
Research
Security News
Malicious npm Packages Inject SSH Backdoors via Typosquatted Libraries
Socket’s threat research team has detected six malicious npm packages typosquatting popular libraries to insert SSH backdoors.
Provides colorful and semantic labels in console. Tailored for message display and interaction in automated scripts.
colorlabels is a console message display library for Python. Equipped with various kinds of colorful and semantic labels, it is tailored for message display and interaction in automated scripts (e.g. test scripts, installation scripts and hacker tools).
import time
import colorlabels as cl
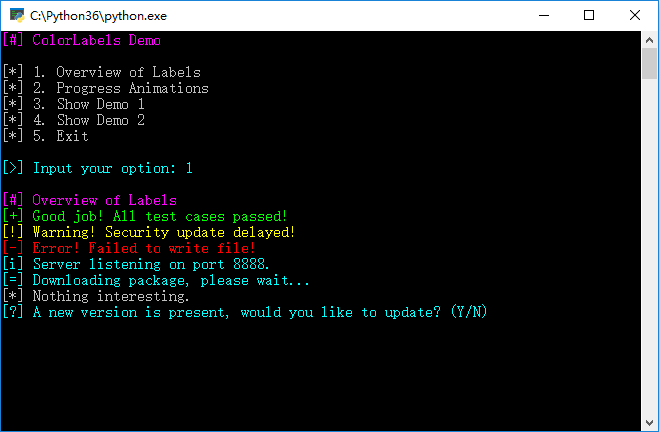
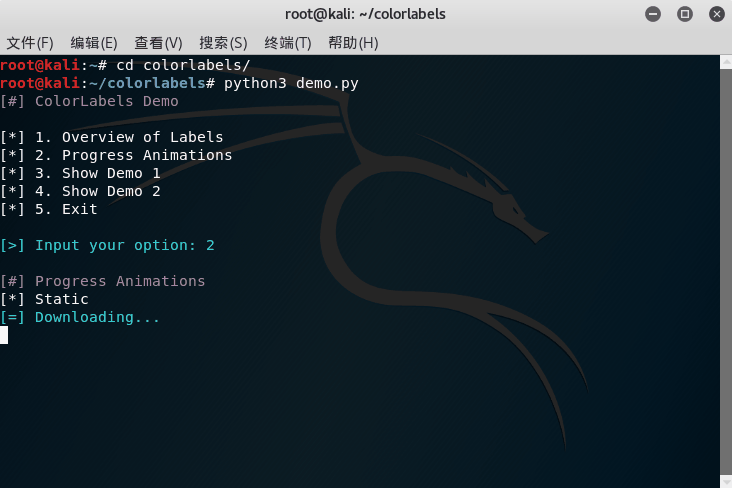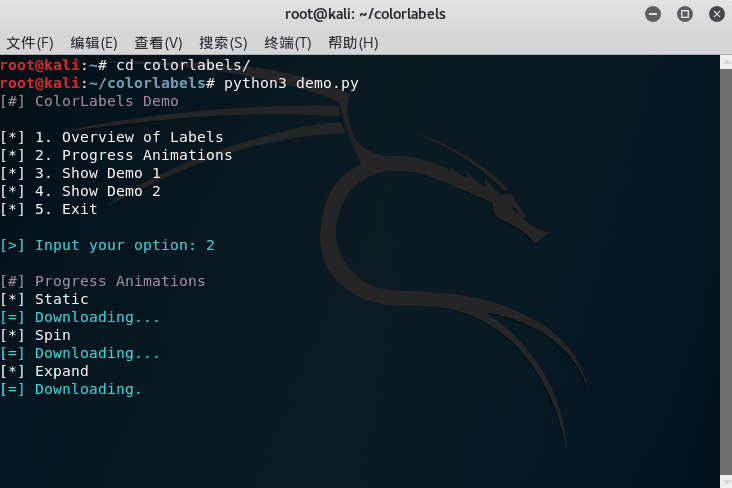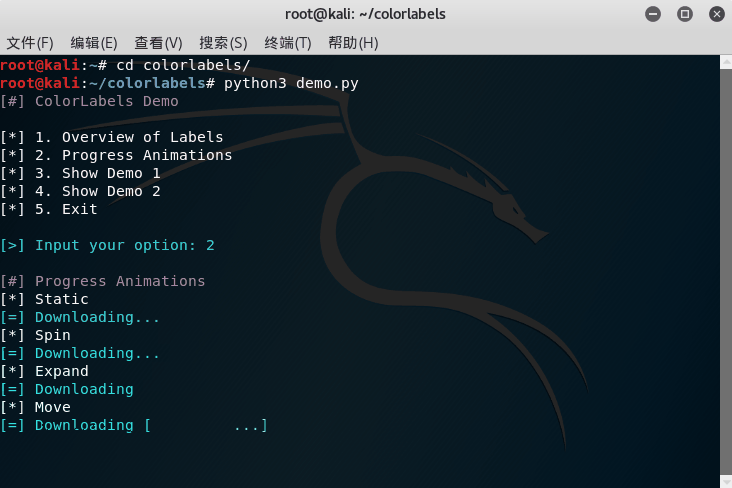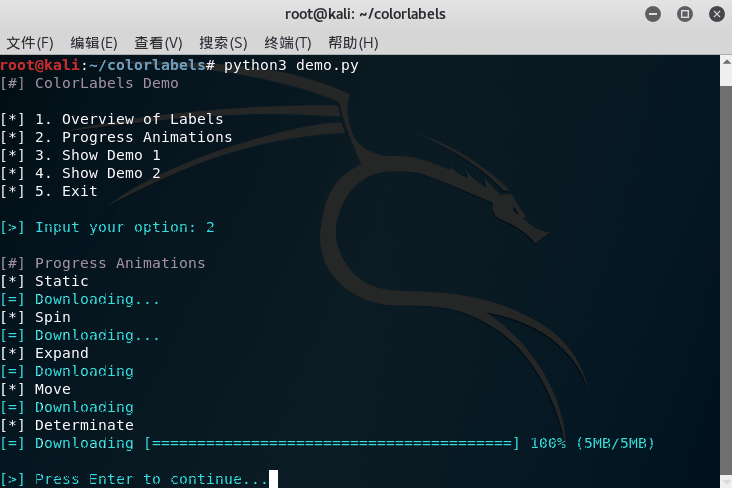
cl.section('Overview of Labels')
cl.success('Good job! All test cases passed!')
cl.warning('Warning! Security update delayed!')
cl.error('Error! Failed to write file!')
cl.info('Server listening on port 8888.')
cl.progress('Downloading package, please wait...')
cl.plain('Nothing interesting.')
choice = cl.question('A new version is present, would you like to update? (Y/N)')
with cl.progress('Downloading...', mode=cl.PROGRESS_SPIN):
time.sleep(3)
with cl.progress('Downloading ', mode=cl.PROGRESS_DETERMINATE) as p:
time.sleep(1)
p.update(0.5, ' 50% (2.5MB/5MB) ETA 1s')
