
Security News
PyPI Expands Trusted Publishing to GitLab Self-Managed as Adoption Passes 25 Percent
PyPI adds Trusted Publishing support for GitLab Self-Managed as adoption reaches 25% of uploads
github.com/spacemonkeygo/monkit/v3
Advanced tools

Package monkit is a flexible code instrumenting and data collection library.
See documentation at https://godoc.org/github.com/spacemonkeygo/monkit/v3
Software is hard. Like, really hard. Just the worst. Sometimes it feels like we've constructed a field where the whole point is to see how tangled we can get ourselves before seeing if we can get tangled up more while trying to get untangled.
Many software engineering teams are coming to realize (some slower than others) that collecting data over time about how their systems are functioning is a super power you can't turn back from. Some teams are calling this Telemetry, Observability, or describing it more basically through subcomponents such as distributed tracing, time-series data, or even just metrics. We've been calling it monitoring, but geez, I suppose if trends continue and you want to do this yourself your first step should be to open a thesaurus and pick an unused term.
I'm not here to tell you about our whole platform. Instead, I'm here to explain a redesign of a Go library for instrumenting your Go programs that we rather quietly launched a few years ago. If you are already using version 1 of our old library, we're sorry, but we rewrote it from scratch and renamed it to monkit. This one (this one!) is better - you should switch!
I'm going to try and sell you as fast as I can on this library.
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"log"
"math/rand"
"net/http"
"time"
"github.com/spacemonkeygo/monkit/v3"
"github.com/spacemonkeygo/monkit/v3/environment"
"github.com/spacemonkeygo/monkit/v3/present"
)
var mon = monkit.Package()
func main() {
environment.Register(monkit.Default)
go http.ListenAndServe("127.0.0.1:9000", present.HTTP(monkit.Default))
for {
time.Sleep(time.Second)
log.Println(DoStuff(context.Background()))
}
}
func DoStuff(ctx context.Context) (err error) {
defer mon.Task()(&ctx)(&err)
result, err := ComputeThing(ctx, 1, 2)
if err != nil {
return err
}
fmt.Println(result)
return
}
func ComputeThing(ctx context.Context, arg1, arg2 int) (res int, err error) {
defer mon.Task()(&ctx)(&err)
timer := mon.Timer("subcomputation").Start()
res = arg1 + arg2
timer.Stop()
if res == 3 {
mon.Event("hit 3")
}
mon.BoolVal("was-4").Observe(res == 4)
mon.IntVal("res").Observe(int64(res))
mon.DurationVal("took").Observe(time.Second + time.Duration(rand.Intn(int(10*time.Second))))
mon.Counter("calls").Inc(1)
mon.Gauge("arg1", func() float64 { return float64(arg1) })
mon.Meter("arg2").Mark(arg2)
return arg1 + arg2, nil
}
We've got tools that capture distribution information (including quantiles) about int64, float64, and bool types. We have tools that capture data about events (we've got meters for deltas, rates, etc). We have rich tools for capturing information about tasks and functions, and literally anything that can generate a name and a number.
Almost just as importantly, the amount of boilerplate and code you have to write to get these features is very minimal. Data that's hard to measure probably won't get measured.
This data can be collected and sent to Graphite or any other time-series database.
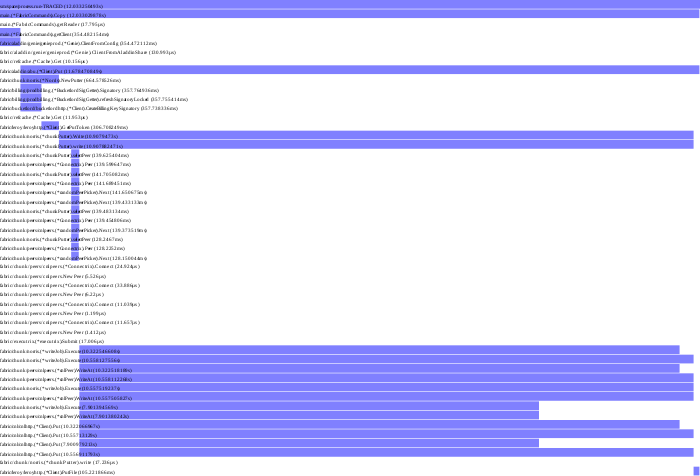
Here's a selection of live stats from one of our storage nodes:
env.os.fds 120.000000
env.os.proc.stat.Minflt 81155.000000
env.os.proc.stat.Cminflt 11789.000000
env.os.proc.stat.Majflt 10.000000
env.os.proc.stat.Cmajflt 6.000000
...
