
Security News
Research
Data Theft Repackaged: A Case Study in Malicious Wrapper Packages on npm
The Socket Research Team breaks down a malicious wrapper package that uses obfuscation to harvest credentials and exfiltrate sensitive data.

| License | Fossa | Zenodo |
|---|---|---|
 |
| Linux & macOS Build | Code Coverage | Code Quality | Coverity Scan | Issues |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Hypergraphs are a generalization of graphs, where each (hyper)edge (also called net) can connect more than two vertices. The k-way hypergraph partitioning problem is the generalization of the well-known graph partitioning problem: partition the vertex set into k disjoint blocks of bounded size (at most 1 + ε times the average block size), while minimizing an objective function defined on the nets.
The two most prominent objective functions are the cut-net and the connectivity (or λ − 1) metrics. Cut-net is a straightforward generalization of the edge-cut objective in graph partitioning (i.e., minimizing the sum of the weights of those nets that connect more than one block). The connectivity metric additionally takes into account the actual number λ of blocks connected by a net. By summing the (λ − 1)-values of all nets, one accurately models the total communication volume of parallel sparse matrix-vector multiplication and once more gets a metric that reverts to edge-cut for plain graphs.


KaHyPar is a multilevel hypergraph partitioning framework for optimizing the cut- and the (λ − 1)-metric. It supports both recursive bisection and direct k-way partitioning. As a multilevel algorithm, it consist of three phases: In the coarsening phase, the hypergraph is coarsened to obtain a hierarchy of smaller hypergraphs. After applying an initial partitioning algorithm to the smallest hypergraph in the second phase, coarsening is undone and, at each level, a local search method is used to improve the partition induced by the coarser level. KaHyPar instantiates the multilevel approach in its most extreme version, removing only a single vertex in every level of the hierarchy. By using this very fine grained n-level approach combined with strong local search heuristics, it computes solutions of very high quality. Its algorithms and detailed experimental results are presented in several research publications.
Hypergraph partitioning with variable block weights
KaHyPar has support for variable block weights. If command line option --use-individual-part-weights=true is used, the partitioner tries to partition the hypergraph such that each block Vx has a weight of at most Bx, where Bx can be specified for each block individually using the command line parameter --part-weights= B1 B2 B3 ... Bk-1. Since the framework does not yet support perfectly balanced partitioning, upper bounds need to be slightly larger than the total weight of all vertices of the hypergraph. Note that this feature is still experimental.
Hypergraph partitioning with fixed vertices
Hypergraph partitioning with fixed vertices is a variation of standard hypergraph partitioning. In this problem, there is an additional constraint on the block assignment of some vertices, i.e., some vertices are preassigned to specific blocks prior to partitioning with the condition that, after partitioning the remaining “free” vertices, the fixed vertices are still in the block that they were assigned to. The command line parameter --fixed / -f can be used to specify a fix file in hMetis fix file format. For a hypergraph with V vertices, the fix file consists of V lines - one for each vertex. The ith line either contains -1 to indicate that the vertex is free to move or <part id> to indicate that this vertex should be preassigned to block <part id>. Note that part ids start from 0.
KaHyPar currently supports three different contraction policies for partitioning with fixed vertices:
free_vertex_only allows all contractions in which the contraction partner is a free vertex, i.e., it allows contractions of vertex pairs where either both vertices are free, or one vertex is fixed and the other vertex is free.fixed_vertex_allowed additionally allows contractions of two fixed vertices provided that both are preassigned to the same block. Based on preliminary experiments, this is currently the default policy.equivalent_vertices only allows contractions of vertex pairs that consist of either two free vertices or two fixed vertices preassigned to the same block.Evolutionary framework (KaHyPar-E)
KaHyPar-E enhances KaHyPar with an evolutionary framework as described in our GECCO'18 publication. Given a fairly large amount of running time, this memetic multilevel algorithm performs better than repeated executions of nonevolutionary KaHyPar configurations, hMetis, and PaToH. The command line parameter --time-limit=xxx can be used to set the maximum running time (in seconds). Parameter --partition-evolutionary=true enables evolutionary partitioning.
