




[ English | 中文 | Deutsch | Español | Français | Italiano | 日本語 | 한국어 | Português | Русский | Türkçe | Українська ]
Pyxel is a retro game engine for Python.
With simple specifications inspired by retro gaming consoles, such as displaying only 16 colors and supporting 4 sound channels, you can easily enjoy making pixel-art-style games.

The development of Pyxel is driven by user feedback. Please give Pyxel a star on GitHub!




Pyxel's specifications and APIs are inspired by PICO-8 and TIC-80.
Pyxel is open source under the MIT License and free to use. Let's start making retro games with Pyxel!
Specifications
- Runs on Windows, Mac, Linux, and Web
- Programming in Python
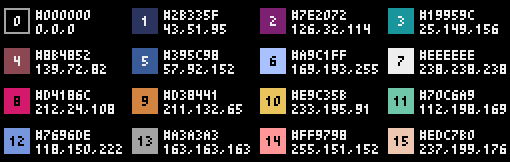
- 16-color palette
- 3 256x256-sized image banks
- 8 256x256-sized tilemaps
- 4 channels with 64 definable sounds
- 8 music tracks combining any sounds
- Keyboard, mouse, and gamepad inputs
- Image and sound editing tools
- User-extensible colors, channels, and banks
Color Palette

How to Install
Windows
After installing Python3 (version 3.8 or higher), run the following command:
pip install -U pyxel
When installing Python using the official installer, make sure to check the Add Python 3.x to PATH option to enable the pyxel command.
Mac
After installing Homebrew, run the following commands:
brew install pipx
pipx ensurepath
pipx install pyxel
To upgrade Pyxel after installation, run pipx upgrade pyxel.
Linux
After installing the SDL2 package (libsdl2-dev for Ubuntu), Python3 (version 3.8 or higher), and python3-pip, run the following command:
sudo pip3 install -U pyxel
If the previous command fails, consider building Pyxel from source by following the instructions in the Makefile.
Web
The web version of Pyxel does not require Python or Pyxel installation and runs on PCs, smartphones, and tablets with supported web browsers.
For detailed instructions, please refer to this page.
Try Examples
After installing Pyxel, you can copy the examples to the current directory with the following command:
pyxel copy_examples
The following examples will be copied to your current directory:
| 01_hello_pyxel.py | Simplest application | Demo | Code |
| 02_jump_game.py | Jump game with Pyxel resource file | Demo | Code |
| 03_draw_api.py | Demonstration of drawing APIs | Demo | Code |
| 04_sound_api.py | Demonstration of sound APIs | Demo | Code |
| 05_color_palette.py | Color palette list | Demo | Code |
| 06_click_game.py | Mouse click game | Demo | Code |
| 07_snake.py | Snake game with BGM | Demo | Code |
| 08_triangle_api.py | Demonstration of triangle drawing APIs | Demo | Code |
| 09_shooter.py | Shoot'em up game with screen transitions | Demo | Code |
| 10_platformer.py | Side-scrolling platform game with map | Demo | Code |
| 11_offscreen.py | Offscreen rendering with Image class | Demo | Code |
| 12_perlin_noise.py | Perlin noise animation | Demo | Code |
| 13_bitmap_font.py | Drawing a bitmap font | Demo | Code |
| 14_synthesizer.py | Synthesizer using audio expansion features | Demo | Code |
| 15_tiled_map_file.py | Loading and drawing a Tile Map File (.tmx) | Demo | Code |
| 16_transform.py | Image rotation and scaling | Demo | Code |
| 99_flip_animation.py | Animation with flip function (non-web platforms only) | Demo | Code |
| 30sec_of_daylight.pyxapp | 1st Pyxel Jam winning game by Adam | Demo | Code |
| megaball.pyxapp | Arcade ball physics game by Adam | Demo | Code |
| 8bit-bgm-gen.pyxapp | Background music generator by frenchbread | Demo | Code |
The examples can be executed with the following commands:
cd pyxel_examples
pyxel run 01_hello_pyxel.py
pyxel play 30sec_of_daylight.pyxapp
How to Use
Create Application
In your Python script, import the Pyxel module, specify the window size with the init function, and then start the Pyxel application with the run function.
import pyxel
pyxel.init(160, 120)
def update():
if pyxel.btnp(pyxel.KEY_Q):
pyxel.quit()
def draw():
pyxel.cls(0)
pyxel.rect(10, 10, 20, 20, 11)
pyxel.run(update, draw)
The arguments of the run function are the update function, which processes frame updates, and the draw function, which handles screen drawing.
