🕵 duplicate-package-checker-webpack-plugin





Webpack plugin that warns when your bundle contains multiple versions of the same package.
This package is a modified fork of darrenscerri's duplicate-package-checker-webpack-plugin.
Why?
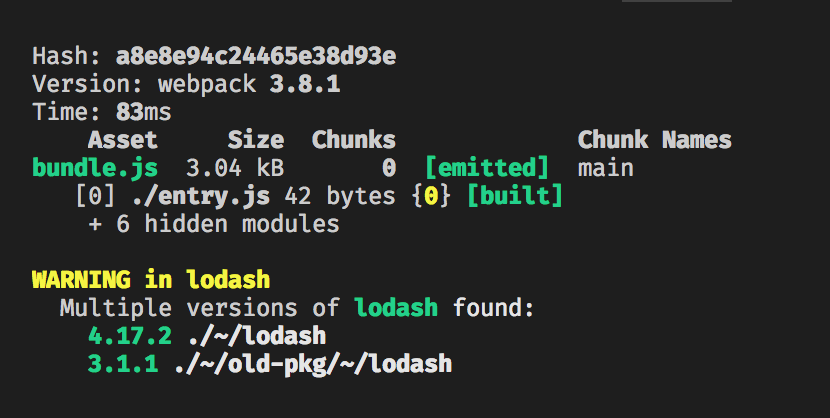
It might be possible that a single package gets included multiple times in a Webpack bundle due to different package versions. This situation may happen without any warning, resulting in extra bloat in your bundle and may lead to hard-to-find bugs.
This plugin will warn you of such cases to minimize bundle size and avoid bugs caused by unintended duplicate packages.
Motivation: https://github.com/webpack/webpack/issues/385 and https://github.com/webpack/webpack/issues/646.
Install
npm install @cerner/duplicate-package-checker-webpack-plugin --save-dev
Configuration
Add the plugin to your webpack config:
var DuplicatePackageCheckerPlugin = require("@cerner/duplicate-package-checker-webpack-plugin");
module.exports = {
plugins: [new DuplicatePackageCheckerPlugin()]
};
You can also pass an object with configurable options:
new DuplicatePackageCheckerPlugin({
verbose: true,
emitError: true,
showHelp: false,
strict: false,
exclude: instance => instance.name === "fbjs",
alwaysEmitErrorsFor: ['react', 'react-router'],
});
Strict mode
Strict mode warns when multiple packages with different major versions (such as v1.0.0 vs v2.0.0) exist in the bundle.
Packages with different major versions introduce backward incompatible changes and require either interventions on third-party packages or unsafe workarounds (such as resolving differing package major versions dependencies with a single version).
It is suggested that strict mode is kept enabled since this improves visibility into your bundle and can help in solving and identifying potential issues.
Node version support
This package was developed and tested using Node 10 up to Node 14. Consumers using Node 16 or greater are advised to use it at their own risk since those versions are not officially supported due to lack of thorough testing.
Resolving duplicate packages in your bundle
There are multiple ways you can go about resolving duplicate packages in your bundle, the right solution mostly depends on what tools you're using and on each particular case.
Webpack resolve.alias
Add an entry in resolve.alias which will configure Webpack to route any package references to a single specified path.
For example, if Lodash is duplicated in your bundle, the following configuration would render all Lodash imports to always refer to the Lodash instance found at ./node_modules/lodash.
alias: {
lodash: path.resolve(__dirname, 'node_modules/lodash'),
}
Note: Aliasing packages with different major versions may break your app. Use only if you're sure that all required versions are compatible, at least in the context of your app
Yarn install --flat
Yarn allows flat installations (yarn install --flat) which will only allow one version of each package to be installed.
Yarn resolutions
If you want more control over your overridden dependency versions and don't feel like using yarn install --flat, yarn supports "selective version resolution" which allows you to enforce specific versions for each dependency.
package.json
{
"dependencies": {
"lodash": "4.17.0",
"old-package-with-old-lodash": "*"
},
"resolutions": {
"old-package-with-old-lodash/lodash": "4.17.0"
}
}
NPM Dedupe
If you use NPM and not Yarn, you can try running npm dedupe. NPM may leave multiple versions of the same package installed even if a single version satisfies each semver of all of its dependants.
Bump your dependencies
If your project is using an old version of a package and a dependency is using a newer version of that package, consider upgrading your project to use the newer version.
File issues!
If your project has a dependency and it's using an outdated version of a package, file an issue and notify the author to update the dependencies. Let's help keep our projects green and our applications secure, performant and bug-free!






