
Research
PyPI Package Disguised as Instagram Growth Tool Harvests User Credentials
A deceptive PyPI package posing as an Instagram growth tool collects user credentials and sends them to third-party bot services.
@napi-rs/image
Advanced tools
@napi-rs/imageTransform and optimize images library.
See Examples for usage.
This library support encode/decode these formats:
| Format | Input | Output |
|---|---|---|
| RawPixels | RGBA 8 bits pixels | |
| JPEG | Baseline and progressive | Baseline JPEG |
| PNG | All supported color types | Same as decoding |
| BMP | ✅ | Rgb8, Rgba8, Gray8, GrayA8 |
| ICO | ✅ | ✅ |
| TIFF | Baseline(no fax support) + LZW + PackBits | Rgb8, Rgba8, Gray8 |
| WebP | ✅ | ✅ |
| AVIF | ✅ | ✅ |
| PNM | PBM, PGM, PPM, standard PAM | ✅ |
| DDS | DXT1, DXT3, DXT5 | No |
| TGA | ✅ | Rgb8, Rgba8, Bgr8, Bgra8, Gray8, GrayA8 |
| OpenEXR | Rgb32F, Rgba32F (no dwa compression) | Rgb32F, Rgba32F (no dwa compression) |
| farbfeld | ✅ | ✅ |
See index.d.ts for API reference.
import { Transformer } from '@napi-rs/image'
const transformer = new Transformer(input)
import { Transformer } from '@napi-rs/image'
import { decode } from 'blurhash'
// Uint8ClampedArray
const pixels = decode('LEHV6nWB2yk8pyo0adR*.7kCMdnj', 32, 32)
const transformer = Transformer.fromRgbaPixels(pixels, 32, 32)
metadata(withExif?: boolean | undefined | null, signal?: AbortSignal | undefined | null): Promise<Metadata>
export interface Metadata {
width: number
height: number
exif?: Record<string, string> | undefined | null
orientation?: number | undefined | null
format: string
colorType: JsColorType
}
export enum JsColorType {
/** Pixel is 8-bit luminance */
L8 = 0,
/** Pixel is 8-bit luminance with an alpha channel */
La8 = 1,
/** Pixel contains 8-bit R, G and B channels */
Rgb8 = 2,
/** Pixel is 8-bit RGB with an alpha channel */
Rgba8 = 3,
/** Pixel is 16-bit luminance */
L16 = 4,
/** Pixel is 16-bit luminance with an alpha channel */
La16 = 5,
/** Pixel is 16-bit RGB */
Rgb16 = 6,
/** Pixel is 16-bit RGBA */
Rgba16 = 7,
/** Pixel is 32-bit float RGB */
Rgb32F = 8,
/** Pixel is 32-bit float RGBA */
Rgba32F = 9
}
Example:
import { promises as fs } from 'fs'
import { Transformer } from '@napi-rs/image'
const WITH_EXIF_JPG = await fs.readFile('with-exif.jpg')
const decoder = new Transformer(WITH_EXIF_JPG)
const metadata = await decoder.metadata(true)
The metadata will be
{
colorType: 2,
exif: {
Orientation: 'Unknown (5)',
'Resolution Unit': 'in',
'This image has an Exif SubIFD': '90',
'X Resolution': '72 pixels per in',
'Y Resolution': '72 pixels per in',
},
format: 'jpeg',
height: 450,
orientation: 5,
width: 600,
}
import { promises as fs } from 'fs'
import { Transformer } from '@napi-rs/image'
const PNG = await fs.readFile('./un-optimized.png')
const webp = await new Transformer(PNG).webp()
await fs.writeFile('optimized.webp)
The quality factor
quality_factorranges from 0 to 100 and controls the loss and quality during compression.The value 0 corresponds to low quality and small output sizes, whereas 100 is the highest quality and largest output size.
https://developers.google.com/speed/webp/docs/api#simple_encoding_api
Default is 90
webp(qualityFactor: number, signal?: AbortSignal | undefined | null): Promise<Buffer>
webpSync(qualityFactor: number): Buffer
/// Encode lossless webp image
webpLossless(signal?: AbortSignal | undefined | null): Promise<Buffer>
webpLosslessSync(): Buffer
Config:
export interface AvifConfig {
/** 0-100 scale 100 is lossless */
quality?: number | undefined | null
/** 0-100 scale */
alphaQuality?: number | undefined | null
/** rav1e preset 1 (slow) 10 (fast but crappy), default is 4 */
speed?: number | undefined | null
/** How many threads should be used (0 = match core count) */
threads?: number | undefined | null
/** set to '4:2:0' to use chroma subsampling, default '4:4:4' */
chromaSubsampling?: ChromaSubsampling | undefined | null
}
/**
* https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chroma_subsampling#Types_of_sampling_and_subsampling
* https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/Media/Formats/Video_concepts
*/
export enum ChromaSubsampling {
/**
* Each of the three Y'CbCr components has the same sample rate, thus there is no chroma subsampling. This scheme is sometimes used in high-end film scanners and cinematic post-production.
* Note that "4:4:4" may instead be wrongly referring to R'G'B' color space, which implicitly also does not have any chroma subsampling (except in JPEG R'G'B' can be subsampled).