In an actual application, it is recommended to wrap Pyxel code in a class, as shown below:
import pyxel
class App:
def __init__(self):
pyxel.init(160, 120)
self.x = 0
pyxel.run(self.update, self.draw)
def update(self):
self.x = (self.x + 1) % pyxel.width
def draw(self):
pyxel.cls(0)
pyxel.rect(self.x, 0, 8, 8, 9)
App()
For creating simple graphics without animation, you can use the show function to simplify your code.
import pyxel
pyxel.init(120, 120)
pyxel.cls(1)
pyxel.circb(60, 60, 40, 7)
pyxel.show()
Run Application
A created script can be executed using the python command:
python PYTHON_SCRIPT_FILE
It can also be run with the pyxel run command:
pyxel run PYTHON_SCRIPT_FILE
Additionally, the pyxel watch command monitors changes in a specified directory and automatically re-runs the program when changes are detected:
pyxel watch WATCH_DIR PYTHON_SCRIPT_FILE
Directory monitoring can be stopped by pressing Ctrl(Command)+C.
Special Key Controls
The following special key actions are available while a Pyxel application is running:
Esc
Quit the applicationAlt(Option)+1
Save the screenshot to the desktopAlt(Option)+2
Reset the recording start time of the screen capture videoAlt(Option)+3
Save a screen capture video to the desktop (up to 10 seconds)Alt(Option)+8 or A+B+X+Y+DL on gamepad
Toggles screen scaling between maximum and integerAlt(Option)+9 or A+B+X+Y+DR on gamepad
Switch between screen modes (Crisp/Smooth/Retro)Alt(Option)+0 or A+B+X+Y+DU on gamepad
Toggle the performance monitor (fps/update time/draw time)Alt(Option)+Enter or A+B+X+Y+DD on gamepad
Toggle fullscreenShift+Alt(Option)+1/2/3
Save image bank 0, 1, or 2 to the desktopShift+Alt(Option)+0
Save the current color palette to the desktop
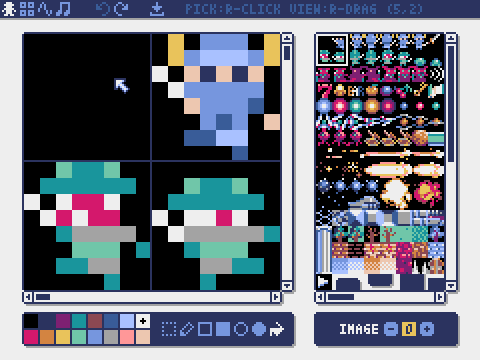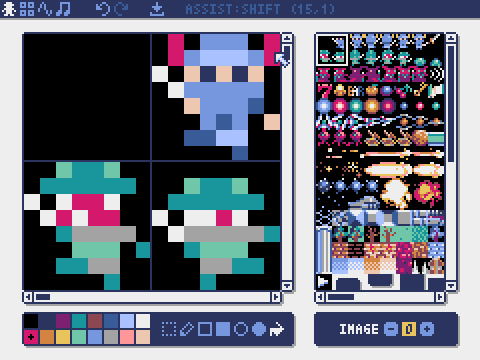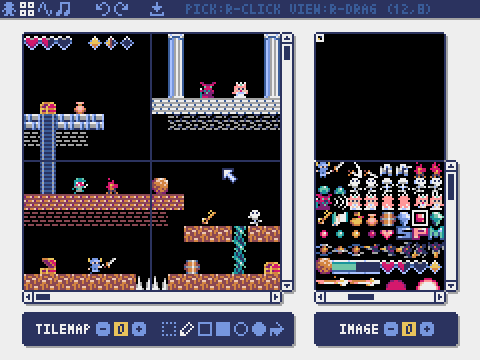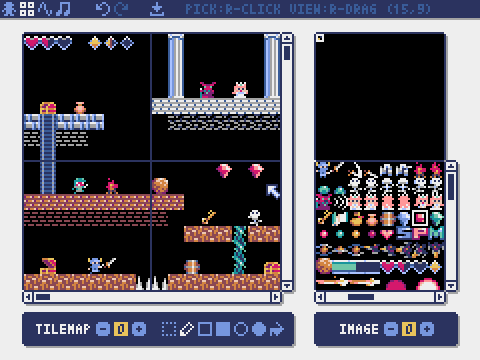
How to Create Resources
Pyxel Editor can create images and sounds used in a Pyxel application.
