
Security Fundamentals
Turtles, Clams, and Cyber Threat Actors: Shell Usage
The Socket Threat Research Team uncovers how threat actors weaponize shell techniques across npm, PyPI, and Go ecosystems to maintain persistence and exfiltrate data.
github.com/StratoDem/sd-range-slider
A range slider with compressed page usage
Go to this link to learn about Dash.
# Install dependencies
$ npm install
# Watch source for changes and build to `lib/`
$ npm start
You can start up a demo development server to see a demo of the rendered components:
$ builder run demo
$ open http://localhost:9000
You have to maintain the list of components in demo/Demo.react.js.
$ npm test
$ npm run test-watch
$ npm run test-debug
Cmd+opt+i).webpack:// -> . -> spec/components to find your test source files.webpack:// -> [your/repo/path]] -> sd-range-slider -> src to find your component source files.In your test, append .only to a describe or it statement:
describe.only('Foo component', () => {
// ...
})l
Build development bundle to lib/ and watch for changes
# Once this is started, you can just leave it running.
$ npm start
Install module locally (after every change)
# Generate metadata, and build the JavaScript bundle
$ npm run install-local
# Now you're done. For subsequent changes, if you've got `npm start`
# running in a separate process, it's enough to just do:
$ python setup.py install
Run the dash layout you want to test
# Import sd-range-slider to your layout, then run it:
$ python my_dash_layout.py
TODO: There is a workflow that links your module into site-packages which would
make it unnecessary to re-run 2. on every change: python setup.py develop.
Unfortunately, this doesn't seem to work with resources defined in
package_data.
See https://github.com/plotly/dash-components-archetype/issues/20
Before publishing to PyPi, you can test installing the module locally:
# Install in `site-packages` on your machine
$ npm run install-local
$ npm run uninstall-local
For now, multiple steps are necessary for publishing to NPM and PyPi, respectively. TODO: #5 will roll up publishing steps into one workflow.
Ask @chriddyp to get NPM / PyPi package publishing accesss.
Preparing to publish to NPM
# Bump the package version
$ npm version major|minor|patch
# Push branch and tags to repo
$ git push --follow-tags
Preparing to publish to PyPi
# Bump the PyPi package to the same version
$ vi setup.py
# Commit to github
$ git add setup.py
$ git commit -m "Bump pypi package version to vx.x.x"
Publish to npm and PyPi
$ npm run publish-all
We use Builder to centrally manage build configuration, dependencies, and scripts.
To see all builder scripts available:
$ builder help
See the dash-components-archetype repo for more information.
FAQs
Unknown package
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security Fundamentals
The Socket Threat Research Team uncovers how threat actors weaponize shell techniques across npm, PyPI, and Go ecosystems to maintain persistence and exfiltrate data.

Security News
At VulnCon 2025, NIST scrapped its NVD consortium plans, admitted it can't keep up with CVEs, and outlined automation efforts amid a mounting backlog.
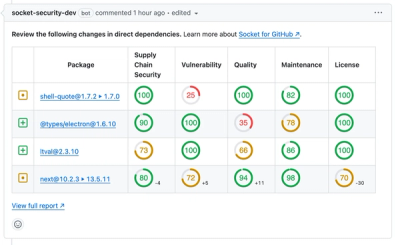
Product
We redesigned our GitHub PR comments to deliver clear, actionable security insights without adding noise to your workflow.