Improving existing partitions
KaHyPar uses direct k-way V-cycles to try to improve an existing partition specified via parameter --part-file=</path/to/file>. The maximum number of V-cycles can be controlled via parameter --vcycles=.
Partitioning directed acyclic hypergraphs
While the code has not been merged into the main repository yet, there exists a fork that supports acyclic hypergraph partitioning. More details can be found in the corresponding conference publication.
We use the performance profiles to compare KaHyPar to other partitioning algorithms in terms of solution quality.
For a set of 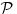 algorithms and a benchmark set
algorithms and a benchmark set 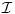 containing
containing  instances, the performance ratio
instances, the performance ratio  relates the cut computed by
partitioner p for instance i to the smallest minimum cut of all algorithms, i.e.,
relates the cut computed by
partitioner p for instance i to the smallest minimum cut of all algorithms, i.e.,
 .
.
The performance profile  of algorithm p is then given by the function
of algorithm p is then given by the function
 .
.
For connectivity optimization, the performance ratios are computed using the connectivity values  instead of the cut values.
The value of
instead of the cut values.
The value of  corresponds to the fraction of instances for which partitioner p computed the best solution, while
corresponds to the fraction of instances for which partitioner p computed the best solution, while  is the probability
that a performance ratio
is the probability
that a performance ratio  is within a factor of
is within a factor of  of the best possible ratio.
Note that since performance profiles only allow to assess the performance of each algorithm relative to the best algorithm, the
of the best possible ratio.
Note that since performance profiles only allow to assess the performance of each algorithm relative to the best algorithm, the  values
cannot be used to rank algorithms (i.e., to determine which algorithm is the second best etc.).
values
cannot be used to rank algorithms (i.e., to determine which algorithm is the second best etc.).
In our experimental analysis, the performance profile plots are based on the best solutions (i.e., minimum connectivity/cut) each algorithm found for each instance.
Furthermore, we choose parameters  for all p, i, and
for all p, i, and  such that a performance ratio
such that a performance ratio  if and only if algorithm p computed an infeasible solution
for instance i, and
if and only if algorithm p computed an infeasible solution
for instance i, and  if and only if the algorithm could not compute a solution for instance i within the given time limit. In our performance profile plots, performance ratios corresponding to infeasible solutions will be shown on the x-tick on the x-axis, while
instances that could not be partitioned within the time limit are shown implicitly by a line that exits the plot below
if and only if the algorithm could not compute a solution for instance i within the given time limit. In our performance profile plots, performance ratios corresponding to infeasible solutions will be shown on the x-tick on the x-axis, while
instances that could not be partitioned within the time limit are shown implicitly by a line that exits the plot below  .
Since the performance ratios are heavily right-skewed, the performance profile plots are divided into three segments with different ranges for parameter
.
Since the performance ratios are heavily right-skewed, the performance profile plots are divided into three segments with different ranges for parameter  to reflect various areas of interest.
The first segment highlights small values (
to reflect various areas of interest.
The first segment highlights small values (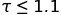 ), while the second segment contains results for all instances
that are up to a factor of
), while the second segment contains results for all instances
that are up to a factor of 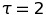 worse than the best possible ratio. The last segment contains all remaining ratios, i.e., instances for which
some algorithms performed considerably worse than the best algorithm, instances for which algorithms produced infeasible solutions, and instances which could not be partitioned within
the given time limit.
worse than the best possible ratio. The last segment contains all remaining ratios, i.e., instances for which
some algorithms performed considerably worse than the best algorithm, instances for which algorithms produced infeasible solutions, and instances which could not be partitioned within
the given time limit.
