
Research
2025 Report: Destructive Malware in Open Source Packages
Destructive malware is rising across open source registries, using delays and kill switches to wipe code, break builds, and disrupt CI/CD.
github.com/mitchellh/go-server-timing
Advanced tools
This is a library including middleware for using HTTP Server-Timing with Go. This header allows a server to send timing information from the backend, such as database access time, file reads, etc. The timing information can be then be inspected in the standard browser developer tools:
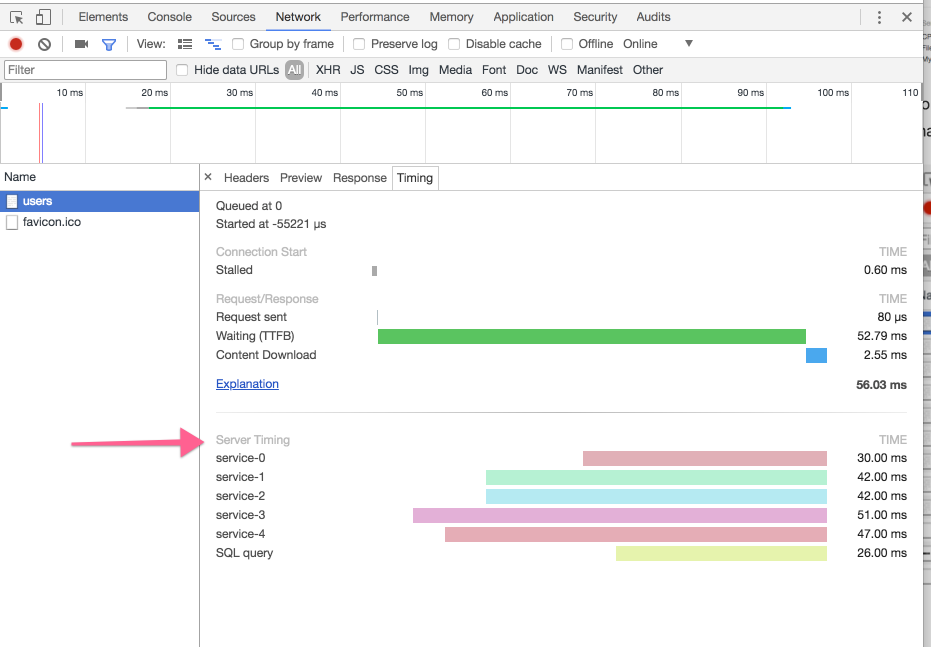
Middleware for injecting the server timing struct into the request Context
and writing the Server-Timing header.
Concurrency-safe structures for easily recording timings of multiple concurrency tasks.
Parse Server-Timing headers as a client.
Note: No browser properly supports sending the Server-Timing header as an HTTP Trailer so the Middleware only supports a normal header currently.
Browser support is required to view server timings easily. Because server timings are sent as an HTTP header, there is no negative impact to sending the header to unsupported browsers.
Chrome 65 or higher is required to properly display server timings in the devtools.
Firefox is pending with an open bug report (ID 1403051)
IE, Opera, and others are unknown at this time.
Example usage is shown below. A fully runnable example is available in
the example/ directory.
func main() {
// Our handler. In a real application this might be your root router,
// or some subset of your router. Wrapping this ensures that all routes
// handled by this handler have access to the server timing header struct.
var h http.Handler = http.HandlerFunc(handler)
// Wrap our handler with the server timing middleware
h = servertiming.Middleware(h, nil)
// Start!
http.ListenAndServe(":8080", h)
}
func handler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
// Get our timing header builder from the context
timing := servertiming.FromContext(r.Context())
// Imagine your handler performs some tasks in a goroutine, such as
// accessing some remote service. timing is concurrency safe so we can
// record how long that takes. Let's simulate making 5 concurrent requests
// to various servicse.
var wg sync.WaitGroup
for i := 0; i < 5; i++ {
wg.Add(1)
name := fmt.Sprintf("service-%d", i)
go func(name string) {
// This creats a new metric and starts the timer. The Stop is
// deferred so when the function exits it'll record the duration.
defer timing.NewMetric(name).Start().Stop()
time.Sleep(random(25, 75))
wg.Done()
}(name)
}
// Imagine this is just some blocking code in your main handler such
// as a SQL query. Let's record that.
m := timing.NewMetric("sql").WithDesc("SQL query").Start()
time.Sleep(random(20, 50))
m.Stop()
// Wait for the goroutine to end
wg.Wait()
// You could continue recording more metrics, but let's just return now
w.WriteHeader(200)
w.Write([]byte("Done. Check your browser inspector timing details."))
}
func random(min, max int) time.Duration {
return (time.Duration(rand.Intn(max-min) + min)) * time.Millisecond
}
FAQs
Unknown package
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Research
Destructive malware is rising across open source registries, using delays and kill switches to wipe code, break builds, and disrupt CI/CD.

Security News
Socket CTO Ahmad Nassri shares practical AI coding techniques, tools, and team workflows, plus what still feels noisy and why shipping remains human-led.

Research
/Security News
A five-month operation turned 27 npm packages into durable hosting for browser-run lures that mimic document-sharing portals and Microsoft sign-in, targeting 25 organizations across manufacturing, industrial automation, plastics, and healthcare for credential theft.