remove();
onProviderChange.remove();
}
}, []);
React.useEffect(() => {
if (enabled) {
BackgroundGeolocation.start();
} else {
BackgroundGeolocation.stop();
setLocation('');
}
}, [enabled]);
return (
<View style={{alignItems:'center'}}>
<Text>Click to enable BackgroundGeolocation</Text>
<Switch value={enabled} onValueChange={setEnabled} />
<Text style={{fontFamily:'monospace', fontSize:12}}>{location}</Text>
</View>
)
}
export default HelloWorld;
Example 2. — React Class Component
Show Source
import React from 'react';
import {
Switch,
Text,
View,
} from 'react-native';
import BackgroundGeolocation, {
Location,
Subscription
} from "react-native-background-geolocation-android";
export default class HelloWorld extends React.Component {
subscriptions:Subscription[] = [];
state:any = {};
constructor(props:any) {
super(props);
this.state = {
enabled: false,
location: ''
}
}
componentDidMount() {
this.subscriptions.push(BackgroundGeolocation.onLocation((location) => {
console.log('[onLocation]', location);
this.setState({location: JSON.stringify(location, null, 2)})
}, (error) => {
console.log('[onLocation] ERROR:', error);
}))
this.subscriptions.push(BackgroundGeolocation.onMotionChange((event) => {
console.log('[onMotionChange]', event);
}))
this.subscriptions.push(BackgroundGeolocation.onActivityChange((event) => {
console.log('[onActivityChange]', event);
}))
this.subscriptions.push(BackgroundGeolocation.onProviderChange((event) => {
console.log('[onProviderChange]', event);
}))
BackgroundGeolocation.ready({
desiredAccuracy: BackgroundGeolocation.DESIRED_ACCURACY_HIGH,
distanceFilter: 10,
stopTimeout: 5,
debug: true,
logLevel: BackgroundGeolocation.LOG_LEVEL_VERBOSE,
stopOnTerminate: false,
startOnBoot: true,
url: 'http://yourserver.com/locations',
batchSync: false,
autoSync: true,
headers: {
"X-FOO": "bar"
},
params: {
"auth_token": "maybe_your_server_authenticates_via_token_YES?"
}
}).then((state) => {
this.setState({enabled: state.enabled});
console.log("- BackgroundGeolocation is configured and ready: ", state.enabled);
})
}
componentWillUnmount() {
this.subscriptions.forEach((subscription) => subscription.remove());
}
onToggleEnabled(value:boolean) {
console.log('[onToggleEnabled]', value);
this.setState({enabled: value})
if (value) {
BackgroundGeolocation.start();
} else {
this.setState({location: ''});
BackgroundGeolocation.stop();
}
}
render() {
return (
<View style={{alignItems:'center'}}>
<Text>Click to enable BackgroundGeolocation</Text>
<Switch value={this.state.enabled} onValueChange={this.onToggleEnabled.bind(this)} />
<Text style={{fontFamily:'monospace', fontSize:12}}>{this.state.location}</Text>
</View>
)
}
}
Promise API
The BackgroundGeolocation Javascript API supports Promises for nearly every method (the exceptions are #watchPosition and adding event-listeners via #onXXX method (eg: onLocation). For more information, see the API Documentation
BackgroundGeolocation.ready({
desiredAccuracy: BackgroundGeolocation.DESIRED_ACCURACY_HIGH,
distanceFilter: 50
}).then(state => {
console.log('- BackgroundGeolocation is ready: ', state);
}).catch(error => {
console.warn('- BackgroundGeolocation error: ', error);
});
try {
const state = await BackgroundGeolocation.ready({
desiredAccuracy: BackgroundGeolocation.DESIRED_ACCURACY_HIGH,
distanceFilter: 50
})
console.log('- BackgroundGeolocation is ready: ', state);
} catch (error) {
console.warn('- BackgroundGeolocation error: ', error);
}
A fully-featured Demo App is available in its own public repo. After first cloning that repo, follow the installation instructions in the README there. This demo-app includes a settings-screen allowing you to quickly experiment with all the different settings available for each platform.


A simple Node-based web-application with SQLite database is available for field-testing and performance analysis. If you're familiar with Node, you can have this server up-and-running in about one minute.