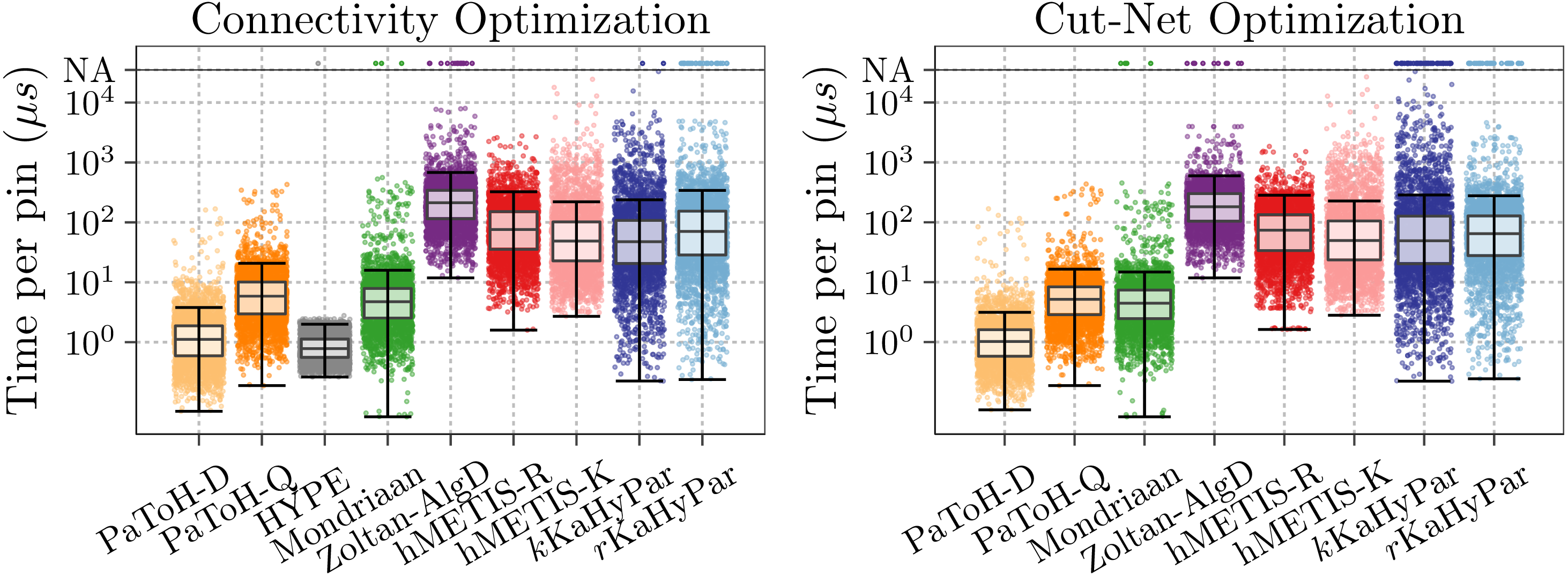
In the figures, we compare KaHyPar with PaToH in quality (PaToH-Q) and default mode (PaToH-D), the k-way (hMETIS-K) and the recursive bisection variant (hMETIS-R) of hMETIS 2.0 (p1), Zoltan using algebraic distance-based coarsening (Zoltan-AlgD), Mondriaan v.4.2.1 and the recently published HYPE algorithm.
Solution Quality

Running Time
We provide additional resources for all KaHyPar-related publications:
| kKaHyPar-SEA20 / rKaHyPar-SEA20 | SEA'20 | Paper | TR | Slides | Experimental Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| kKaHyPar / rKaHyPar | - | Dissertation | - | Slides | Experimental Results |
| KaHyPar-MF / KaHyPar-R-MF | SEA'18 / JEA'19 | SEA Paper / JEA Paper | TR | Slides | Experimental Results: SEA / JEA |
| KaHyPar-E (EvoHGP) | GECCO'18 | Paper | TR | Slides | Experimental Results |
| KaHyPar-CA | SEA'17 | Paper | - | Slides | Experimental Results |
| KaHyPar-K | ALENEX'17 | Paper | - | Slides | Experimental Results |
| KaHyPar-R | ALENEX'16 | Paper | TR | Slides | Experimental Results |
The Karlsruhe Hypergraph Partitioning Framework requires:
 -ready compiler such as
-ready compiler such as g++ version 9 or higher or clang version 11.0.3 or higher.-DKAHYPAR_USE_MINIMAL_BOOST=ON flag to the cmake command to download, extract, and build the necessary dependencies automatically.Clone the repository including submodules:
git clone --depth=1 --recursive git@github.com:SebastianSchlag/kahypar.git
Create a build directory: mkdir build && cd build
Run cmake: cmake .. -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=RELEASE
Run make: make
Tests are automatically executed while project is built. Additionally a test target is provided.
