
Security News
Research
Data Theft Repackaged: A Case Study in Malicious Wrapper Packages on npm
The Socket Research Team breaks down a malicious wrapper package that uses obfuscation to harvest credentials and exfiltrate sensitive data.
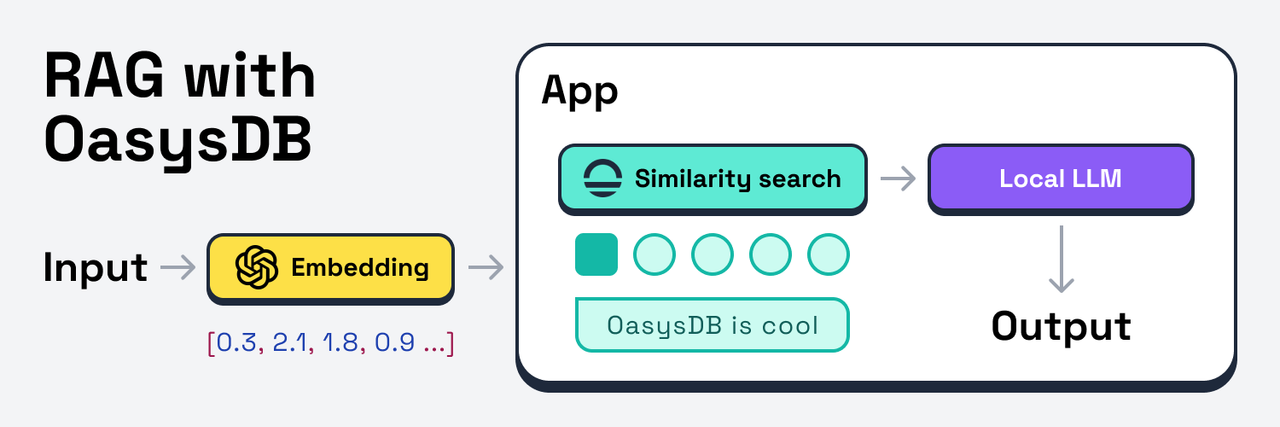
OasysDB is a flexible and easy-to-use vector database written in Rust. It is designed with simplicity in mind to help you focus on building your AI application without worrying about database setup and configuration.
With 3 different runtime modes, OasysDB will accompany you throughout your journey from the early stages of development to scaling up your AI application for production workloads.
OasysDB is very flexible! You can use it for almost any systems related with vector search such as:
🔸 Embedded Database: Zero setup and no dedicated server or process required.
🔸 Optional Persistence: In-memory vector collections that can be persisted to disk.
🔸 Incremental Ops: Insert, modify, and delete vectors without rebuilding indexes.
🔸 Flexible Schema: Store additional and flexible metadata for each vector record.
🔹 Fast HNSW: Efficient and accurate vector search with state-of-the-art algorithm.
🔹 Configurable Metric: Use Euclidean or Cosine distance depending on your use-case.
🔹 Parallel Processing: Multi-threaded & SIMD-optimized vector distance calculation.
🔹 Built-in vector ID: No headache record management with guaranteed ID uniqueness.

To get started with OasysDB in Rust, you need to add oasysdb to your Cargo.toml. You can do so by running the command below which will add the latest version of OasysDB to your project.
cargo add oasysdb
After that, you can use the code snippet below as a reference to get started with OasysDB. In short, use Collection to store your vector records or search similar vector and use Database to persist a vector collection to the disk.
use oasysdb::prelude::*;
fn main() {
// Vector dimension must be uniform.
let dimension = 128;
// Replace with your own data.
let records = Record::many_random(dimension, 100);
let mut config = Config::default();
// Optionally set the distance function. Default to Euclidean.
config.distance = Distance::Cosine;
// Create a vector collection.
let collection = Collection::build(&config, &records).unwrap();
// Optionally save the collection to persist it.
let mut db = Database::new("data/test").unwrap();
db.save_collection("vectors", &collection).unwrap();
// Search for the nearest neighbors.
let query = Vector::random(dimension);
let result = collection.search(&query, 5).unwrap();
for res in result {
let (id, distance) = (res.id, res.distance);
println!("{distance:.5} | ID: {id}");
}
}
OasysDB provides several feature flags to enable or disable certain features. You can do this by adding the feature flags to your project Cargo.toml file. Below are the available feature flags and their descriptions:
json: Enables easy Serde's JSON conversion from and to the metadata type. This feature is very useful if you have a complex metadata type or if you use APIs that communicate using JSON.
gen: Enables the vector generator trait and modules to extract vector embeddings from your contents using OpenAI or other embedding models. This feature allows OasysDB to handle vector embedding extraction for you without separate dependencies.