time.sleep(1)
p.update(1, ' 100% (5MB/5MB)')
Install with pip: pip install -U colorlabels
colorlabels mimics the famous Bootstrap library in Web front-end developing, providing a number of components (called labels) to facilitate message display and interaction in automated scripts.
In colorlabels, most of the configurable options are organized in three layers:
config(), apply to the whole running process)Runtime global settings can override default settings, and per-call settings can override runtime global settings and default settings.
A label is a line of message composed of a header and its content. A header is a mark with a pair of brackets.
Here is an anatomy of a label:
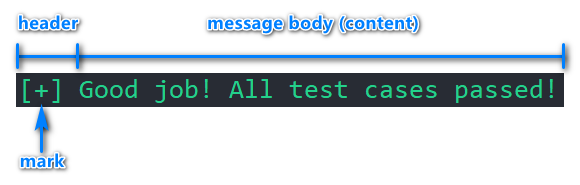
When using colorlabels, you will be able to customize a label's mark and color settings. However, the default settings should already look nice under most operating systems and terminals with a dark background.
colorlabels provides the following kinds of labels with semantic names: section, item, success, warning, error, info, progress, plain, question, input and password. The section, item, success, warning, error, info and plain labels print a message to the console. The progress label can alternatively display some animation. The question, input and password labels prompt for user input. Behaviors of all the labels can be demonstrated by running demo.py.