End-to-end integration tests can be started with: make integration_tests. Profiling can be enabled via cmake flag: -DENABLE_PROFILE=ON.
The standalone program can be built via make KaHyPar. The binary will be located at: build/kahypar/application/.
KaHyPar has several configuration parameters. For a list of all possible parameters please run: ./KaHyPar --help.
We use the hMetis format for the input hypergraph file as well as the partition output file.
The command line parameter --quiet=1 can be used to suppress all logging output. If you are using the library interfaces, adding quiet=1 to the corresponding .ini configuration file has the same effect.
We provide two default framework configurations - one for recursive bipartitioning (rKaHyPar) and one for direct k-way partitioning (kKaHyPar).
In general, we recommend using kKaHyPar as it performs better than rKaHyPar in terms of both running time and solution quality.
To start kKaHyPar optimizing the (connectivity - 1) objective run:
./KaHyPar -h <path-to-hgr> -k <# blocks> -e <imbalance (e.g. 0.03)> -o km1 -m direct -p ../../../config/km1_kKaHyPar_sea20.ini
To start kKaHyPar optimizing the cut net objective run:
./KaHyPar -h <path-to-hgr> -k <# blocks> -e <imbalance (e.g. 0.03)> -o cut -m direct -p ../../../config/cut_kKaHyPar_sea20.ini
To start rKaHyPar optimizing the (connectivity - 1) objective run:
./KaHyPar -h <path-to-hgr> -k <# blocks> -e <imbalance (e.g. 0.03)> -o km1 -m recursive -p ../../../config/km1_rKaHyPar_sea20.ini
To start rKaHyPar optimizing the cut net objective run:
./KaHyPar -h <path-to-hgr> -k <# blocks> -e <imbalance (e.g. 0.03)> -o cut -m recursive -p ../../../config/cut_rKaHyPar_sea20.ini
To start the memetic algorithm kKaHyPar-E optimizing the (connectivity - 1) objective run:
./KaHyPar -h <path-to-hgr> -k <# blocks> -e <imbalance (e.g. 0.03)> -o km1 -m direct -p ../../../config/km1_kKaHyPar-E_sea20.ini
Additionally, we provide different presets that correspond to the configurations used in the publications at ALENEX'16, ALENEX'17, SEA'17, SEA'18, GECCO'18, as well as in our JEA journal paper and in the dissertation of Sebastian Schlag. These configurations are located in the config/old_reference_configs folder. In order to use these configurations, you have to checkout KaHyPar release 1.1.0, since some old code as been removed in the most current release.
To start KaHyPar-MF (using flow-based refinement) optimizing the (connectivity - 1) objective using direct k-way mode run:
./KaHyPar -h <path-to-hgr> -k <# blocks> -e <imbalance (e.g. 0.03)> -o km1 -m direct -p ../../../config/old_reference_configs/km1_kahypar_mf_jea19.ini
To start KaHyPar-MF (using flow-based refinement) optimizing the cut-net objective using direct k-way mode run:
./KaHyPar -h <path-to-hgr> -k <# blocks> -e <imbalance (e.g. 0.03)> -o cut -m direct -p ../../../config/old_reference_configs/cut_kahypar_mf_jea19.ini
To start EvoHGP/KaHyPar-E optimizing the (connectivity - 1) objective using direct k-way mode run
./KaHyPar -h <path-to-hgr> -k <# blocks> -e <imbalance (e.g. 0.03)> -o km1 -m direct -p ../../../config/old_reference_configs/km1_direct_kway_gecco18.ini
Note that the configuration km1_direct_kway_gecco18.ini is based on KaHyPar-CA. However, KaHyPar-E also works with flow-based local improvements. In our JEA publication the km1_kahypar_e_mf_jea19.ini configuration was used.
