
Research
Security News
Malicious npm Packages Inject SSH Backdoors via Typosquatted Libraries
Socket’s threat research team has detected six malicious npm packages typosquatting popular libraries to insert SSH backdoors.
react-hook-form-jsonschema
Advanced tools
Wrapper arround react-hook-form to create forms from a JSON schema.
Small project based on react-hook-form that exposes an API for easily creating customizable forms based on a JSON Schema with built-in validation.
react-hook-form-jsonschema is a React hooks library that manages all the stateful logic needed to make a functional form based on a JSON Schema. It returns a set of props that are meant to be called and their results destructured on the desired input field.
Suppose you have a simple JSON Schema that stores a person's first name:
const personSchema = {
$id: 'https://example.com/person.schema.json',
$schema: 'http://json-schema.org/draft-07/schema#',
title: 'Person',
type: 'object',
properties: {
firstName: {
type: 'string',
description: "The person's first name.",
},
},
}
And suppose you want to create a form field for the firstName field, simply use the useInput() hook and render the form using react:
function FirstNameField(props) {
const inputMethods = useInput('#/firstName');
return (
<FormContext schema={personSchema}>
<label {...inputMethods.getLabelProps()}>
{inputMethods.name}
</label>
<input {...inputMethods.getInputProps()} />
</FormContext>
)
}
With npm:
npm install react-hook-form-jsonschema --save
Or with yarn:
yarn add react-hook-form-jsonschema
This is the API documentation, react-hook-form-jsonschema also re-exports all the react-hook-form types and the Controller component. All of the other functionalities are abstracted by this library.
This component is the top-level component that creates the context with the schema and options all the hooks will need to be usable. So bear in mind that you need to define all the other components as children of FormContext.
schema: JSON Schema object which will be passed down by context for the inputs to use it for validation and the structure of the form itself.validationMode: String to indicate when to validate the input, default is 'onSubmit'.
'onBlur': Validate when an input field is blurred.'onChange': Validate when an input field value changes.'onSubmit': Validate when the submit is triggered.revalidateMode: String to indicate when inputs with errors get re-validated, default is 'onChange'.
'onblur': Validate when an input field is blurred.'onChange': Validate when an input field value changes.'onSubmit': Validate when the submit is triggered.submitFocusError: Boolean, when true focus on the first field with error after submit validates, if there is any. Defaults to true.onSubmit: Callback function that the form values are passed to when submit is triggered.noNativeValidate: Boolean, when true disables the default browser validation (notice that react-hook-form-jsonschema does NOT yet implement validation for URIs and email addresses).The following are the common fields returned in the object from every use'SomeInputType' hook:
type: The type of the input, as defined in InputTypes:
generic: the default type, a non specialized type, only contains the common fieldsradio: Type used for <input type='radio' \>select: Type used for <select>input: Type used for generic <input \>textArea: Type used for <textarea>checkbox: Type used for <input type='checkbox' \>path: Path in the jsonschema this input is validated against. The path is always in the form: #/some/child/data/field/here where # represents the root of the schema, and the some/child/data/field/here represents the tree of objects (from some to here) to get to the desired field, which in this case is here.name: The last object/data field name in the tree. In the case of #/some/child/data/field/here the name value will be here.isRequired: indicates whether the field is required or not.validator: is the object passed to react-hook-form to validate the form. See the react-hook-form for more informationformContext: If you want to access internal react-hook-form context use thisgetError(): Returns an ErrorMessage, which has the following format:
{message: ErrorTypes, expected: ErrorMessageValues}ErrorTypes, is an enum, with the following values:
required: the field is required to be filledmaxLength: maximum length of string input was surpassedminLength: minimum length of string input was not metmaxValue: maximum value of number input was surpassedminValue: minimum value of number input was not metpattern: the pattern or type defined in the schema was not metmultipleOf: the number is not a multiple of the number defined in the schemaundefinedError: the error type could not be definedErrorMessageValues, is the expected value to be met, it will be true for required, and the minimum value expected for minValue for example.getObject(): Returns the data field in the schema that this input refers toPlease notice that in all of the following examples it is assumed the components are already children of a FormContext component
Description
Use this hook to build a single or multiple checkbox field in your form.