You can start Pyxel Editor with the following command:
pyxel edit PYXEL_RESOURCE_FILE
If the specified Pyxel resource file (.pyxres) exists, it will be loaded. If it does not exist, a new file with the specified name will be created. If the resource file is omitted, a new file named my_resource.pyxres will be created.
After starting Pyxel Editor, you can switch to another resource file by dragging and dropping it onto Pyxel Editor.
The created resource file can be loaded using the load function.
Pyxel Editor has the following editing modes.
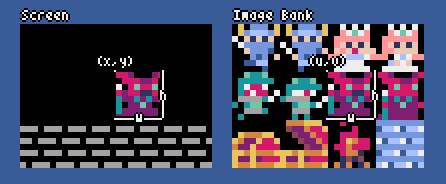
Image Editor
The mode for editing the image in each image bank.
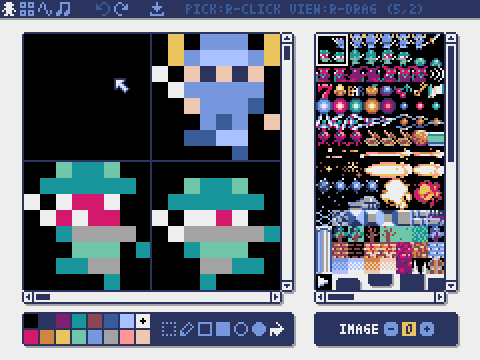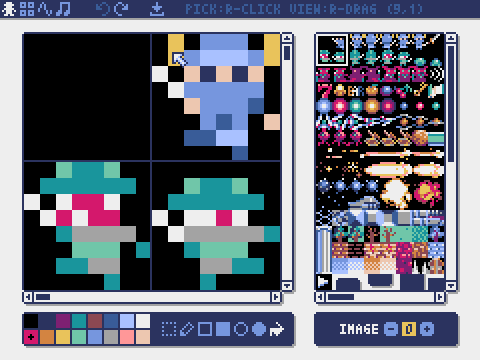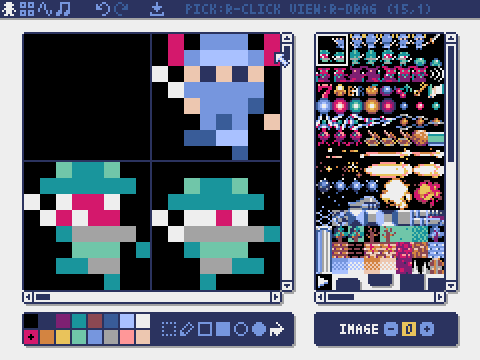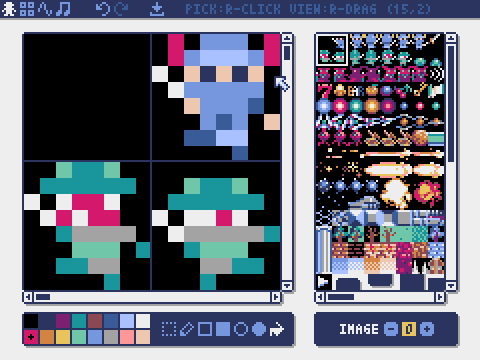
You can drag and drop an image file (PNG/GIF/JPEG) into the image editor to load the image into the currently selected image bank.
Tilemap Editor
The mode for editing tilemaps that arrange images from the image banks in a tile pattern.