env.process.control 1.000000
env.process.crc 3819014369.000000
env.process.uptime 163225.292925
env.runtime.goroutines 52.000000
env.runtime.memory.Alloc 2414080.000000
...
env.rusage.Maxrss 26372.000000
...
sm/flud/csl/client.(*CSLClient).Verify.current 0.000000
sm/flud/csl/client.(*CSLClient).Verify.success 788.000000
sm/flud/csl/client.(*CSLClient).Verify.error volume missing 91.000000
sm/flud/csl/client.(*CSLClient).Verify.error dial error 1.000000
sm/flud/csl/client.(*CSLClient).Verify.panics 0.000000
sm/flud/csl/client.(*CSLClient).Verify.success times min 0.102214
sm/flud/csl/client.(*CSLClient).Verify.success times avg 1.899133
sm/flud/csl/client.(*CSLClient).Verify.success times max 8.601230
sm/flud/csl/client.(*CSLClient).Verify.success times recent 2.673128
sm/flud/csl/client.(*CSLClient).Verify.failure times min 0.682881
sm/flud/csl/client.(*CSLClient).Verify.failure times avg 3.936571
sm/flud/csl/client.(*CSLClient).Verify.failure times max 6.102318
sm/flud/csl/client.(*CSLClient).Verify.failure times recent 2.208020
sm/flud/csl/server.store.avg 710800.000000
sm/flud/csl/server.store.count 271.000000
sm/flud/csl/server.store.max 3354194.000000
sm/flud/csl/server.store.min 467.000000
sm/flud/csl/server.store.recent 1661376.000000
sm/flud/csl/server.store.sum 192626890.000000
...
This library generates call graphs of your live process for you.
These call graphs aren't created through sampling. They're full pictures of all of the interesting functions you've annotated, along with quantile information about their successes, failures, how often they panic, return an error (if so instrumented), how many are currently running, etc.
The data can be returned in dot format, in json, in text, and can be about just the functions that are currently executing, or all the functions the monitoring system has ever seen.
Here's another example of one of our production nodes:
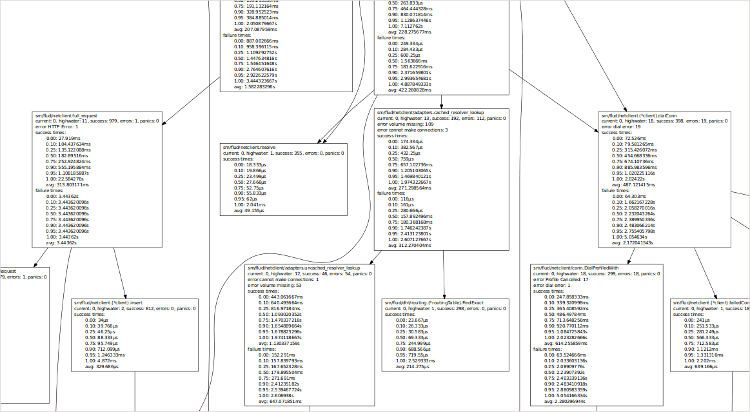
This library generates trace graphs of your live process for you directly, without requiring standing up some tracing system such as Zipkin (though you can do that too).
Inspired by Google's Dapper and Twitter's Zipkin, we have process-internal trace graphs, triggerable by a number of different methods.
You get this trace information for free whenever you use Go contexts and function monitoring. The output formats are svg and json.
Additionally, the library supports trace observation plugins, and we've written a plugin that sends this data to Zipkin.
Before our crazy Go rewrite of everything (and before we had even seen Google's Dapper paper), we were a Python shop, and all of our "interesting" functions were decorated with a helper that collected timing information and sent it to Graphite.