Parameters:
path: String which represents the path to the data field of the JSON Schema that this input will be built for.Return:
Returns an object with the following fields, besides the common one's:
isSingle: indicates whether there is just a single option inside the checkboxgetItems(): use this to get which values should be listed inside the radio input fields. This function derives the items by the defined type and properties inside the JSON Schema and returns all the required items to comply with the definition.getItemInputProps(index): use this with the spread operator inside an <input> tag and get the benefit of the validator, id field, name and an associated label with it for the item in the specified index from getItems()getItemLabelProps(index): the label props related to the input at the specified index from getItems()Example:
function InputField(props) {
const inputMethods = useCheckbox(props.path)
return (
<React.Fragment>
{inputMethods.getItems().map((value, index) => {
return (
<label {...inputMethods.getItemLabelProps(index)} key={`${value}${index}`}>
{inputMethods.isSingle ? inputMethods.getObject().title : value}
<input {...inputMethods.getItemInputProps(index)} />
</label>
)
})}
{inputMethods.getError() && <p>This is an error!</p>}
</React.Fragment>
)
}
Description
Use this hook to build a hidden field in the form, the user will not be able to change it or see it, but it will be there when submitted.
Parameters:
path: String which represents the path to the data field of the JSON Schema that this input will be built for.Return:
Returns an object with the following fields, besides the common one's:
getLabelProps(): use this with the spread operator inside a <label> tag and get the benefit of having all the important fields of the label filled in for you and the associated input (the for property) with it.getInputProps(): use this with the spread operator inside an <input> tag and get the benefit of the validator, id field, name and an associated label with itExample:
function HiddenField(props) {
const inputMethods = useHidden('#/some/child/you/want/hidden');
return (
<React.Fragment>
<label {...inputMethods.getLabelProps()}>
{inputMethods.name}
</label>
<input {...inputMethods.getInputProps()} />
</React.Fragment>
)
}
Description
Use this hook to build a generic input field in your form, with validation based on the type of input the JSON Schema requires.
Parameters:
path: String which represents the path to the data field of the JSON Schema that this input will be built for.Return:
Returns an object with the following fields, besides the common one's:
getLabelProps(): use this with the spread operator inside a <label> tag and get the benefit of having all the important fields of the label filled in for you and the associated input (the for property) with it.getInputProps(): use this with the spread operator inside an <input> tag and get the benefit of the validator, id field, name and an associated label with it.Example:
function InputField(props) {
const inputMethods = useInput('#/some/child/you/want/as/input');
return (
<React.Fragment>
<label {...inputMethods.getLabelProps()}>
{inputMethods.name}
</label>
<input {...inputMethods.getInputProps()} />
</React.Fragment>
)
}
Description
This hook works a little differently than the others. useObject returns an array of which each of its elements corresponds to the return type of one of the other hooks.
Parameters:
path: String which represents the path to the data field of the JSON Schema that this input will be built for.UISchema (Optional): This UISchema is a modified schema type, relative to the object passed in the path prop, the format of the UISchema is the following:const UISchema = {
/*
* This is the type that will be used to choose what type of input will be
* used to build the specified field. Please note that the type of a node
* that is an object will be ignored, as there would make no sense to render
* an object without it's children inside a form.
*/
type: UITypes,
properties: {
// Note that the definition is recursive
child1NameHere: UISchema,
child2NameHere: UISchema,
// ...
childXNameHere: UISchema,
},
}
UITypes is an enum with the following values:
default: input will have a default type based on what react-hook-form-jsonschema thinks is better.radio: input will be of the radio type, just as returned by the useRadio hookselect: input will be of the select type, just as returned by the useSelect hookinput: input will be of the input type, just as returned by the useInput hookhidden: input will be of the hidden type, just as returned by the useHidden hookpassword: input will be of the password type, just as returned by the usePassword hooktextArea: input will be of the textarea type, just as returned by the useTextArea hookcheckbox: input will be of the checkbox type, just as returned by the useCheckbox hookReturn:
Returns an array, with each element being the return of a different call to a hook for each child of the object that was passed in the path.
