
Security News
Research
Data Theft Repackaged: A Case Study in Malicious Wrapper Packages on npm
The Socket Research Team breaks down a malicious wrapper package that uses obfuscation to harvest credentials and exfiltrate sensitive data.
graphql-schema-linter
Advanced tools
Command line tool and package to validate GraphQL schemas against a set of rules.
This package provides a command line tool to validate GraphQL schema definitions against a set of rules.
If you're looking to lint your GraphQL queries, check out this ESLint plugin: apollographql/eslint-plugin-graphql.
Yarn:
yarn global add graphql-schema-linter
npm:
npm install -g graphql-schema-linter
Usage: graphql-schema-linter [options] [schema.graphql ...]
Options:
-r, --rules <rules>
only the rules specified will be used to validate the schema
example: --rules fields-have-descriptions,types-have-descriptions
-f, --format <format>
choose the output format of the report
possible values: compact, json, text
-s, --stdin
schema definition will be read from STDIN instead of specified file
-c, --config-directory <path>
path to begin searching for config files
-p, --custom-rule-paths <paths>
path to additional custom rules to be loaded. Example: rules/*.js
--comment-descriptions
use old way of defining descriptions in GraphQL SDL
--old-implements-syntax
use old way of defining implemented interfaces in GraphQL SDL
--version
output the version number
-h, --help
output usage information
Using lint-staged and husky, you can lint your staged GraphQL schema file before you commit. First, install these packages:
yarn add --dev lint-staged husky
Then add a precommit script and a lint-staged key to your package.json like so:
{
"scripts": {
"precommit": "lint-staged"
},
"lint-staged": {
"*.graphql": ["graphql-schema-linter path/to/*.graphql"]
}
}
The above configuration assumes that you have either one schema.graphql file or multiple .graphql files that should
be concatenated together and linted as a whole.
If your project has .graphql query files and .graphql schema files, you'll likely need multiple entries in the
lint-staged object - one for queries and one for schema. For example:
{
"scripts": {
"precommit": "lint-staged"
},
"lint-staged": {
"client/*.graphql": ["eslint . --ext .js --ext .gql --ext .graphql"],
"server/*.graphql": ["graphql-schema-linter server/*.graphql"]
}
}
If you have multiple schemas in the same folder, your lint-staged configuration will need to be more specific, otherwise
graphql-schema-linter will assume they are all parts of one schema. For example:
Correct:
{
"scripts": {
"precommit": "lint-staged"
},
"lint-staged": {
"server/schema.public.graphql": ["graphql-schema-linter"],
"server/schema.private.graphql": ["graphql-schema-linter"]
}
}
Incorrect (if you have multiple schemas):
{
"scripts": {
"precommit": "lint-staged"
},
"lint-staged": {
"server/*.graphql": ["graphql-schema-linter"]
}
}
In addition to being able to configure graphql-schema-linter via command line options, it can also be configured via
one of the following configuration files.
For now, only rules, customRulePaths and schemaPaths can be configured in a configuration file, but more options may be added in the future.
package.json{
"graphql-schema-linter": {
"rules": ["enum-values-sorted-alphabetically"],
"schemaPaths": ["path/to/my/schema/files/**.graphql"],
"customRulePaths": ["path/to/my/custom/rules/*.js"]
}
}
.graphql-schema-linterrc{
"rules": ["enum-values-sorted-alphabetically"],
"schemaPaths": ["path/to/my/schema/files/**.graphql"],
"customRulePaths": ["path/to/my/custom/rules/*.js"]
}
graphql-schema-linter.config.jsmodule.exports = {
rules: ['enum-values-sorted-alphabetically'],
schemaPaths: ['path/to/my/schema/files/**.graphql'],
customRulePaths: ['path/to/my/custom/rules/*.js'],
};
arguments-have-descriptionsThis rule will validate that all field arguments have a description.
defined-types-are-usedThis rule will validate that all defined types are used at least once in the schema.
deprecations-have-a-reasonThis rule will validate that all deprecations have a reason.
descriptions-are-capitalizedThis rule will validate that all descriptions, if present, start with a capital letter.
enum-values-all-capsThis rule will validate that all enum values are capitalized.
enum-values-have-descriptionsThis rule will validate that all enum values have a description.
enum-values-sorted-alphabeticallyThis rule will validate that all enum values are sorted alphabetically.
fields-are-camel-casedThis rule will validate that object type field and interface type field names are camel cased.
fields-have-descriptionsThis rule will validate that object type fields and interface type fields have a description.
input-object-fields-sorted-alphabeticallyThis rule will validate that all input object fields are sorted alphabetically.
input-object-values-are-camel-casedThis rule will validate that input object value names are camel cased.
input-object-values-have-descriptionsThis rule will validate that input object values have a description.
relay-connection-types-specThis rule will validate the schema adheres to section 2 (Connection Types) of the Relay Cursor Connections Specification.
More specifically:
Connection. These object types are considered connection types.edges field that returns a list type.pageInfo field that returns a non-null PageInfo object.relay-connection-arguments-specThis rule will validate the schema adheres to section 4 (Arguments) of the Relay Cursor Connections Specification.
More specifically:
Connection must include forward pagination arguments, backward pagination arguments, or both.first: Int and after: *.last: Int and before: *.Note: If only forward pagination is enabled, the first argument can be specified as non-nullable (i.e., Int! instead of Int). Similarly, if only backward pagination is enabled, the last argument can be specified as non-nullable.
This rule will validate the schema adheres to section 5 (PageInfo) of the Relay Cursor Connections Specification.
