
Research
/Security News
9 Malicious NuGet Packages Deliver Time-Delayed Destructive Payloads
Socket researchers discovered nine malicious NuGet packages that use time-delayed payloads to crash applications and corrupt industrial control systems.
@chronobank/smart-contracts
Advanced tools
ChronoBank Smart Contracts ecosystem is built around two things simple for understanding: platforms and assets.
ChronoBank platforms act as a base for all token operations (like issuing, balance storage, transfer) and embodied in ChronoBankPlatform contact.
ChronoBank assets (instances of ChronoBankAsset contract) add interface layout and define some custom internal logic to allow implementing different behavior, for example, adding a fee to token transactions (look at ChronoBankAssetWithFee contract).
Since assets define just internal behavior, there are so-called ChronoBank asset proxies (see ChronoBankAssetProxy contract) which provide an ERC20 standard interface (described in ERC20Interface.sol) and acts as a transaction proxy. It allows to add/change token logic by updating asset implementation and to recover a wallet access in case of key loss.
While looking into details it could be spotted that ChronoBank Smart Contracts ecosystem is more than just platforms and assets. These core entities represent important but small part of all functionality.
For more details please refer to chronobank.github.io.
Tests are included and can be run using truffle.
NodeJS 10+ required.
yarn
export NODE_OPTIONS="--max_old_space_size=4096"
export PATH=$PATH:$(pwd)/node_modules/.bin
yarn build
Then run tests in a project dir by doing
yarn test:ci
We have copy of our system in a presentation of ganache database so you need to unpack it first and then run ganache-cli
yarn migrate:unpack
yarn ganache
To migrate system on a fully empty blockchain
yarn migrate:full:dev --network=[network name]
The next foundational block in the ecosystem is a top-level contracts module (a handful of managers) that provides all needed interfaces to organize flexible and powerful tools.
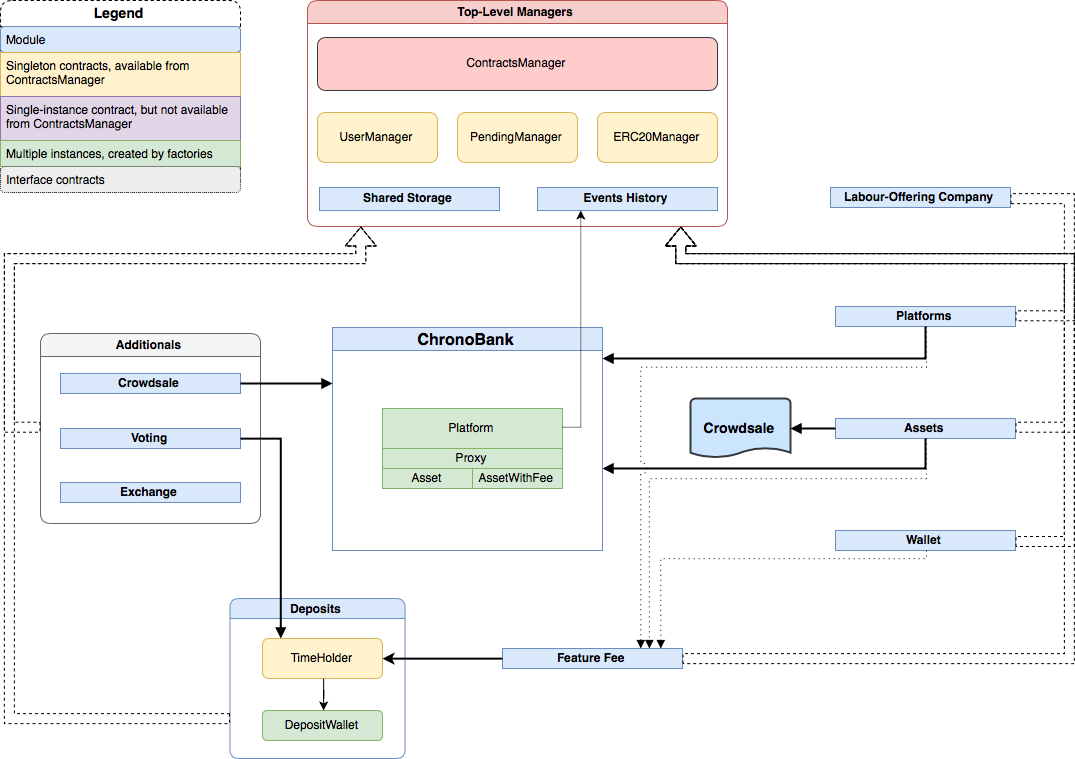 PDF version for detailed preview.