When we transliterated to Go, we wanted to preserve that functionality, so the first version of our monitoring package was born.
Over time it started to get janky, especially as we found Zipkin and started adding tracing functionality to it. We rewrote all of our Go code to use Google contexts, and then realized we could get call graph information. We decided a refactor and then an all-out rethinking of our monitoring package was best, and so now we have this library.
Sometimes you really want callstack contextual information without having to pass arguments through everything on the call stack. In other languages, many people implement this with thread-local storage.
Example: let's say you have written a big system that responds to user requests. All of your libraries log using your log library. During initial development everything is easy to debug, since there's low user load, but now you've scaled and there's OVER TEN USERS and it's kind of hard to tell what log lines were caused by what. Wouldn't it be nice to add request ids to all of the log lines kicked off by that request? Then you could grep for all log lines caused by a specific request id. Geez, it would suck to have to pass all contextual debugging information through all of your callsites.
Google solved this problem by always passing a context.Context interface
through from call to call. A Context is basically just a mapping of arbitrary
keys to arbitrary values that users can add new values for. This way if you
decide to add a request context, you can add it to your Context and then all
callsites that descend from that place will have the new data in their contexts.
It is admittedly very verbose to add contexts to every function call. Painfully so. I hope to write more about it in the future, but Google also wrote up their thoughts about it, which you can go read. For now, just swallow your disgust and let's keep moving.
Let's make a super simple Varnish clone. Open up gedit! (Okay just kidding, open whatever text editor you want.)
For this motivating program, we won't even add the caching, though there's comments for where to add it if you'd like. For now, let's just make a barebones system that will proxy HTTP requests. We'll call it VLite, but maybe we should call it VReallyLite.
package main
import (
"flag"
"net/http"
"net/http/httputil"
"net/url"
)
type VLite struct {
target *url.URL
proxy *httputil.ReverseProxy
}
func NewVLite(target *url.URL) *VLite {
return &VLite{
target: target,
proxy: httputil.NewSingleHostReverseProxy(target),
}
}
func (v *VLite) Proxy(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
r.Host = v.target.Host // let the proxied server get the right vhost
v.proxy.ServeHTTP(w, r)
}
func (v *VLite) ServeHTTP(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
// here's where you'd put caching logic
v.Proxy(w, r)
}
func main() {
target := flag.String(
"proxy",
"http://hasthelargehadroncolliderdestroyedtheworldyet.com/",
"server to cache")
flag.Parse()
targetURL, err := url.Parse(*target)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
panic(http.ListenAndServe(":8080", NewVLite(targetURL)))
}
Run and build this and open localhost:8080 in your browser. If you use the
default proxy target, it should inform you that the world hasn't been
destroyed yet.
The first thing you'll want to do is add the small amount of boilerplate to make the instrumentation we're going to add to your process observable later.
Import the basic monkit packages:
"github.com/spacemonkeygo/monkit/v3"
"github.com/spacemonkeygo/monkit/v3/environment"
"github.com/spacemonkeygo/monkit/v3/present"
and then register environmental statistics and kick off a goroutine in your main method to serve debug requests:
environment.Register(monkit.Default)
go http.ListenAndServe("localhost:9000", present.HTTP(monkit.Default))
Rebuild, and then check out localhost:9000/stats (or
localhost:9000/stats/json, if you prefer) in your browser!
Remember what I said about Google's contexts? It might seem a bit overkill for such a small project, but it's time to add them.