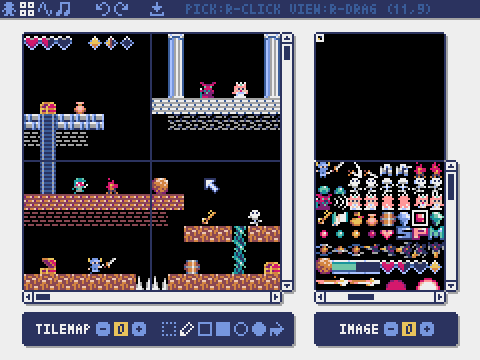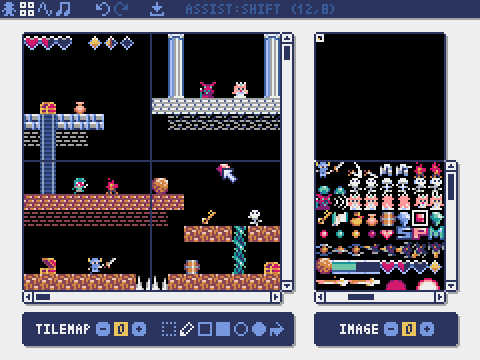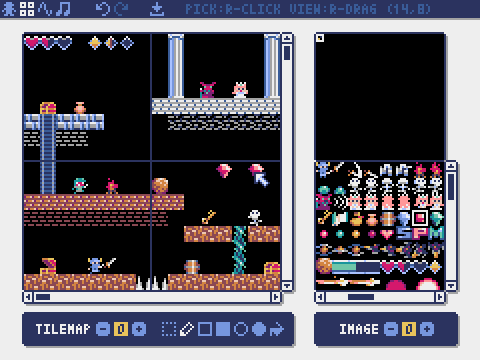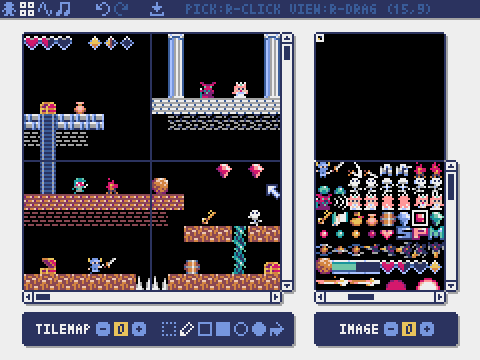
Drag and drop a TMX file (Tiled Map File) onto the tilemap editor to load its layer 0 into the currently selected tilemap.
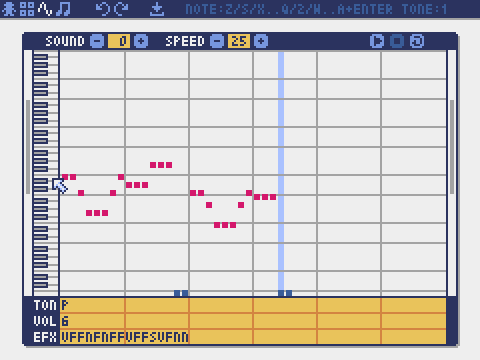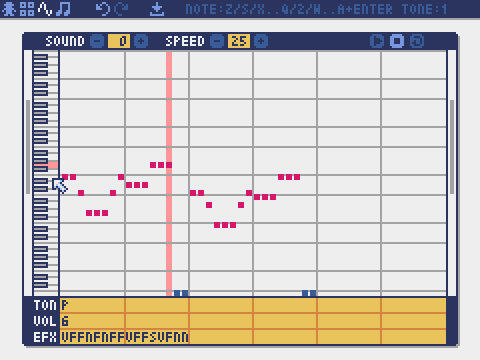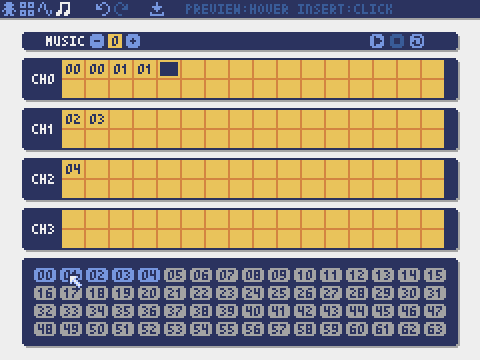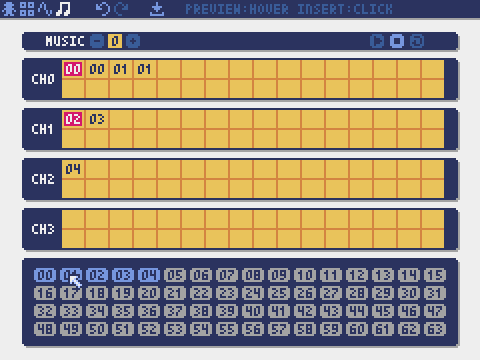