More specifically:
PageInfo object type.PageInfo type must have a hasNextPage: Boolean! field.PageInfo type must have a hasPreviousPage: Boolean! field.type-fields-sorted-alphabeticallyThis rule will validate that all type object fields are sorted alphabetically.
types-are-capitalizedThis rule will validate that interface types and object types have capitalized names.
types-have-descriptionsThis will will validate that interface types, object types, union types, scalar types, enum types and input types have descriptions.
The format of the output can be controlled via the --format option.
The following formatters are currently available: text, compact, json.
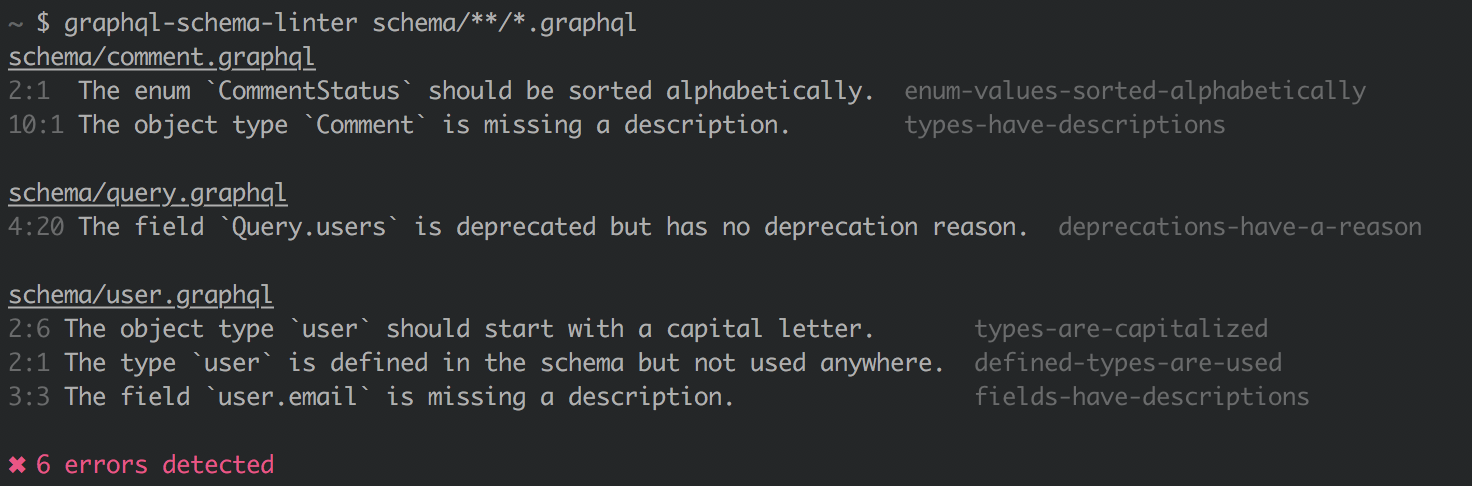
Sample output:
app/schema.graphql
5:1 The object type `QueryRoot` is missing a description. types-have-descriptions
6:3 The field `QueryRoot.songs` is missing a description. fields-have-descriptions
app/songs.graphql
1:1 The object type `Song` is missing a description. types-have-descriptions
3 errors detected
Each error is prefixed with the line number and column the error occurred on.
Sample output:
app/schema.graphql:5:1 The object type `QueryRoot` is missing a description. (types-have-descriptions)
app/schema.graphql:6:3 The field `QueryRoot.a` is missing a description. (fields-have-descriptions)
app/songs.graphql:1:1 The object type `Song` is missing a description. (types-have-descriptions)
Each error is prefixed with the path, the line number and column the error occurred on.
Sample output:
{
"errors": [
{
"message": "The object type `QueryRoot` is missing a description.",
"location": {
"line": 5,
"column": 1,
"file": "schema.graphql"
},
"rule": "types-have-descriptions"
},
{
"message": "The field `QueryRoot.a` is missing a description.",
"location": {
"line": 6,
"column": 3,
"file": "schema.graphql"
},
"rule": "fields-have-descriptions"
}
]
}
Verifying the exit code of the graphql-schema-lint process is a good way of programmatically knowing the
result of the validation.
If the process exits with 0 it means all rules passed.
If the process exits with 1 it means one or many rules failed. Information about these failures can be obtained by
reading the stdout and using the appropriate output formatter.
If the process exits with 2 it means an invalid configuration was provided. Information about this can be obtained by
reading the stderr.
If the process exits with 3 it means an uncaught error happened. This most likely means you found a bug.
graphql-schema-linter comes with a set of rules, but it's possible that it doesn't exactly match your expectations.
The --rules <rules> allows you pick and choose what rules you want to use to validate your schema.
In some cases, you may want to write your own rules. graphql-schema-linter leverages GraphQL.js' visitor.js
in order to validate a schema.
You may define custom rules by following the usage of visitor.js and saving your newly created rule as a .js file.
You can then instruct graphql-schema-linter to include this rule using the --custom-rule-paths <paths> option flag.
For sample rules, see the src/rules folder of this repository or
GraphQL.js' src/validation/rules folder.
0.4.0 (May 5th, 2020)
v0.3.0. They were re-added in this version. #230FAQs
Command line tool and package to validate GraphQL schemas against a set of rules.
The npm package graphql-schema-linter receives a total of 54,743 weekly downloads. As such, graphql-schema-linter popularity was classified as popular.
We found that graphql-schema-linter demonstrated a not healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security News
Research
The Socket Research Team breaks down a malicious wrapper package that uses obfuscation to harvest credentials and exfiltrate sensitive data.

Research
Security News
Attackers used a malicious npm package typosquatting a popular ESLint plugin to steal sensitive data, execute commands, and exploit developer systems.

Security News
The Ultralytics' PyPI Package was compromised four times in one weekend through GitHub Actions cache poisoning and failure to rotate previously compromised API tokens.