To help out here, I've created a library that constructs contexts for you for incoming HTTP requests. Nothing that's about to happen requires my webhelp library, but here is the code now refactored to receive and pass contexts through our two per-request calls.
package main
import (
"context"
"flag"
"net/http"
"net/http/httputil"
"net/url"
"github.com/jtolds/webhelp"
"github.com/spacemonkeygo/monkit/v3"
"github.com/spacemonkeygo/monkit/v3/environment"
"github.com/spacemonkeygo/monkit/v3/present"
)
type VLite struct {
target *url.URL
proxy *httputil.ReverseProxy
}
func NewVLite(target *url.URL) *VLite {
return &VLite{
target: target,
proxy: httputil.NewSingleHostReverseProxy(target),
}
}
func (v *VLite) Proxy(ctx context.Context, w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
r.Host = v.target.Host // let the proxied server get the right vhost
v.proxy.ServeHTTP(w, r)
}
func (v *VLite) HandleHTTP(ctx context.Context, w webhelp.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) error {
// here's where you'd put caching logic
v.Proxy(ctx, w, r)
return nil
}
func main() {
target := flag.String(
"proxy",
"http://hasthelargehadroncolliderdestroyedtheworldyet.com/",
"server to cache")
flag.Parse()
targetURL, err := url.Parse(*target)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
environment.Register(monkit.Default)
go http.ListenAndServe("localhost:9000", present.HTTP(monkit.Default))
panic(webhelp.ListenAndServe(":8080", NewVLite(targetURL)))
}
You can create a new context for a request however you want. One reason to use something like webhelp is that the cancelation feature of Contexts is hooked up to the HTTP request getting canceled.
Let's start to get statistics about how many requests we receive! First, this package (main) will need to get a monitoring Scope. Add this global definition right after all your imports, much like you'd create a logger with many logging libraries:
var mon = monkit.Package()
Now, make the error return value of HandleHTTP named (so, (err error)), and add this defer line as the very first instruction of HandleHTTP:
func (v *VLite) HandleHTTP(ctx context.Context, w webhelp.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) (err error) {
defer mon.Task()(&ctx)(&err)
Let's also add the same line (albeit modified for the lack of error) to Proxy, replacing &err with nil:
func (v *VLite) Proxy(ctx context.Context, w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
defer mon.Task()(&ctx)(nil)
You should now have something like:
package main
import (
"context"
"flag"
"net/http"
"net/http/httputil"
"net/url"
"github.com/jtolds/webhelp"
"github.com/spacemonkeygo/monkit/v3"
"github.com/spacemonkeygo/monkit/v3/environment"
"github.com/spacemonkeygo/monkit/v3/present"
)
var mon = monkit.Package()
type VLite struct {
target *url.URL
proxy *httputil.ReverseProxy
}
func NewVLite(target *url.URL) *VLite {
return &VLite{
target: target,
proxy: httputil.NewSingleHostReverseProxy(target),
}
}
func (v *VLite) Proxy(ctx context.Context, w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
defer mon.Task()(&ctx)(nil)
r.Host = v.target.Host // let the proxied server get the right vhost
v.proxy.ServeHTTP(w, r)
}
func (v *VLite) HandleHTTP(ctx context.Context, w webhelp.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) (err error) {
defer mon.Task()(&ctx)(&err)
// here's where you'd put caching logic
v.Proxy(ctx, w, r)
return nil
}
func main() {
target := flag.String(
"proxy",
"http://hasthelargehadroncolliderdestroyedtheworldyet.com/",
"server to cache")
flag.Parse()
targetURL, err := url.Parse(*target)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
environment.Register(monkit.Default)
go http.ListenAndServe("localhost:9000", present.HTTP(monkit.Default))
panic(webhelp.ListenAndServe(":8080", NewVLite(targetURL)))
}
We'll unpack what's going on here, but for now:
localhost:8080 to make sure your new HTTP
handler runslocalhost:9000/stats and then localhost:9000/funcsFor this new funcs dataset, if you want a graph, you can download a dot
graph at localhost:9000/funcs/dot and json information from
localhost:9000/funcs/json.