PDF version for detailed preview.
ContractsManager plays a role in the central registry which holds references to all services registered in a system.
To get to the central registry contracts should be added by a contract owner of ContractsManager or those contacts that are allowed to do so (based on ACL in StorageManger).
It's worth mentioning that a set of managers (top-level and others) do not store their data directly in storage, but use instead Storage contract to pass responsibility for saving data. This Storage contracts besides StorageManager are included in Shared Storage set of contracts.
UserManager contract which role is to provide system-wide user registry where simple users and admins (CBE) live together. It also provides a part of multisignature infrastructure by keeping a number of admins required to confirm operations.
PendingManager contract which provides the rest of multisignature functionality by holding and tracking operations performed in a system and carrying them out when a critical number of confirmations were received.
ERC20Manager contract which keeps track of all ERC20-based tokens registered in a system.
Events History is a submodule which performs like a gate for all events happen in a system. All system managers are using the same instance of EventsHistory (see MultiEventsHistory contract), other contracts created during the system's work could use different event histories instances.
Labour-Offering Companies (LOCManager) is a particular module that organizes work of ChronoBank with third-party companies and allows them to participate in the ChronoBank ecosystem (read the Whitepaper for more details).
The next part of modules is designed to make users' life easier by providing additional layers of abstraction on top of existing core contracts.
The key contract is PlatformsManager that makes it possible to manipulate multiple ChronoBank platforms and create brand new platforms.
The key contract is AssetsManager that allows users to build their own tokens, organize their crowdsale.
The key contract is WalletManager that give the ability to create wallets for storing tokens and organize multisignature access to its balance and transfers (it's important to note that multisignature mechanism is independently implemented and isn't based on PendingManager contract).
Besides aforementioned modules there are also modules that manipulate tokens (TIME and other ERC20) tokens to allow to:
For providing such ability for a system, there is a contract with Deposit and Feature Fee modules. Deposit module includes:
Feature Fee module organizes an instrument for signing system's functions as payable by system tokens (in case of ChronoBank it is TIME tokens).
Last but not least is Additionals modules that provided extended functionalities for ChronoBank ecosystem:
Crowdsale - the key contract is CrowdsaleManager and it organizes token crowdsale. It was made available to use only through AssetsManager.
Voting - the key contract is VotingManager which arranges poll creation where users that hold their TIME tokens in TimeHolder could vote to participate in system's decisions.
Exchange - the key contract is ExchangeManager which coordinates exchanges between different tokens and allows users to sell/buy tokens for other tokens.
A more detailed version of the scheme contains internal entities and connections that participate in module's work.
As were said ChronoBank ecosystem has its own token called TIME that fuels work of many functions. We gather them in one place to provide a more specific overview of their responsibilities.
