Product
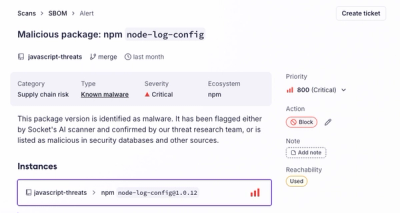
Introducing the Alert Details Page: A Better Way to Explore Alerts
Socket's new Alert Details page is designed to surface more context, with a clearer layout, reachability dependency chains, and structured review.
@jswf/redux-module
Advanced tools
Make Redux operations modular
Associate ModuleReducer with Store
//Store create
const store = createStore(ModuleReducer);
ReactDOM.render(
<Provider store={store}>
<App />
</Provider>,
document.getElementById("root") as HTMLElement
);
When using TypeScript, the structure of module data can be specified defaultState can be omitted, but in that case undefined is returned when data is accepted.
//Store module data type
export interface State {
msg: string;
count: number;
}
export class TestModule extends ReduxModule<State> {
//init value
static defaultState: State = {
msg: "init",
count: 0,
};
}
function HooksApp() {
const module = useModule(TestModule);
const value = module.getState()!;
return (
<div
style={{ border: "solid 1px", display: "inline-block", padding: "1em" }}
>
<div>AppComponent</div>
<button
onClick={() => {
module.setState({ msg: "click!", count: value.count + 1 });
}}
>
button
</button>
<div>{value.msg}</div>
<div>{value.count}</div>
</div>
);
}
class _ClassApp extends Component {
render() {
const module = mapModule(this.props, TestModule);
const value = module.getState()!;
return (
<div
style={{ border: "solid 1px", display: "inline-block", padding: "1em" }}
>
<div>AppComponent</div>
<button
onClick={() => {
//Set data
module.setState({ msg: "click!", count: value.count + 1 });
}}
>
button
</button>
<div>{value.msg}</div>
<div>{value.count}</div>
</div>
);
}
}
const ClassApp = mapConnect(_ClassApp, TestModule);
export interface TestState2 {
text: string;
}
export class TestModule2 extends ReduxModule<TestState2> {
static includes = [TestModule]; //Declare the external class used here
static defaultState: TestState2 = {
text:"A"
};
getMessage() {
//Call external class with getModule
return this.getModule(TestModule).getState("msg");
}
setMessage(msg: string) {
this.getModule(TestModule).setState({ msg });
}
getCount() {
return this.getModule(TestModule).getState("count")!;
}
setCount(count: number) {
this.getModule(TestModule).setState({ count });
}
addText() {
return this.setState(this.getText()+"a","text")!;
}
getText() {
return this.getState("text")!;
}
}
If you use the ReduxModule inheritance class in the component without specifying it, side effects will occur whenever the data under class management is updated.
If it is used only for writing, useless processing will occur. In that case, it can be avoided by attaching the writeOnly attribute.
const testModule = useModule(TestModule,undefined,true);
const ClassApp = mapConnect(_ClassApp, [{module:TestModule,writeOnly:true}]);
static includes = [{module:TestModule,writeOnly:true}];
import React, { Component } from "react";
import * as ReactDOM from "react-dom";
import { createStore } from "redux";
import { Provider } from "react-redux";
import {
ModuleReducer,
useModule,
ReduxModule,
mapModule,
mapConnect
} from "@jswf/redux-module";
/**
*Data structure definition (when using TypeScript)
*
* @export
* @interface TestState
*/
export interface TestState {
msg: string;
}
/**
* Store access class
* (Automatically allocate space in the store for each class)
* @export
* @class TestModule
* @extends {ReduxModule<TestState>}
*/
export class TestModule extends ReduxModule<TestState> {
//Initial value can be set here
protected static defaultState: TestState = {
msg: "初期値"
};
// It is not always necessary to create the following access methods
// getState and setState are public so you can rewrite directly from the outside
public getMessage() {
return this.getState("msg")!;
}
public setMessage(msg: string) {
this.setState({ msg });
}
}
/**
*Sample for Hooks
*
* @returns
*/
function HooksApp() {
// Receive module instance
// The limit of the useModule can be used is the same as other hooks
const testModule = useModule(TestModule);
// The same class can have different areas by attaching a prefix as shown below
//const testModule = useModule(TestModule,"Prefix");
return (
<>
<div>FunctionComponent</div>
<input
value={testModule.getMessage()}
onChange={e => testModule.setMessage(e.target.value)}
/>
<hr />
</>
);
}
/**
*Sample for Class
*
* @class _ClassApp
* @extends {Component}
*/
class _ClassApp extends Component {
render() {
// Receive module instance
// Note that the name and argument are slightly different from Hooks
const testModule = mapModule(this.props, TestModule);
return (
<>
<div>ClassComponent</div>
<input
value={testModule.getMessage()}
onChange={e => testModule.setMessage(e.target.value)}
/>
<hr />
</>
);
}
}
// When using class components, map as follows
// Only modules declared here can be used in classes
// Multiple modules can be specified in an array
const ClassApp = mapConnect(_ClassApp, TestModule);
// Associate a dedicated reducer with Redux
// Can be used with other reducers
const store = createStore(ModuleReducer);
ReactDOM.render(
<Provider store={store}>
<HooksApp />
<ClassApp />
</Provider>,
document.getElementById("root") as HTMLElement
);
MIT
FAQs
Make Redux operations modular
We found that @jswf/redux-module demonstrated a not healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Product
Socket's new Alert Details page is designed to surface more context, with a clearer layout, reachability dependency chains, and structured review.
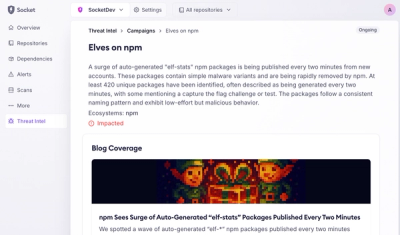
Product
Campaign-level threat intelligence in Socket now shows when active supply chain attacks affect your repositories and packages.

Research
Malicious PyPI package sympy-dev targets SymPy users, a Python symbolic math library with 85 million monthly downloads.