
Product
Introducing Webhook Events for Pull Request Scans
Add real-time Socket webhook events to your workflows to automatically receive pull request scan results and security alerts in real time.
Package eval implements evaluation of GoLang expression at runtime.
Suggestions:
Simple:
src:="int8(1*(1+2))"
expr,err:=ParseString(src,"")
if err!=nil{
return err
}
r,err:=expr.EvalToInterface(nil)
if err!=nil{
return err
}
fmt.Printf("%v %T", r, r) // "3 int8"
Complicated:
type exampleString string
func (s exampleString) String() exampleString { return "!" + s + "!" }
type exampleStruct struct {
A, B int
}
func (s exampleStruct) Sum() int { return s.A + s.B }
func main(){
c := make(chan int64, 10)
c <- 2
src := `exampleString(fmt.Sprint(interface{}(math.MaxInt64/exampleStruct(struct{ A, B int }{3, 5}).Sum()+int(<-(<-chan int64)(c))-cap(make([]string, 1, 100))))).String().String() + "."`
expr, err := ParseString(src, "")
if err != nil {
return
}
a := Args{
"exampleString": MakeTypeInterface(exampleString("")),
"fmt.Sprint": MakeDataRegularInterface(fmt.Sprint),
"math.MaxInt64": MakeDataUntypedConst(constanth.MakeUint(math.MaxInt64)),
"exampleStruct": MakeTypeInterface(exampleStruct{}),
"c": MakeDataRegularInterface(c),
}
r, err := expr.EvalToInterface(a)
if err != nil {
return
}
if r != testR {
return
}
fmt.Printf("%v %T\n", r, r) // "!!1152921504606846877!!. exampleString"
return
}
With error:
src := `exampleString(fmt.Sprint(interface{}(math.MaxInt64/exampleStruct(struct{ A, B int }{3, 5}).Sum()+int(<-(<-chan int64)(c))-cap(make([]string, 1, 100))))).String().String() + "."`
expr, err := ParseString(src, "")
if err != nil {
t.Error(err)
}
a := Args{
"exampleString": MakeTypeInterface(exampleString("")),
"fmt.Sprint": MakeDataRegularInterface(fmt.Sprint),
"math.MaxInt64": MakeDataUntypedConst(constanth.MakeUint(math.MaxInt64)),
"exampleStruct": MakeTypeInterface(exampleStruct{}),
// Remove "c" from passed arguments:
// "c": MakeDataRegularInterface(c),
}
_, err = expr.EvalToInterface(a)
fmt.Println(err) // "expression:1:119: undefined: c"
Please report bug if you found it.
FAQs
Unknown package
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Product
Add real-time Socket webhook events to your workflows to automatically receive pull request scan results and security alerts in real time.

Research
The Socket Threat Research Team uncovered malicious NuGet packages typosquatting the popular Nethereum project to steal wallet keys.
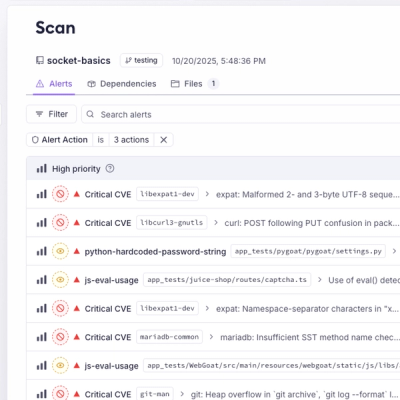
Product
A single platform for static analysis, secrets detection, container scanning, and CVE checks—built on trusted open source tools, ready to run out of the box.