Marks and colors are carefully selected to visually symbolize the semantic meaning of a label, which makes labels pretty and easy for visual grepping.
A mark is a non-empty string to be enclosed in a pair of brackets to comprise a header. By default all marks for labels are composed of only one character, but you can customize them to contain more than one character, or even emojis if you wish to.
If you prefer labels without headers, you can set the show_header option to False to remove them.
A color is an ANSI escape sequence representing color in terminal. colorlabels utilizes colorama to achieve cross-platform color printing compatibility. By default all colors for labels only contain the classic and ubiquitous 16 colors (code 30-37, 90-97), but you can customize them to include 8-bit colors and 24-bit colors if you wish to.
The color_span option specifies the range that color covers in a label. There are four values for color_span:
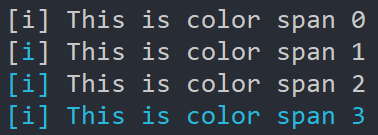
The default marks and colors for different kinds of labels are as follows:
| Label Type | Default Mark | Default Color |
|---|---|---|
section | # | Bright Magenta (95) |
item | * | No Color |
success | + | Bright Green (92) |
warning | ! | Bright Yellow (93) |
error | - | Bright Red (91) |
info | i | Bright Cyan (96) |
progress | = | Bright Cyan (96) |
plain | * | No Color |
question | ? | Bright Cyan (96) |
input | > | Bright Cyan (96) |
password | > | Bright Cyan (96) |
The progress label supports different modes:
| Progress Mode | Animation | Determinate |
|---|---|---|
PROGRESS_STATIC | None | N/A |
PROGRESS_SPIN | Spinning | No |
PROGRESS_EXPAND | Expanding Characters | No |
PROGRESS_MOVE | Moving Characters | No |
PROGRESS_DETERMINATE | Progress Bar | Yes |
The static progress label only prints a message without any animation, just like non-progress labels. Non-static progress labels can be classified as determinate and indeterminate. A determinate progress label has a concrete progress value (percentage) associated with it, and user should notify the progress label to update the percentage value (and alternatively other messages about the progress). An indeterminate progress label does not have a concrete percentage value (we cannot estimate the end of the progress), and user should notify the progress label to stop the animation when the progress ends.
For a detailed list of configurable options regarding progress labels, please refer to the corresponding content in the API Reference part of this documentation.
By default, colorlabels will detect whether the standard output is interactive (i.e. connected to a terminal/tty device). If it is not interactive, colorlabels will operate in non-TTY mode, where color output and progress animations will be disabled (i.e. no ANSI escape sequence printed, all progress labels become static), to make output parsing easier. However, you can override this behavior by setting the COLORLABELS_TTY environment variable. If COLORLABELS_TTY is set to one of '1', 'yes', 'y', 'true', 'on' (case-insensitive), this will force the use of TTY mode (i.e. treat standard output as interactive and display color output and progress animations as usual); if COLORLABELS_TTY is set to one of '0', 'no', 'n', 'false', 'off' (case-insensitive), this will force the use of non-TTY mode.
color_code(color_number)
Generate an ANSI escape sequence with the given color number or description string.
Arguments:
any, color number or description stringReturn: str, an ANSI escape sequence
config(**kwargs)
Set up runtime global settings.
Arguments:
str, runtime global settings of color for section labelsstr, runtime global settings of color for item labelsstr, runtime global settings of color for success labelsstr, runtime global settings of color for warning labelsstr, runtime global settings of color for error labelsstr, runtime global settings of color for info labelsstr, runtime global settings of color for progress labelsstr, runtime global settings of color for plain labelsstr, runtime global settings of color for question labelsstr, runtime global settings of color for input labelsstr, runtime global settings of color for password labelsstr, runtime global settings of mark for section labelsstr, runtime global settings of mark for item labelsstr, runtime global settings of mark for success labelsstr, runtime global settings of mark for warning labelsstr, runtime global settings of mark for error labelsstr, runtime global settings of mark for info labelsstr, runtime global settings of mark for progress labelsstr, runtime global settings of mark for plain labelsstr, runtime global settings of mark for question labelsstr, runtime global settings of mark for input labelsstr, runtime global settings of mark for password labelsint, runtime global settings of color span, should be in [0, 1, 2, 3]bool, runtime global settings of whether to display headers for labelsReturn: None
section(msg, **kwargs)
Display a section label containing the given message.