To start KaHyPar-CA (using community-aware coarsening) optimizing the (connectivity - 1) objective using direct k-way mode run:
./KaHyPar -h <path-to-hgr> -k <# blocks> -e <imbalance (e.g. 0.03)> -o km1 -m direct -p ../../../config/old_reference_configs/km1_direct_kway_sea17.ini
To start KaHyPar in direct k-way mode (KaHyPar-K) optimizing the (connectivity - 1) objective run:
./KaHyPar -h <path-to-hgr> -k <# blocks> -e <imbalance (e.g. 0.03)> -o km1 -m direct -p ../../../config/old_reference_configs/km1_direct_kway_alenex17.ini
To start KaHyPar in recursive bisection mode (KaHyPar-R) optimizing the cut-net objective run:
./KaHyPar -h <path-to-hgr> -k <# blocks> -e <imbalance (e.g. 0.03)> -o cut -m recursive -p ../../../config/old_reference_configs/cut_rb_alenex16.ini
All preset parameters can be overwritten by using the corresponding command line options.
When creating a hypergraph KaHyPar validates that the input is actually a correct hypergraph, otherwise printing an error and aborting.
This applies to hgr input files, the C interface and the Python interface. The runtime cost of the validation should be negligible in almost all cases.
However, the input validation can also be disabled using the cmake flag -DKAHYPAR_INPUT_VALIDATION=OFF.
Additionally, warnings are printed for non-fatal issues (e.g. hyperedges with duplicate pins).
To treat non-fatal issues as hard errors instead, use the cmake flag -DKAHYPAR_INPUT_VALIDATION_PROMOTE_WARNINGS_TO_ERRORS=ON.
We provide a simple C-style interface to use KaHyPar as a library. Note that this interface is not thread-safe yet. However there are some existing workarounds. The library can be built and installed via
make install.library
and can be used like this:
#include <memory>
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <libkahypar.h>
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
kahypar_context_t* context = kahypar_context_new();
kahypar_configure_context_from_file(context, "/path/to/config.ini");
kahypar_set_seed(context, 42);
const kahypar_hypernode_id_t num_vertices = 7;
const kahypar_hyperedge_id_t num_hyperedges = 4;
std::unique_ptr<kahypar_hyperedge_weight_t[]> hyperedge_weights = std::make_unique<kahypar_hyperedge_weight_t[]>(4);
// force the cut to contain hyperedge 0 and 2
hyperedge_weights[0] = 1; hyperedge_weights[1] = 1000;
hyperedge_weights[2] = 1; hyperedge_weights[3] = 1000;
std::unique_ptr<size_t[]> hyperedge_indices = std::make_unique<size_t[]>(5);
hyperedge_indices[0] = 0; hyperedge_indices[1] = 2;
hyperedge_indices[2] = 6; hyperedge_indices[3] = 9;
hyperedge_indices[4] = 12;
std::unique_ptr<kahypar_hyperedge_id_t[]> hyperedges = std::make_unique<kahypar_hyperedge_id_t[]>(12);
// hypergraph from hMetis manual page 14
hyperedges[0] = 0; hyperedges[1] = 2;
hyperedges[2] = 0; hyperedges[3] = 1;
hyperedges[4] = 3; hyperedges[5] = 4;
hyperedges[6] = 3; hyperedges[7] = 4;
hyperedges[8] = 6; hyperedges[9] = 2;
hyperedges[10] = 5; hyperedges[11] = 6;
const double imbalance = 0.03;
const kahypar_partition_id_t k = 2;
kahypar_hyperedge_weight_t objective = 0;
std::vector<kahypar_partition_id_t> partition(num_vertices, -1);
kahypar_partition(num_vertices, num_hyperedges,
imbalance, k,
/*vertex_weights */ nullptr, hyperedge_weights.get(),
hyperedge_indices.get(), hyperedges.get(),
&objective, context, partition.data());
for(int i = 0; i != num_vertices; ++i) {
std::cout << i << ":" << partition[i] << std::endl;
}
kahypar_context_free(context);
}
To compile the program using g++ run:
g++ -std=c++14 -DNDEBUG -O3 -I/usr/local/include -L/usr/local/lib program.cc -o program -lkahypar
Note: If boost is not found during linking, you might need to add -L/path/to/boost/lib -I/path/to/boost/include -lboost_program_options to the command.