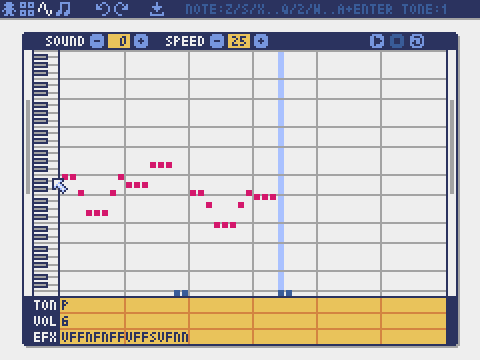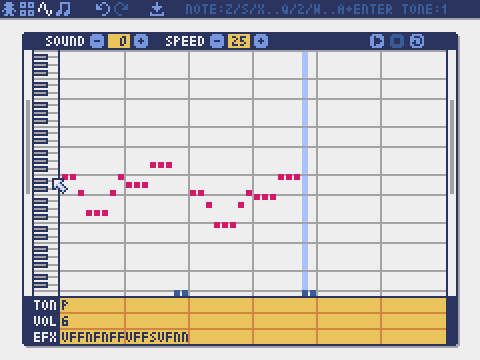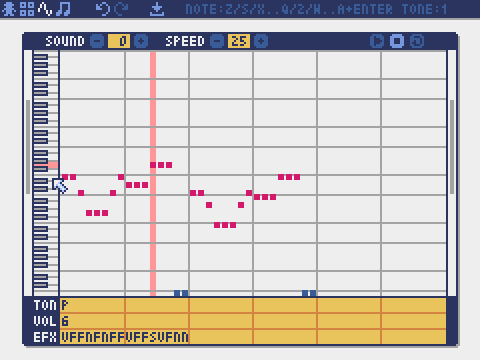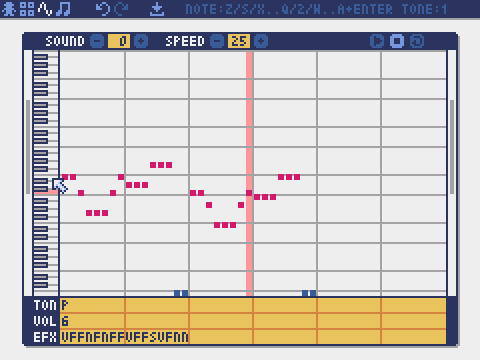
Sound Editor
The mode for editing sounds used for melodies and sound effects.
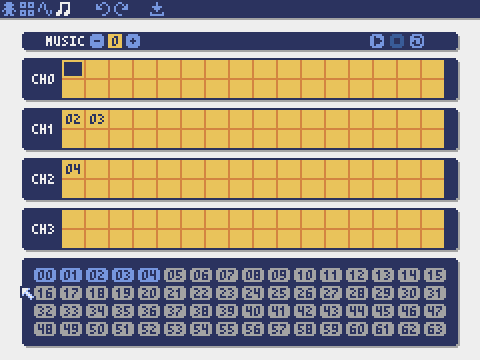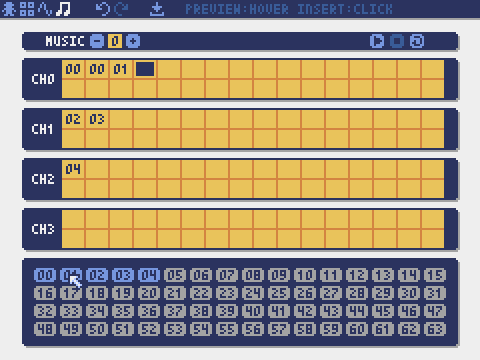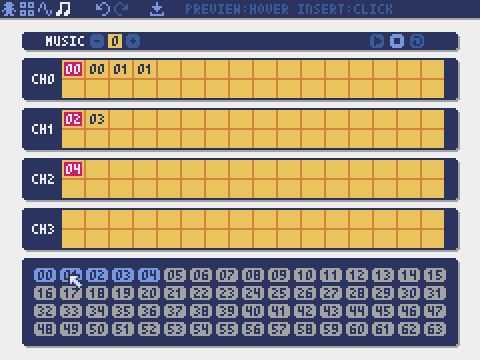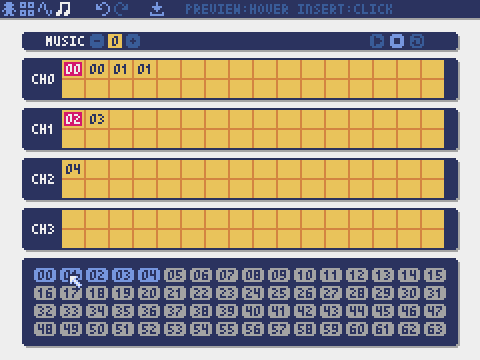
Music Editor
The mode for editing musics in which the sounds are arranged in order of playback.