Arguments:
any, the message content to displaystr, the color for this labelstr, the mark for this labelint, the color span for this label, should be in [0, 1, 2, 3]bool, whether to display header for this labelReturn: None
item(msg, **kwargs)
Display an item label containing the given message.
Arguments: The same as section().
Return: None
success(msg, **kwargs)
Display a success label containing the given message.
Arguments: The same as section().
Return: None
warning(msg, **kwargs)
Display a warning label containing the given message.
Arguments: The same as section().
Return: None
error(msg, **kwargs)
Display an error label containing the given message.
Arguments: The same as section().
Return: None
info(msg, **kwargs)
Display an info label containing the given message.
Arguments: The same as section().
Return: None
plain(msg, **kwargs)
Display a plain label containing the given message.
Arguments: The same as section().
Return: None
question(msg, **kwargs)
Display a question label containing the given message and prompt for user input.
Arguments: The same as section().
Return: str, the string that user inputs
input(msg, **kwargs)
Display an input label containing the given message and prompt for user input.
Arguments: The same as section().
Return: str, the string that user inputs
password(msg, **kwargs)
Display a password label containing the given message and prompt for user input. The password will not be echoed on the terminal.
Arguments: The same as section().
Return: str, the password that user inputs
progress(msg, mode=PROGRESS_STATIC, **kwargs)
Display a progress label containing the given message.
Arguments: Accept all arguments for section(). In addition:
PROGRESS_STATIC, PROGRESS_SPIN, PROGRESS_EXPAND, PROGRESS_MOVE, PROGRESS_DETERMINATE]PROGRESS_SPIN:
str, the position of spinner, should be one of ['mark', 'tail'], default is 'mark'float, the refreshing interval (in seconds), default is 0.1bool, whether to erase the whole label when animation finished, default is FalsePROGRESS_EXPAND:
char, the character to expand, default is '.'int, the maximum width to expand, default is 3float, the refreshing interval (in seconds), default is 1bool, whether to erase the whole label when animation finished, default is FalsePROGRESS_MOVE:
char, the character to move, default is '.'int, the number of characters to move, default is 3int, the width of range that characters move in, default is 12str, the style of moving, can be one of:
float, the refreshing interval (in seconds), default is 0.1bool, whether to erase the whole label when animation finished, default is FalsePROGRESS_DETERMINATE:
char, the character to represent done percentage, default is '='char, the character to display at the head of the progress bar, default is '>'char, the character to represent undone percentage, default is ' 'int, the width of the progress bar, default is 40bool, whether to remove the progress bar when animation finished (original label message will remain), default is Falsebool, whether to erase the whole label when animation finished, default is FalseReturn:
PROGRESS_STATIC, return NoneProgressLabel objectnewline()
Print an empty line.
Return: None
ProgressLabel MethodsWe recommend using context managers (with statements) to manage progress labels with animations, as in our demo, which automatically stop the animation and clean up the side effects whether the progress normally ends or some exceptions occur. However, you may still call the stop() method if you want to manually stop the animation.
stop()
Stop progress animation. This is automatically called by the __exit__() of the context manager, but you can also manually call it if you wish to.
Arguments: None
Return: None
update(percent, text='')
Update progress to the given percentage in determinate mode. You can provide additional text to describe current status.
Arguments:
float, the percentage of the progressstr, additional text to describe current status, will be appended after the progress barReturn: None
FAQs
Provides colorful and semantic labels in console. Tailored for message display and interaction in automated scripts.
We found that colorlabels demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Research
Security News
Socket’s threat research team has detected six malicious npm packages typosquatting popular libraries to insert SSH backdoors.

Security News
MITRE's 2024 CWE Top 25 highlights critical software vulnerabilities like XSS, SQL Injection, and CSRF, reflecting shifts due to a refined ranking methodology.

Security News
In this segment of the Risky Business podcast, Feross Aboukhadijeh and Patrick Gray discuss the challenges of tracking malware discovered in open source softare.