You should see something like:
[3693964236144930897] main.(*VLite).HandleHTTP
parents: entry
current: 0, highwater: 1, success: 2, errors: 0, panics: 0
success times:
0.00: 63.930436ms
0.10: 70.482159ms
0.25: 80.309745ms
0.50: 96.689054ms
0.75: 113.068363ms
0.90: 122.895948ms
0.95: 126.17181ms
1.00: 129.447675ms
avg: 96.689055ms
failure times:
0.00: 0
0.10: 0
0.25: 0
0.50: 0
0.75: 0
0.90: 0
0.95: 0
1.00: 0
avg: 0
with a similar report for the Proxy method, or a graph like:
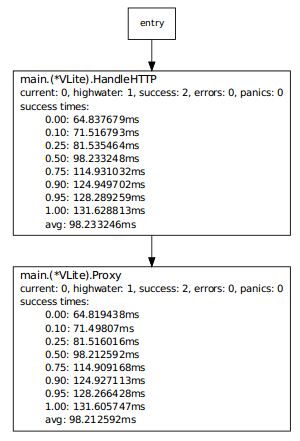
This data reports the overall callgraph of execution for known traces, along with how many of each function are currently running, the most running concurrently (the highwater), how many were successful along with quantile timing information, how many errors there were (with quantile timing information if applicable), and how many panics there were. Since the Proxy method isn't capturing a returned err value, and since HandleHTTP always returns nil, this example won't ever have failures.
If you're wondering about the success count being higher than you expected, keep in mind your browser probably requested a favicon.ico.
Cool, eh?
defer mon.Task()(&ctx)(&err)
is an interesting line of code - there's three function calls. If you look at the Go spec, all of the function calls will run at the time the function starts except for the very last one.
The first function call, mon.Task(), creates or looks up a wrapper around a Func. You could get this yourself by requesting mon.Func() inside of the appropriate function or mon.FuncNamed(). Both mon.Task() and mon.Func() are inspecting runtime.Caller to determine the name of the function. Because this is a heavy operation, you can actually store the result of mon.Task() and reuse it somehow else if you prefer, so instead of
func MyFunc(ctx context.Context) (err error) {
defer mon.Task()(&ctx)(&err)
}
you could instead use
var myFuncMon = mon.Task()
func MyFunc(ctx context.Context) (err error) {
defer myFuncMon(&ctx)(&err)
}
which is more performant every time after the first time. runtime.Caller only gets called once.
Careful! Don't use the same myFuncMon in different functions unless you want to screw up your statistics!
The second function call starts all the various stop watches and bookkeeping to keep track of the function. It also mutates the context pointer it's given to extend the context with information about what current span (in Zipkin parlance) is active. Notably, you can pass nil for the context if you really don't want a context. You just lose callgraph information.
The last function call stops all the stop watches ad makes a note of any observed errors or panics (it repanics after observing them).
Turns out, we don't even need to change our program anymore to get rich tracing information!
Open your browser and go to localhost:9000/trace/svg?regex=HandleHTTP. It
won't load, and in fact, it's waiting for you to open another tab and refresh
localhost:8080 again. Once you retrigger the actual application behavior,
the trace regex will capture a trace starting on the first function that
matches the supplied regex, and return an svg. Go back to your first tab, and
you should see a relatively uninteresting but super promising svg.
Let's make the trace more interesting. Add a
time.Sleep(200 * time.Millisecond)
to your HandleHTTP method, rebuild, and restart. Load localhost:8080, then
start a new request to your trace URL, then reload localhost:8080 again. Flip
back to your trace, and you should see that the Proxy method only takes a
portion of the time of HandleHTTP!
There's multiple ways to select a trace. You can select by regex using the preselect method (default), which first evaluates the regex on all known functions for sanity checking. Sometimes, however, the function you want to trace may not yet be known to monkit, in which case you'll want to turn preselection off. You may have a bad regex, or you may be in this case if you get the error "Bad Request: regex preselect matches 0 functions."
Another way to select a trace is by providing a trace id, which we'll get to next!
Make sure to check out what the addition of the time.Sleep call did to the other reports.
It's easy to write plugins for monkit! Check out our first one that exports data to Zipkin's Scribe API:
We plan to have more (for HTrace, OpenTracing, etc, etc), soon!
Copyright (C) 2016 Space Monkey, Inc.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
FAQs
Unknown package
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security News
PyPI adds Trusted Publishing support for GitLab Self-Managed as adoption reaches 25% of uploads

Research
/Security News
A malicious Chrome extension posing as an Ethereum wallet steals seed phrases by encoding them into Sui transactions, enabling full wallet takeover.

Security News
Socket is heading to London! Stop by our booth or schedule a meeting to see what we've been working on.