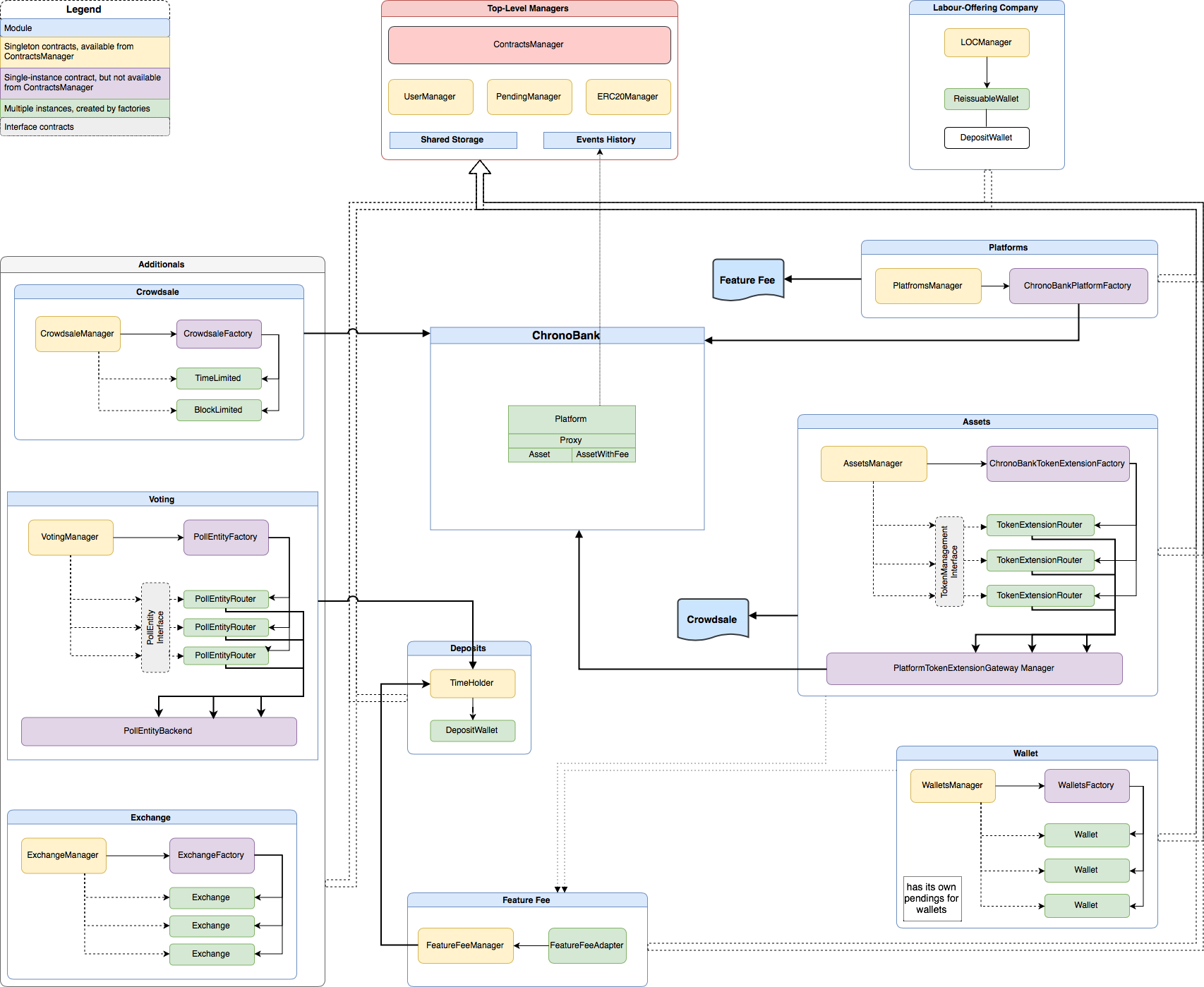 PDF version for detailed preview.
PDF version for detailed preview.
Main contracts:
Deposit holder. Allows to deposit/withdraw TIME tokens. Users, who have deposits, are allowed to use some key features of the system such as creating ERC20 tokens, starting crowdsale for it, create exchanges and so forth.
Users could deposit and withdraw at any time and those changes will appropriately update functionalities that are bound to TimeHolder (such as voting and so forth).
