Product
Introducing Immutable Scans
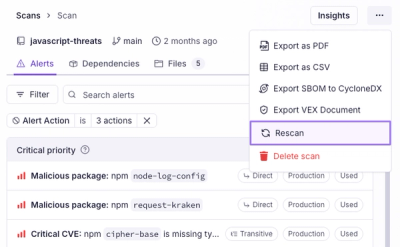
Scan results now load faster and remain consistent over time, with stable URLs and on-demand rescans for fresh security data.
www.github.com/openshift/console.git
Advanced tools
Any external service that integrates with console should satisfy the following requirements:
Codename: "Bridge"
quay.io/coreos/tectonic-console
The Tectonic Console is a more friendly kubectl in the form of a single page webapp. It also integrates with other tectonic services like monitoring, chargeback, ALM, and identity. Some things that go on behind the scenes include:
/api/kubernetesgo get github.com/Masterminds/glide) & glide-vcjq (for contrib/environment.sh)./build
Backend binaries are output to /bin.
If you have a working kubectl on your path, you can run the application with:
export KUBECONFIG=/path/to/kubeconfig
source ./contrib/environment.sh
./bin/bridge
The script in contrib/environment.sh sets sensible defaults in the environment, and uses kubectl to query your cluster for endpoint and authentication information.
To configure the application to run by hand, (or if environment.sh doesn't work for some reason) you can manually provide a Kubernetes bearer token with the following steps.
First get the secret ID that has a type of kubernetes.io/service-account-token by running:
kubectl get secrets
then get the secret contents:
kubectl describe secrets/<secret-id-obtained-previously>
Use this token value to set the BRIDGE_K8S_BEARER_TOKEN environment variable when running Bridge.
Registering an OpenShift OAuth client requires administrative privileges for the entire cluster not just a local project. If you've got a working kubectl and oc on your path, but aren't a system administrator, run the following command to attempt to elevate privileges:
oc login -u system:admin
oc adm policy --as system:admin add-cluster-role-to-user cluster-admin admin
oc login -u admin
To run bridge locally connected to a remote OpenShift cluster, create an OAuthClient resource with a generated secret and read that secret:
oc process -f examples/tectonic-console-oauth-client.yaml | oc apply -f -
export OAUTH_SECRET=$( oc get oauthclient tectonic-console -o jsonpath='{.secret}' )
If the CA bundle of the OpenShift API server is unavailable, fetch the CA certificates from a service account secret. Otherwise copy the CA bundle to examples/ca.crt:
oc get secrets -n default --field-selector type=kubernetes.io/service-account-token -o json | \
jq '.items[0].data."service-ca.crt"' -r | openssl base64 -d > examples/ca.crt
# Note: use "openssl base64" because the "base64" tool is different between mac and linux
Set the OPENSHIFT_API environment variable to tell the script the API endpoint:
export OPENSHIFT_API="https://127.0.0.1:8443"
Finally run the Console and visit localhost:9000:
./examples/run-bridge.sh
The builder-run script will run any command from a docker container to ensure a consistent build environment.
For example to build with docker run:
./builder-run ./build
The docker image used by builder-run is itself built and pushed by the
script push-builder, which uses the file Dockerfile-builder to
define an image. To update the builder-run build environment, first make
your changes to Dockerfile-builder, then run push-builder, and
then update the BUILDER_VERSION variable in builder-run to point to
your new image. Our practice is to manually tag images builder images in the form
Builder-v$SEMVER once we're happy with the state of the push.
(Almost no reason to ever do this manually, Jenkins handles this automation)
Build a docker image, tag it with the current git sha, and pushes it to the quay.io/coreos/tectonic-console repo.
Must set env vars DOCKER_USER and DOCKER_PASSWORD or have a valid .dockercfg file.
./build-docker-push
Master branch:
Pull requests:
Jenkins rebuild to manually trigger a re-buildJenkins push to push an image to Quay, tagged with:
pr_[pr #]_build_[jenkins build #]If changes are ever required for the Jenkins job configuration, apply them to both the regular console job and PR image job.
See CONTRIBUTING for workflow & convention details.
See STYLEGUIDE for file format and coding style guide.
go, glide, glide-vc, nodejs/yarn, kubectl
All frontend code lives in the frontend/ directory. The frontend uses node, yarn, and webpack to compile dependencies into self contained bundles which are loaded dynamically at run time in the browser. These bundles are not commited to git. Tasks are defined in package.json in the scripts section and are aliased to yarn run <cmd> (in the frontend directory).
To install the build tools and dependencies:
yarn install
You must run this command once, and every time the dependencies change. node_modules are not commited to git.
The following build task will watch the source code for changes and compile automatically. You must reload the page in your browser!
yarn run dev
Run all unit tests:
./test
Run backend tests:
./test-backend
Run frontend tests:
./test-frontend
Integration tests are run in a headless Chrome driven by protractor. Requirements include Chrome, a working cluster, kubectl, and bridge itself (see building above).
Setup (or any time you change node_modules - yarn add or yarn install)
cd frontend && yarn run webdriver-update
Run integration tests:
yarn run test-gui
Run integration tests on an OpenShift cluster:
yarn run test-gui-openshift
This will include the normal k8s CRUD tests and CRUD tests for OpenShift resources. It doesn't include ALM tests since it assumes ALM is not set up on an OpenShift cluster.
Remove the --headless flag to Chrome (chromeOptions) in frontend/integration-tests/protractor.conf.ts to see what the tests are actually doing.
Checkout and build dex.
./bin/dex serve ../../coreos-inc/bridge/contrib/dex-config-dev.yaml
Run bridge with the following options:
./bin/bridge \
--user-auth=oidc \
--user-auth-oidc-issuer-url='http://127.0.0.1:5556' \
--user-auth-oidc-client-id='example-app' \
--user-auth-oidc-client-secret='ZXhhbXBsZS1hcHAtc2VjcmV0' \
--base-address='http://localhost:9000/' \
--kubectl-client-id='example-app' \
--kubectl-client-secret='ZXhhbXBsZS1hcHAtc2VjcmV0'
Dependencies should be pinned to an exact semver, sha, or git tag (eg, no ^).
Whenever making vendor changes:
vendor/ (eg, server: add x feature)vendor/ (eg, vendor: revendor)Add new backend dependencies:
glide.yaml./revendorUpdate existing backend dependencies:
glide.yaml file to the desired verison (most likely a git hash)./revendorglide.lock will have been updated to reflect the changes to glide.yaml and the package will have been updated in vendor.Add new frontend dependencies:
yarn add <package@version>
Update existing frontend dependencies:
yarn upgrade <package@version>
We support the latest versions of the following browsers:
FAQs
Unknown package
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Product
Scan results now load faster and remain consistent over time, with stable URLs and on-demand rescans for fresh security data.
Product
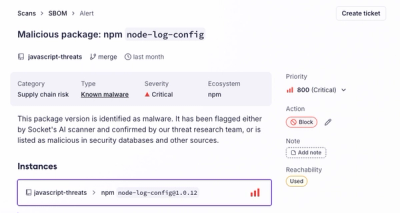
Socket's new Alert Details page is designed to surface more context, with a clearer layout, reachability dependency chains, and structured review.
Product
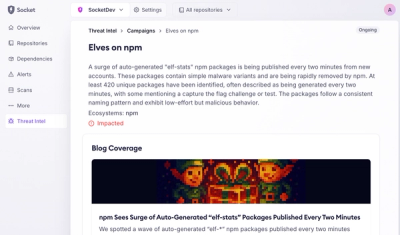
Campaign-level threat intelligence in Socket now shows when active supply chain attacks affect your repositories and packages.