OasysDB also provides a Python binding which allows you to add it directly to your project. You can install the Python library of OasysDB by running the command below:
pip install oasysdb
This command will install the latest version of OasysDB to your Python environment. After you're all set with the installation, you can use the code snippet below as a reference to get started with OasysDB in Python.
from oasysdb.prelude import *
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Open the database.
db = Database("data/example")
# Replace with your own records.
records = Record.many_random(dimension=128, len=100)
# Create a vector collection.
config = Config.create_default()
collection = Collection.from_records(config, records)
# Optionally, persist the collection to the database.
db.save_collection("my_collection", collection)
# Replace with your own query.
query = Vector.random(128)
# Search for the nearest neighbors.
result = collection.search(query, n=5)
# Print the result.
print("Nearest neighbors ID: {}".format(result[0].id))
OasysDB uses a built-in benchmarking suite using Rust's Criterion crate which we use to measure the performance of the vector database.
Currently, the benchmarks are focused on the performance of the collection's vector search functionality. We are working on adding more benchmarks to measure the performance of other operations.
If you are curious and want to run the benchmarks, you can use the command below to run the benchmarks. If you do run it, please share the results with us 😉
cargo bench
OasysDB uses HNSW which is known to be a memory hog compared to other indexing algorithms. We decided to use it because of its performance even when storing large datasets of vectors with high dimension.
If you are curious about the memory usage of OasysDB, you can use the command below to run the memory usage measurement script. You can tweak the parameters in the examples/measure-memory.rs file to see how the memory usage changes.
cargo run --example measure-memory
In vector databases, recall is the percentage of relevant items that are successfully retrieved compared to the true set of relevant items also known as the ground truth.
To measure the recall rate, you can use the command below to run the recall rate measurement script. You can tweak the parameters in the examples/measure-recall.rs to see how OasysDB performs under different requirements.
cargo run --example measure-recall
Note: This script uses random vector records to measure the recall rate. This might not represent the real-world performance of OasysDB with proper datasets.
The easiest way to contribute to this project is to star this project and share it with your friends. This will help us grow the community and make the project more visible to others.
If you want to go further and contribute your expertise, we will gladly welcome your code contributions. For more information and guidance about this, please see contributing.md.
If you have deep experience in the space but don't have the free time to contribute codes, we also welcome advices, suggestions, or feature requests. We are also looking for advisors to help guide the project direction and roadmap.
If you are interested about the project in any way, please join us on Discord. Help us grow the community and make OasysDB better 😁
We are committed to creating a welcoming community. Any participant in our project is expected to act respectfully and to follow the Code of Conduct.
This project is still in the early stages of development. We are actively working on it and we expect the API and functionality to change. We do not recommend using this in production yet.
FAQs
Fast & flexible embedded vector database with incremental HNSW indexing.
We found that oasysdb demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security News
Research
The Socket Research Team breaks down a malicious wrapper package that uses obfuscation to harvest credentials and exfiltrate sensitive data.

Research
Security News
Attackers used a malicious npm package typosquatting a popular ESLint plugin to steal sensitive data, execute commands, and exploit developer systems.

Security News
The Ultralytics' PyPI Package was compromised four times in one weekend through GitHub Actions cache poisoning and failure to rotate previously compromised API tokens.