Other Resource Creation Methods
Pyxel images and tilemaps can also be created using the following methods:
- Create an image from a list of strings using the
Image.set function or the Tilemap.set function - Load an image file (PNG/GIF/JPEG) in Pyxel palette with
Image.load function
Pyxel sounds can also be created using the following method:
- Create a sound from strings with
Sound.set function or Music.set function
Refer to the API reference for the usage of these functions.
How to Distribute Applications
Pyxel supports a dedicated application distribution file format (Pyxel application file) that is cross-platform.
A Pyxel application file (.pyxapp) is created using the pyxel package command:
pyxel package APP_DIR STARTUP_SCRIPT_FILE
If you need to include resources or additional modules, place them in the application directory.
Metadata can be displayed at runtime by specifying it in the following format within the startup script. Fields other than title and author are optional.
The created application file can be run using the pyxel play command:
pyxel play PYXEL_APP_FILE
A Pyxel application file can also be converted to an executable or an HTML file using the pyxel app2exe or pyxel app2html commands.
API Reference
System
-
width, height
The width and height of the screen
-
frame_count
The number of the elapsed frames
-
init(width, height, [title], [fps], [quit_key], [display_scale], [capture_scale], [capture_sec])
Initialize the Pyxel application with the screen size (width, height). The following options can be specified: the window title with title, the frame rate with fps, the key to quit the application with quit_key, the display scale with display_scale, the screen capture scale with capture_scale, and the maximum recording time of the screen capture video with capture_sec.
Example: pyxel.init(160, 120, title="My Pyxel App", fps=60, quit_key=pyxel.KEY_NONE, capture_scale=3, capture_sec=0)
-
run(update, draw)
Start the Pyxel application and call the update function for frame update and the draw function for drawing.
-
show()
Show the screen and wait until the Esc key is pressed.
-
flip()
Refresh the screen by one frame. The application exits when the Esc key is pressed. This function is not available in the web version.
-
quit()
Quit the Pyxel application.
Resource
-
load(filename, [excl_images], [excl_tilemaps], [excl_sounds], [excl_musics])
Load the resource file (.pyxres). If an option is set to True, the corresponding resource will be excluded from loading. If a palette file (.pyxpal) with the same name exists in the same location as the resource file, the palette display colors will also be updated. The palette file contains hexadecimal entries for the display colors (e.g. 1100FF), separated by newlines. The palette file can also be used to change the colors displayed in Pyxel Editor.
-
user_data_dir(vendor_name, app_name)
Returns the user data directory created based on vendor_name and app_name. If the directory does not exist, it will be created automatically. It is used to store high scores, game progress, and similar data.
Example: print(pyxel.user_data_dir("Takashi Kitao", "Pyxel Shooter"))
Input
-
mouse_x, mouse_y
The current position of the mouse cursor
-
mouse_wheel
The current value of the mouse wheel
-
btn(key)
Return True if the key is pressed, otherwise return False. (Key definition list)
-
btnp(key, [hold], [repeat])
Return True if the key is pressed in that frame, otherwise return False. If hold and repeat are specified, after the key has been held down for hold frames or more, True is returned every repeat frames.
-
btnr(key)
Return True if the key is released in that frame, otherwise return False.
-
mouse(visible)
Show the mouse cursor if visible is True, and hide it if visible is False. The cursor's position continues to update even when it is hidden.
Graphics
-
colors
List of the palette display colors. The display color is specified by a 24-bit numerical value. Use colors.from_list and colors.to_list to directly assign and retrieve Python lists.
Example: old_colors = pyxel.colors.to_list(); pyxel.colors.from_list([0x111111, 0x222222, 0x333333]); pyxel.colors[15] = 0x112233
-
images
List of the image banks (instances of the Image class) (0-2)
Example: pyxel.images[0].load(0, 0, "title.png")
-
tilemaps
List of the tilemaps (instances of the Tilemap class) (0-7)
-
clip(x, y, w, h)
Set the drawing area of the screen from (x, y) with a width of w and a height of h. Call clip() to reset the drawing area to full screen.