Example:
const personSchema = {
title: 'Person',
type: 'object',
properties: {
firstName: {
type: 'string',
description: "The person's first name.",
},
lastName: {
type: 'string',
description: "The person's last name.",
},
birthYear: {
description: "The person's birth year.",
type: 'integer',
minimum: 1930,
maximum: 2010,
},
},
}
function SpecializedObject(props) {
switch (props.baseObject.type) {
case InputTypes.input: {
return (
<React.Fragment>
<label {...props.baseObject.getLabelProps()}>
{props.baseObject.name}
</label>
<input {...props.baseObject.getInputProps()} />
</React.Fragment>
)
}
case InputTypes.radio: {
return (
<React.Fragment>
<label {...props.baseObject.getLabelProps()}>
{props.baseObject.name}
</label>
{props.baseObject.getItems().map((value, index) => {
return (
<label
{...props.baseObject.getItemLabelProps(index)}
key={`${value}${index}`}
>
{value}
<input {...props.baseObject.getItemInputProps(index)} />
</label>
)
})}
</React.Fragment>
)
}
case InputTypes.select: {
return (
<React.Fragment>
<label {...props.baseObject.getLabelProps()}>
{props.baseObject.name}
</label>
<select {...props.baseObject.getSelectProps()}>
{props.baseObject.getItems().map((value, index) => {
return (
<option
{...props.baseObject.getItemOptionProps(index)}
key={`${value}${index}`}
>
{value}
</option>
)
})}
</select>
</React.Fragment>
)
}
}
return <React.Fragment></React.Fragment>
}
function ObjectRenderer(props) {
const inputMethods = useObject({ path: props.path, UISchema: props.UISchema })
const objectForm = []
// Note that we also add error checking here and show a message in case there
// is one. Remember that you can also check for the type of error returned
// anb give a more specialized warning to the user.
for (const obj of inputMethods) {
objectForm.push(
<div key={`${obj.type}${obj.path}`}>
<SpecializedObject baseObject={obj} />
{obj.getError() && <p>This is an error!</p>}
</div>
)
}
return <React.Fragment>{objectForm}</React.Fragment>
}
function RenderMyJSONSchema() {
// Notice that even though only one child was specified, all the children of
// the root object are rendered, using the choosen default for each field.
const UISchema = {
type: UITypes.default,
properties: {
birthYear: {
type: UITypes.select,
},
},
}
return (
<FormContext schema={personSchema}>
<ObjectRenderer path="#" UISchema={UISchema} />
</FormContext>
)
}
This is the result of this example:
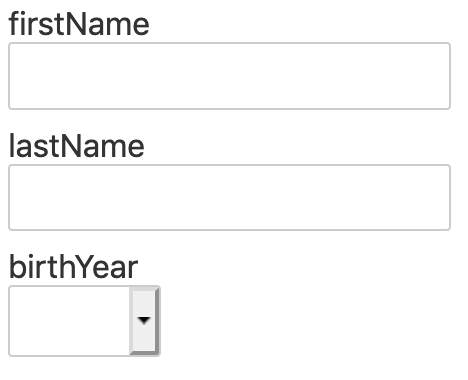
Description
Use this hook to build a password input field in your form, with validation based on the type of input the JSON Schema requires.
Parameters:
path: String which represents the path to the data field of the JSON Schema that this input will be built for.Return:
Returns an object with the following fields, besides the common one's:
getLabelProps(): use this with the spread operator inside a <label> tag and get the benefit of having all the important fields of the label filled in for you and the associated input (the for property) with it.getInputProps(): use this with the spread operator inside an <input> tag and get the benefit of the validator, id field, name and an associated label with itExample:
function PasswordField(props) {
const inputMethods = usePassword('#/some/child/you/want/as/input');
return (
<React.Fragment>
<label {...inputMethods.getLabelProps()}>
{inputMethods.name}
</label>
<input {...inputMethods.getInputProps()} />
</React.Fragment>
)
}
Description
Use this hook to build a radio field in your form.
