
Product
Introducing Socket Scanning for OpenVSX Extensions
Socket now scans OpenVSX extensions, giving teams early detection of risky behaviors, hidden capabilities, and supply chain threats in developer tools.
@dabh/colors
Advanced tools
Please check out the roadmap for upcoming features and releases. Please open Issues to provide feedback, and check the develop branch for the latest bleeding-edge updates.
npm install colors
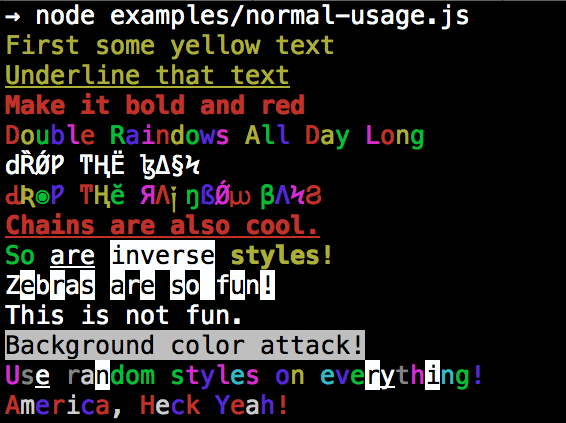
By popular demand, colors now ships with two types of usages!
The super nifty way
var colors = require('colors');
console.log('hello'.green); // outputs green text
console.log('i like cake and pies'.underline.red); // outputs red underlined text
console.log('inverse the color'.inverse); // inverses the color
console.log('OMG Rainbows!'.rainbow); // rainbow
console.log('Run the trap'.trap); // Drops the bass
or a slightly less nifty way which doesn't extend String.prototype
var colors = require('colors/safe');
console.log(colors.green('hello')); // outputs green text
console.log(colors.red.underline('i like cake and pies')); // outputs red underlined text
console.log(colors.inverse('inverse the color')); // inverses the color
console.log(colors.rainbow('OMG Rainbows!')); // rainbow
console.log(colors.trap('Run the trap')); // Drops the bass
I prefer the first way. Some people seem to be afraid of extending String.prototype and prefer the second way.
If you are writing good code you will never have an issue with the first approach. If you really don't want to touch String.prototype, the second usage will not touch String native object.
The package will auto-detect whether your terminal can use colors and enable/disable accordingly. When colors are disabled, the color functions do nothing. You can override this with a command-line flag:
node myapp.js --no-color
node myapp.js --color=false
node myapp.js --color
node myapp.js --color=true
node myapp.js --color=always
FORCE_COLOR=1 node myapp.js
Or in code:
var colors = require('colors');
colors.enable();
colors.disable();
var name = 'Marak';
console.log(colors.green('Hello %s'), name);
// outputs -> 'Hello Marak'
var colors = require('colors');
colors.setTheme({
silly: 'rainbow',
input: 'grey',
verbose: 'cyan',
prompt: 'grey',
info: 'green',
data: 'grey',
help: 'cyan',
warn: 'yellow',
debug: 'blue',
error: 'red'
});
// outputs red text
console.log("this is an error".error);
// outputs yellow text
console.log("this is a warning".warn);
var colors = require('colors/safe');
// set single property
var error = colors.red;
error('this is red');
// set theme
colors.setTheme({
silly: 'rainbow',
input: 'grey',
verbose: 'cyan',
prompt: 'grey',
info: 'green',
data: 'grey',
help: 'cyan',
warn: 'yellow',
debug: 'blue',
error: 'red'
});
// outputs red text
console.log(colors.error("this is an error"));
// outputs yellow text
console.log(colors.warn("this is a warning"));
var colors = require('colors');
colors.setTheme({
custom: ['red', 'underline']
});
console.log('test'.custom);
Protip: There is a secret undocumented style in colors. If you find the style you can summon him.
FAQs
get colors in your node.js console
We found that @dabh/colors demonstrated a not healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Product
Socket now scans OpenVSX extensions, giving teams early detection of risky behaviors, hidden capabilities, and supply chain threats in developer tools.

Product
Bringing supply chain security to the next generation of JavaScript package managers

Product
A safer, faster way to eliminate vulnerabilities without updating dependencies