-
camera(x, y)
Change the upper-left corner coordinates of the screen to (x, y). Call camera() to reset the upper-left corner coordinates to (0, 0).
-
pal(col1, col2)
Replace color col1 with col2 when drawing. Call pal() to reset to the initial palette.
-
dither(alpha)
Apply dithering (pseudo-transparency) when drawing. Set alpha in the range 0.0-1.0, where 0.0 is transparent and 1.0 is opaque.
-
cls(col)
Clear screen with color col.
-
pget(x, y)
Get the color of the pixel at (x, y).
-
pset(x, y, col)
Draw a pixel of color col at (x, y).
-
line(x1, y1, x2, y2, col)
Draw a line of color col from (x1, y1) to (x2, y2).
-
rect(x, y, w, h, col)
Draw a rectangle of width w, height h and color col from (x, y).
-
rectb(x, y, w, h, col)
Draw the outline of a rectangle of width w, height h and color col from (x, y).
-
circ(x, y, r, col)
Draw a circle of radius r and color col at (x, y).
-
circb(x, y, r, col)
Draw the outline of a circle of radius r and color col at (x, y).
-
elli(x, y, w, h, col)
Draw an ellipse of width w, height h and color col from (x, y).
-
ellib(x, y, w, h, col)
Draw the outline of an ellipse of width w, height h and color col from (x, y).
-
tri(x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3, col)
Draw a triangle with vertices (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (x3, y3) and color col.
-
trib(x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3, col)
Draw the outline of a triangle with vertices (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (x3, y3) and color col.
-
fill(x, y, col)
Fill the area connected with the same color as (x, y) with color col.
-
blt(x, y, img, u, v, w, h, [colkey], [rotate], [scale])
Copy the region of size (w, h) from (u, v) of the image bank img(0-2) to (x, y). If a negative value is assigned to w and/or h, the region will be flipped horizontally and/or vertically. If colkey is specified, it will be treated as a transparent color. If rotate(in degrees), scale(1.0 = 100%), or both are specified, the corresponding transformations will be applied.
bltm(x, y, tm, u, v, w, h, [colkey], [rotate], [scale])
Copy the region of size (w, h) from (u, v) of the tilemap tm(0-7) to (x, y). If a negative value is assigned to w and/or h, the region will be flipped horizontally and/or vertically. If colkey is specified, it will be treated as a transparent color. If rotate(in degrees), scale(1.0 = 100%), or both are specified, the corresponding transformations will be applied. The size of a tile is 8x8 pixels and is stored in a tilemap as a tuple of (image_tx, image_ty).

text(x, y, s, col)
Draw a string s in color col at (x, y).
Audio
-
sounds
List of the sounds (instances of the Sound class) (0-63)
Example: pyxel.sounds[0].speed = 60
-
musics
List of the musics (instances of the Music class) (0-7)
-
play(ch, snd, [tick], [loop], [resume])
Play the sound snd(0-63) on channel ch(0-3). If snd is a list, the sounds will be played in sequence. The playback start position can be specified by tick(1 tick = 1/120 seconds). If loop is set to True, loop playback is performed. To resume the previous sound after playback ends, set resume to True.
-
playm(msc, [tick], [loop])
Play the music msc(0-7). The playback start position can be specified by tick(1 tick = 1/120 seconds). If loop is set to True, loop playback is performed.
-
stop([ch])
Stop playback of the specified channel ch(0-3). Call stop() to stop all channels.
-
play_pos(ch)
Get the sound playback position of channel ch(0-3) as a tuple of (sound_no, note_no). Return None when playback has stopped.
Math
-
ceil(x)
Return the smallest integer that is greater than or equal to x.
-
floor(x)
Return the largest integer that is less than or equal to x.
-
sgn(x)
Return 1 when x is positive, 0 when it is 0, and -1 when it is negative.
-
sqrt(x)
Return the square root of x.
-
sin(deg)
Return the sine of deg degrees.
-
cos(deg)
Return the cosine of deg degrees.
-
atan2(y, x)
Return the arctangent of y/x in degrees.
-
rseed(seed)
Sets the seed of the random number generator.
-
rndi(a, b)
Return a random integer greater than or equal to a and less than or equal to b.
-
rndf(a, b)
Return a random floating-point number greater than or equal to a and less than or equal to b.
-
nseed(seed)
Set the seed of Perlin noise.
