Product
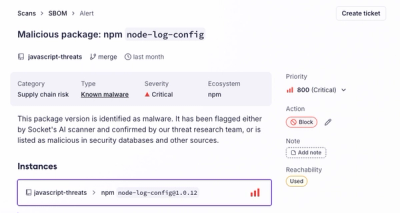
Introducing the Alert Details Page: A Better Way to Explore Alerts
Socket's new Alert Details page is designed to surface more context, with a clearer layout, reachability dependency chains, and structured review.
 OWASP Amass
OWASP AmassThe OWASP Amass tool obtains subdomain names by scraping data sources, recursive brute forcing, crawling web archives, permuting/altering names and reverse DNS sweeping. Additionally, Amass uses the IP addresses obtained during resolution to discover associated netblocks and ASNs. All the information is then used to build maps of the target networks.

A precompiled version is available for each release.
If you are on a distribution such as Kali Linux, and have never used snap previously, follow these steps to access snap packages:
$ sudo apt install snapd
$ sudo systemctl start snapd
Add the snap binaries to your PATH using a method similar to the following:
$ export PATH=$PATH:/snap/bin
If your operating environment supports Snap, you can click here to install, or perform the following from the command-line:
$ sudo snap install amass
If you would like snap to get you the latest unstable build of OWASP Amass, type the following command:
$ sudo snap install --edge amass
If you would prefer to build your own binary from the latest version of the source code, make sure you have a correctly configured Go >= 1.10 environment. More information about how to achieve this can be found on the golang website. Then, take the following steps:
$ go get -u github.com/OWASP/Amass/...
$ cd $GOPATH/src/github.com/OWASP/Amass
$ go install ./...
At this point, the binaries should be in $GOPATH/bin.
$ ls $GOPATH/src/github.com/OWASP/Amass/wordlists/
The most basic use of the tool, which includes reverse DNS lookups and name alterations:
$ amass -d example.com
If you need Amass to run faster and only use the passive data sources:
$ amass -nodns -d example.com
If you are running Amass within a virtual machine, you may want to slow it down a bit:
$ amass -freq 480 -d example.com
The example below is a good place to start with amass:
$ amass -v -ip -brute -min-for-recursive 3 -d example.com
[Google] www.example.com
[VirusTotal] ns.example.com
...
13139 names discovered - archive: 171, cert: 2671, scrape: 6290, brute: 991, dns: 250, alt: 2766
Add some additional domains to the enumeration:
$ amass -d example1.com,example2.com -d example3.com
Additional switches available through the amass CLI:
| Flag | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| -active | Enable active recon methods | amass -active -d example.com net -p 80,443,8080 |
| -bl | Blacklist undesired subdomains from the enumeration | amass -bl blah.example.com -d example.com |
| -blf | Identify blacklisted subdomains from a file | amass -blf data/blacklist.txt -d example.com |
| -brute | Perform brute force subdomain enumeration | amass -brute -d example.com |
| -df | Specify the domains to be enumerated via text file | amass -df domains.txt |
| -freq | Throttle the rate of DNS queries by number per minute | amass -freq 120 -d example.com |
| -h | Show the amass usage information | amass -h |
| -ip | Print IP addresses with the discovered names | amass -ip -d example.com |
| -json | All discoveries written as individual JSON objects | amass -json out.json -d example.com |
| -l | List all the domains to be used during enumeration | amass -whois -l -d example.com |
| -log | Log all error messages to a file | amass -log amass.log -d example.com |
| -min-for-recursive | Discoveries required for recursive brute forcing | amass -brute -min-for-recursive 3 -d example.com |
| -noalts | Disable alterations of discovered names | amass -noalts -d example.com |
| -nodns | A purely passive mode of execution | amass -nodns -d example.com |
| -norecursive | Disable recursive brute forcing | amass -brute -norecursive -d example.com |
| -o | Write the results to a text file | amass -o out.txt -d example.com |
| -oA | Output to all available file formats with prefix | amass -oA amass_scan -d example.com |
| -r | Specify your own DNS resolvers | amass -r 8.8.8.8,1.1.1.1 -d example.com |
| -rf | Specify DNS resolvers with a file | amass -rf data/resolvers.txt -d example.com |
| -v | Output includes data source and summary information | amass -v -d example.com |
| -version | Print the version number of amass | amass -version |
| -w | Change the wordlist used during brute forcing | amass -brute -w wordlist.txt -d example.com |
| -whois | Search using reverse whois information | amass -whois -d example.com |
Have amass send all the DNS and infrastructure enumerations to the Neo4j graph database:
$ amass -neo4j neo4j:DoNotUseThisPassword@localhost:7687 -d example.com
Here are switches for outputting the DNS and infrastructure findings as a network graph:
| Flag | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| -d3 | Output a D3.js v4 force simulation HTML file | amass -d3 network.html -d example |
| -gexf | Output to Graph Exchange XML Format (GEXF) | amass -gephi network.gexf -d example.com |
| -graphistry | Output Graphistry JSON | amass -graphistry network.json -d example.com |
| -visjs | Output HTML that employs VisJS | amass -visjs network.html -d example.com |
Caution: If you use the amass.netnames tool, it will attempt to reach out to every IP address within the identified infrastructure and obtain names from TLS certificates. This is "loud" and can reveal your reconnaissance activities to the organization being investigated.
To discover all domains hosted within target ASNs, use the following option:
$ amass.netnames -asn 13374,14618
To investigate within target CIDRs, use this option:
$ amass.netnames -cidr 192.184.113.0/24,104.154.0.0/15
For specific IPs or address ranges, use this option:
$ amass.netnames -addr 192.168.1.44,192.168.2.1-64
By default, port 443 will be checked for certificates, but the ports can be changed as follows:
$ amass.netnames -cidr 192.168.1.0/24 -p 80,443,8080
If you are using the amass package within your own Go code, be sure to properly seed the default pseudo-random number generator:
import(
"fmt"
"math/rand"
"time"
"github.com/OWASP/Amass/amass"
)
func main() {
output := make(chan *amass.AmassOutput)
go func() {
for result := range output {
fmt.Println(result.Name)
}
}()
// Seed the default pseudo-random number generator
rand.Seed(time.Now().UTC().UnixNano())
// Setup the most basic amass configuration
config := amass.CustomConfig(&amass.AmassConfig{Output: output})
config.AddDomain("example.com")
amass.StartEnumeration(config)
}



FAQs
Unknown package
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Product
Socket's new Alert Details page is designed to surface more context, with a clearer layout, reachability dependency chains, and structured review.
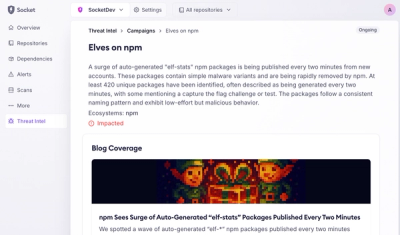
Product
Campaign-level threat intelligence in Socket now shows when active supply chain attacks affect your repositories and packages.

Research
Malicious PyPI package sympy-dev targets SymPy users, a Python symbolic math library with 85 million monthly downloads.