Parameters:
path: String which represents the path to the data field of the JSON Schema that this input will be built for.Return:
Returns an object with the following fields, besides the common one's:
getItems(): use this to get which values should be listed inside the radio input fields. This function derives the items by the defined type and properties inside the JSON Schema and returns all the required items to comply with the definition.getItemInputProps(index): use this with the spread operator inside an <input> tag and get the benefit of the validator, id field, name and an associated label with it for the item in the specified index from getItems()getItemLabelProps(index): the label props related to the input at the specified index from getItems()Example:
function InputField(props) {
const inputMethods = useRadio('#/some/child/with/limited/possible/values');
return (
<React.Fragment>
{inputMethods.getItems().map((value, index) => {
return (
<label {...inputMethods.getItemLabelProps(index)} key={`${value}${index}`}>
{value}
<input {...inputMethods.getItemInputProps(index)} />
</label>
)
})}
{inputMethods.getError() && <p>This is an error!</p>}
</React.Fragment>
)
}
Description
Use this hook to build a select field in your form.
Parameters:
path: String which represents the path to the data field of the JSON Schema that this input will be built for.Return:
Returns an object with the following fields, besides the common one's:
getLabelProps(): use this with the spread operator inside a <label> tag and get the benefit of having all the important fields of the label filled in for you and the associated select (the for property) with it.getItems(): use this to get all the values that are possible to be in the radio buttonsgetItemOptionProps(index): use this with the spread operator inside an <option> tag and get the benefit of the validator, id field and name for the item in the specified index from getItems()getSelectProps(): use this with the spread operator inside a <select> tag to get validation and register it with the react-hook-form-jsonschema.Example:
function InputField(props) {
const inputMethods = useSelect('#/some/child/with/limited/possible/values');
return (
<React.Fragment>
<label {...inputMethods.getLabelProps()}>{inputMethods.name}</label>
<select {...inputMethods.getSelectProps()}>
{inputMethods.getItems().map((value, index) => {
return (
<option
{...inputMethods.getItemOptionProps(index)}
key={`${value}${index}`}
>
{value}
</option>
)
})}
</select>
{inputMethods.getError() && <p>This is an error!</p>}
</React.Fragment>
)
}
Description
Use this hook to build a textarea field in the form.
Parameters:
path: String which represents the path to the data field of the JSON Schema that this input will be built for.Return:
Returns an object with the following fields, besides the common one's:
getLabelProps(): use this with the spread operator inside a <label> tag and get the benefit of having all the important fields of the label filled in for you and the associated input (the for property) with it.getTextAreaProps(): use this with the spread operator inside an <textarea> tag and get the benefit of the validator, id field, name and an associated label with itExample:
function HiddenField(props) {
const inputMethods = useTextArea('#/some/child/you/want/as/TextArea');
return (
<React.Fragment>
<label {...inputMethods.getLabelProps()}>
{inputMethods.name}
</label>
<textarea {...inputMethods.getTextAreaProps()} />
</React.Fragment>
)
}
[0.2.0-beta.4] - 2020-02-05
FAQs
Wrapper arround react-hook-form to create forms from a JSON schema.
The npm package react-hook-form-jsonschema receives a total of 185 weekly downloads. As such, react-hook-form-jsonschema popularity was classified as not popular.
We found that react-hook-form-jsonschema demonstrated a not healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released a year ago. It has 71 open source maintainers collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Research
Security News
Socket’s threat research team has detected six malicious npm packages typosquatting popular libraries to insert SSH backdoors.

Security News
MITRE's 2024 CWE Top 25 highlights critical software vulnerabilities like XSS, SQL Injection, and CSRF, reflecting shifts due to a refined ranking methodology.

Security News
In this segment of the Risky Business podcast, Feross Aboukhadijeh and Patrick Gray discuss the challenges of tracking malware discovered in open source softare.