Provides an entry point to transfer tokens to a sidechain network allowing to lock/unlock tokens throughout atomic swaps and middleware layer. Locked tokens could be only unlocked and not available for a withdraw. Operations description:
TimeHolder#lock(token, amount);TimeHolder#unlockShares(registrationID, secret)Atomic swaps technique and middleware layer in composition provide a way to transfer tokens in and out of the network to a sidechains. From the zoomed out view it looks like this:
unlock operation with a secret; user should call TimeHolder#unlock(registrationID, secret) with provided secret: unlocked tokens immediately will be transferred to user's account.Dev notes: New functionalities and new contracts could take advantage of using TimeHolder’s shares to secure and restrict their features: developers are able to add new contracts and use ListenerInterface to observe changes in TimeHolder’s deposits - this will unlock an access to notifications about deposit/withdrawal actions made by the user.
Main contracts:
This piece of functionality takes place in the system and is responsible for voting functions. It serves as a central point to enter and manipulate (create, navigate, stop) polls.
In general, it aggregates the next functions:
Users, who have TIME deposits, allowed to perform a vote connected actions according to TIME deposit value.
Main contracts:
It’s an exchange registry that holds information about created exchanges and provides some utility methods for managing them.
It serves as the entry point for creating new exchanges.
Standalone Exchange allows users to buy/sell assigned ERC20 token for ether, as long as there is available supply.
Contract owner maintains sufficient token and ether supply, and sets buy/sell prices. In order to be able to sell tokens, the user needs to create an allowance for this contract, using standard ERC20 approve() function, so that an exchange could take tokens from the user when the user orders a sell.
CBE users are permitted to manage fee value against which an exchange will calculate the fee.
Some methods might take a fee in TIME tokens.
Some methods might take a fee in TIME tokens.
| Function | Description | Price |
|---|---|---|
| createExchange | Creates a new exchange with the given params. | TBD |
Main contracts:
Managing system’s and users’ platforms is possible because of this contract. It allows to create and manipulate platforms and considered as an entry point to go through user’s platforms.
Provides system-wide ability to manage user's platforms. This contract allows to:
Some methods could require paying additional fee in TIME tokens during their invocation
Some methods could require to pay additional fee in TIME tokens during their invocation
| Function | Description | Price |
|---|---|---|
| createPlatform | Creates a brand new platform | TBD |
Main contracts:
That is a backend contract specifically created to aggregate main functionality for token manipulations and make less burden on a token creation process as well as on other functions.
Key responsibilities are to:
Some methods might take a fee in TIME tokens.
Dev notes: Since this contract is designed to be used by delegatecall it doesn't inherit from any contract (except FeatureFeeAdapter) and you should be careful when a need will arise to add more functionality by inheritance because the contract uses storage layout from TokenExtensionRouter and it should be preserved.
| Function | Description | Price |
|---|---|---|
| createAssetWithoutFee | Creates asset without fee. Performs asset registration in ERC20Manager. Allowed to be performed only from delegatecall and only by platform owner. | TBD |
| createAssetWithFee | Creates asset with fee. Performs asset registration in ERC20Manager. Allowed to be performed only from delegatecall and only by platform owner. | TBD |
| createCrowdsaleCampaign | Creates crowdsale campaign of a token with provided symbol | TBD |
Main contracts:
Allows to manage multisignature wallets, i.e.
(is under construction)
| Function | Description | Price |
|---|---|---|
| createWallet() | Creates multisignature wallet with given params. | TBD |
FAQs
Chronobank Smart Contracts
The npm package @chronobank/smart-contracts receives a total of 0 weekly downloads. As such, @chronobank/smart-contracts popularity was classified as not popular.
We found that @chronobank/smart-contracts demonstrated a not healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released a year ago. It has 3 open source maintainers collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Research
/Security News
Socket researchers discovered nine malicious NuGet packages that use time-delayed payloads to crash applications and corrupt industrial control systems.

Security News
Socket CTO Ahmad Nassri discusses why supply chain attacks now target developer machines and what AI means for the future of enterprise security.

Security News
Learn the essential steps every developer should take to stay secure on npm and reduce exposure to supply chain attacks.