To remove the library from your system use the provided uninstall target:
make uninstall-kahypar
To compile the Python interface, do the following:
mkdir build && cd buildcmake .. -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=RELEASE -DKAHYPAR_PYTHON_INTERFACE=1. If you don't have boost installed, run: cmake .. -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=RELEASE -DKAHYPAR_PYTHON_INTERFACE=1 -DKAHYPAR_USE_MINIMAL_BOOST=ON instead. This will download, extract, and build the necessary dependencies automatically.cd pythonmakecp kahypar.so <path-to-site-packages>After that you can use the KaHyPar libary like this:
import os
import kahypar as kahypar
num_nodes = 7
num_nets = 4
hyperedge_indices = [0,2,6,9,12]
hyperedges = [0,2,0,1,3,4,3,4,6,2,5,6]
node_weights = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
edge_weights = [11,22,33,44]
k=2
hypergraph = kahypar.Hypergraph(num_nodes, num_nets, hyperedge_indices, hyperedges, k, edge_weights, node_weights)
context = kahypar.Context()
context.loadINIconfiguration("<path/to/config>/km1_kKaHyPar_sea20.ini")
context.setK(k)
context.setEpsilon(0.03)
kahypar.partition(hypergraph, context)
For more information about the python library functionality, please see: module.cpp
We also provide a precompiled version as a , which can be installed via:
python3 -m pip install --index-url https://pypi.org/simple/ --no-deps kahypar
Thanks to Jordan Jalving (@jalving) KaHyPar now also offers a Julia interface, which can currently be found here: kahypar/KaHyPar.jl.
The corresponding dependency can be installed via:
using Pkg
Pkg.add(PackageSpec(url="https://github.com/jalving/KaHyPar.jl.git"))
Pkg.test("KaHyPar")
After that, you can use KaHyPar to partition your hypergraphs like this:
using KaHyPar
using SparseArrays
I = [1,3,1,2,4,5,4,5,7,3,6,7]
J = [1,1,2,2,2,2,3,3,3,4,4,4]
V = Int.(ones(length(I)))
A = sparse(I,J,V)
h = KaHyPar.hypergraph(A)
KaHyPar.partition(h,2,configuration = :edge_cut)
KaHyPar.partition(h,2,configuration = :connectivity)
KaHyPar.partition(h,2,configuration = joinpath(@__DIR__,"../src/config/km1_kKaHyPar_sea20.ini"))
Romain Wallon has created a Java interface for KaHyPar. Please refer to the readme for a detailed description on how to build and use the interface.
We encourage you to report any problems with KaHyPar via the github issue tracking system of the project.
KaHyPar is free software provided under the GNU General Public License (GPLv3). For more information see the COPYING file. We distribute this framework freely to foster the use and development of hypergraph partitioning tools. If you use KaHyPar in an academic setting please cite the appropriate papers. If you are interested in a commercial license, please contact me.