-
noise(x, [y], [z])
Return the Perlin noise value for the specified coordinates.
Image Class
-
width, height
The width and height of the image
-
set(x, y, data)
Set the image at (x, y) using a list of strings.
Example: pyxel.images[0].set(10, 10, ["0123", "4567", "89ab", "cdef"])
-
load(x, y, filename)
Load an image file (PNG/GIF/JPEG) at (x, y).
-
pget(x, y)
Get the color of the pixel at (x, y).
-
pset(x, y, col)
Draw a pixel with the color col at (x, y).
Tilemap Class
-
width, height
The width and height of the tilemap
-
imgsrc
The image bank (0-2) referenced by the tilemap
-
set(x, y, data)
Set the tilemap at (x, y) using a list of strings.
Example: pyxel.tilemap(0).set(0, 0, ["0000 0100 a0b0", "0001 0101 a1b1"])
-
load(x, y, filename, layer)
Load the layer (0-) from the TMX file (Tiled Map File) at (x, y).
-
pget(x, y)
Get the tile at (x, y). A tile is represented as a tuple of (image_tx, image_ty).
-
pset(x, y, tile)
Draw a tile at (x, y). A tile is represented as a tuple of (image_tx, image_ty).
Sound Class
-
notes
List of notes (0-127). The higher the number, the higher the pitch. Note 33 corresponds to 'A2'(440Hz). Rest notes are represented by -1.
-
tones
List of tones (0:Triangle / 1:Square / 2:Pulse / 3:Noise)
-
volumes
List of volumes (0-7)
-
effects
List of effects (0:None / 1:Slide / 2:Vibrato / 3:FadeOut / 4:Half-FadeOut / 5:Quarter-FadeOut)
-
speed
Playback speed. 1 is the fastest, and the larger the number, the slower the playback speed. At 120, the length of one note becomes 1 second.
-
set(notes, tones, volumes, effects, speed)
Set notes, tones, volumes, and effects using a string. If the length of tones, volumes, or effects are shorter than the notes, they will be repeated from the beginning.
-
set_notes(notes)
Set the notes using a string made of 'CDEFGAB'+'#-'+'01234' or 'R'. It is case-insensitive, and whitespace is ignored.
Example: pyxel.sounds[0].set_notes("G2B-2D3R RF3F3F3")
-
set_tones(tones)
Set the tones with a string made of 'TSPN'. Case-insensitive and whitespace is ignored.
Example: pyxel.sounds[0].set_tones("TTSS PPPN")
-
set_volumes(volumes)
Set the volumes with a string made of '01234567'. Case-insensitive and whitespace is ignored.
Example: pyxel.sounds[0].set_volumes("7777 7531")
-
set_effects(effects)
Set the effects with a string made of 'NSVFHQ'. Case-insensitive and whitespace is ignored.
Example: pyxel.sounds[0].set_effects("NFNF NVVS")
Music Class
-
seqs
A two-dimensional list of sounds (0-63) across multiple channels
-
set(seq0, seq1, seq2, ...)
Set the lists of sound (0-63) for each channel. If an empty list is specified, that channel will not be used for playback.
Example: pyxel.musics[0].set([0, 1], [], [3])
Advanced API
Pyxel includes an "Advanced API" that is not mentioned in this reference, as it may confuse users or require specialized knowledge to use.
If you are confident in your skills, try creating amazing works using this as a guide!
How to Contribute
Submitting Issues
Use the Issue Tracker to submit bug reports and feature or enhancement requests. Before submitting a new issue, make sure there are no similar open issues.
Functional Testing
Anyone who manually tests the code and reports bugs or suggestions for enhancements in the Issue Tracker is very welcome!
Submitting Pull Requests
Patches and fixes are accepted in the form of pull requests (PRs). Make sure that the issue the pull request addresses is open in the Issue Tracker.
Submitting a pull request implies that you agree to license your contribution under the MIT License.
Other Information
License
Pyxel is licensed under the MIT License. It can be reused in proprietary software, provided that all copies of the software or its substantial portions include a copy of the MIT License terms and a copyright notice.
Pyxel is looking for sponsors on GitHub Sponsors. Please consider sponsoring Pyxel to support its continued maintenance and feature development. As a benefit, sponsors can consult directly with the Pyxel developer. For more details, please visit this page.
