// Overall KaHyPar framework
@phdthesis{DBLP:phd/dnb/Schlag20,
author = {Sebastian Schlag},
title = {High-Quality Hypergraph Partitioning},
school = {Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, Germany},
year = {2020}
}
@article{10.1145/3529090,
author = {Schlag, Sebastian and
Heuer, Tobias and
Gottesb\"{u}ren, Lars and
Akhremtsev, Yaroslav and
Schulz, Christian and
Sanders, Peter},
title = {High-Quality Hypergraph Partitioning},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1145/3529090},
doi = {10.1145/3529090},
journal = {ACM J. Exp. Algorithmics},
year = {2022},
month = {mar}
}
// KaHyPar-R
@inproceedings{shhmss2016alenex,
author = {Sebastian Schlag and
Vitali Henne and
Tobias Heuer and
Henning Meyerhenke and
Peter Sanders and
Christian Schulz},
title = {k-way Hypergraph Partitioning via \emph{n}-Level Recursive
Bisection},
booktitle = {18th Workshop on Algorithm Engineering and Experiments, (ALENEX 2016)},
pages = {53--67},
year = {2016},
}
// KaHyPar-K
@inproceedings{ahss2017alenex,
author = {Yaroslav Akhremtsev and
Tobias Heuer and
Peter Sanders and
Sebastian Schlag},
title = {Engineering a direct \emph{k}-way Hypergraph Partitioning Algorithm},
booktitle = {19th Workshop on Algorithm Engineering and Experiments, (ALENEX 2017)},
pages = {28--42},
year = {2017},
}
// KaHyPar-CA
@inproceedings{hs2017sea,
author = {Tobias Heuer and
Sebastian Schlag},
title = {Improving Coarsening Schemes for Hypergraph Partitioning by Exploiting Community Structure},
booktitle = {16th International Symposium on Experimental Algorithms, (SEA 2017)},
pages = {21:1--21:19},
year = {2017},
}
// KaHyPar-MF
@inproceedings{heuer_et_al:LIPIcs:2018:8936,
author ={Tobias Heuer and Peter Sanders and Sebastian Schlag},
title ={{Network Flow-Based Refinement for Multilevel Hypergraph Partitioning}},
booktitle ={17th International Symposium on Experimental Algorithms (SEA 2018)},
pages ={1:1--1:19},
year ={2018}
}
@article{KaHyPar-MF-JEA,
author = {Heuer, T. and Sanders, P. and Schlag, S.},
title = {Network Flow-Based Refinement for Multilevel Hypergraph Partitioning},
journal = {ACM Journal of Experimental Algorithmics (JEA)}},
volume = {24},
number = {1},
month = {09},
year = {2019},
pages = {2.3:1--2.3:36},
publisher = {ACM}
}
// KaHyPar-E (EvoHGP)
@inproceedings{Andre:2018:MMH:3205455.3205475,
author = {Robin Andre and Sebastian Schlag and Christian Schulz},
title = {Memetic Multilevel Hypergraph Partitioning},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the Genetic and Evolutionary Computation Conference},
series = {GECCO '18},
year = {2018},
pages = {347--354},
numpages = {8}
}
// KaHyPar-SEA20 (KaHyPar-HFC)
@InProceedings{gottesbren_et_al:LIPIcs:2020:12085,
author = {Lars Gottesb{\"u}ren and Michael Hamann and Sebastian Schlag and Dorothea Wagner},
title = {{Advanced Flow-Based Multilevel Hypergraph Partitioning}},
booktitle = {18th International Symposium on Experimental Algorithms (SEA)},
pages = {11:1--11:15},
series = {Leibniz International Proceedings in Informatics (LIPIcs)},
year = {2020}
}
If you are interested in contributing to the KaHyPar framework feel free to contact me or create an issue on the issue tracking system.
FAQs
Python Inferface for the Karlsruhe Hypergraph Partitioning Framework (KaHyPar)
We found that kahypar demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security News
Research
The Socket Research Team breaks down a malicious wrapper package that uses obfuscation to harvest credentials and exfiltrate sensitive data.

Research
Security News
Attackers used a malicious npm package typosquatting a popular ESLint plugin to steal sensitive data, execute commands, and exploit developer systems.

Security News
The Ultralytics' PyPI Package was compromised four times in one weekend through GitHub Actions cache poisoning and failure to rotate previously compromised API tokens.