* Formats such as HDCAM SR can record 4:4:4 R'G'B' over dual-link HD-SDI.
*/
Yuv444 = 0,
/**
* The two chroma components are sampled at half the horizontal sample rate of luma: the horizontal chroma resolution is halved. This reduces the bandwidth of an uncompressed video signal by one-third.
* Many high-end digital video formats and interfaces use this scheme:
* - [AVC-Intra 100](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/AVC-Intra)
* - [Digital Betacam](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Betacam#Digital_Betacam)
* - [Betacam SX](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Betacam#Betacam_SX)
* - [DVCPRO50](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DV#DVCPRO) and [DVCPRO HD](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DV#DVCPRO_HD)
* - [Digital-S](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Digital-S)
* - [CCIR 601](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rec._601) / [Serial Digital Interface](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Serial_digital_interface) / [D1](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/D-1_(Sony))
* - [ProRes (HQ, 422, LT, and Proxy)](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Apple_ProRes)
* - [XDCAM HD422](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/XDCAM)
* - [Canon MXF HD422](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Canon_XF-300)
*/
Yuv422 = 1,
/**
* n 4:2:0, the horizontal sampling is doubled compared to 4:1:1,
* but as the **Cb** and **Cr** channels are only sampled on each alternate line in this scheme, the vertical resolution is halved.
* The data rate is thus the same.
* This fits reasonably well with the PAL color encoding system, since this has only half the vertical chrominance resolution of [NTSC](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/NTSC).
* It would also fit extremely well with the [SECAM](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SECAM) color encoding system,
* since like that format, 4:2:0 only stores and transmits one color channel per line (the other channel being recovered from the previous line).
* However, little equipment has actually been produced that outputs a SECAM analogue video signal.
* In general, SECAM territories either have to use a PAL-capable display or a [transcoder](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transcoding) to convert the PAL signal to SECAM for display.
*/
Yuv420 = 2,
/**
* What if the chroma subsampling model is 4:0:0?
* That says to use every pixel of luma data, but that each row has 0 chroma samples applied to it. The resulting image, then, is comprised solely of the luminance data—a greyscale image.
*/
Yuv400 = 3,
}
avif(options?: AvifConfig | undefined | null, signal?: AbortSignal | undefined | null): Promise<Buffer>
avifSync(options?: AvifConfig | undefined | null): Buffer
PngEncodeOptions:
export interface PngEncodeOptions {
/** Default is `CompressionType::Default` */
compressionType?: CompressionType | undefined | null
/** Default is `FilterType::NoFilter` */
filterType?: FilterType | undefined | null
}
export enum CompressionType {
/** Default compression level */
Default = 0,
/** Fast, minimal compression */
Fast = 1,
/** High compression level */
Best = 2,
/** Huffman coding compression */
Huffman = 3,
/** Run-length encoding compression */
Rle = 4,
}
export enum FilterType {
/**
* No processing done, best used for low bit depth greyscale or data with a
* low color count
*/
NoFilter = 0,
/** Filters based on previous pixel in the same scanline */
Sub = 1,
/** Filters based on the scanline above */
Up = 2,
/** Filters based on the average of left and right neighbor pixels */
Avg = 3,
/** Algorithm that takes into account the left, upper left, and above pixels */
Paeth = 4,
/**
* Uses a heuristic to select one of the preceding filters for each
* scanline rather than one filter for the entire image
*/
Adaptive = 5,
}
png(options?: PngEncodeOptions | undefined | null, signal?: AbortSignal | undefined | null): Promise<Buffer>
pngSync(options?: PngEncodeOptions | undefined | null): Buffer
/** default `quality` is 90 */
jpeg(quality?: number | undefined | null, signal?: AbortSignal | undefined | null): Promise<Buffer>
/** default `quality` is 90 */
jpegSync(quality?: number | undefined | null): Buffer
bmp(signal?: AbortSignal | undefined | null): Promise<Buffer>
bmpSync(): Buffer
ico(signal?: AbortSignal | undefined | null): Promise<Buffer>
icoSync(): Buffer
tiff(signal?: AbortSignal | undefined | null): Promise<Buffer>
tiffSync(): Buffer
pnm(signal?: AbortSignal | undefined | null): Promise<Buffer>
pnmSync(): Buffer
tga(signal?: AbortSignal | undefined | null): Promise<Buffer>
tgaSync(): Buffer
farbfeld(signal?: AbortSignal | undefined | null): Promise<Buffer>
farbfeldSync(): Buffer
rotateRotate the image with exif orientation, if the input image contains no exif information, this API will have no effect.
/**
* Rotate with exif orientation
* If the orientation param is not null,
* the new orientation value will override the exif orientation value
*/
rotate(): this
Example:
This image has orientation value 5 in exif:

Without rotate:
import { promises as fs } from 'fs'
import { Transformer } from '@napi-rs/image'
const WITH_EXIF_JPG = await fs.readFile('with-exif.jpg')
const imageOutputWithoutRotateWebp = await new Transformer(WITH_EXIF).resize(450 / 2).webp(75)
writeFileSync('output-exif.no-rotate.image.webp', imageOutputWithoutRotateWebp)

With rotate:
import { promises as fs } from 'fs'
import { Transformer } from '@napi-rs/image'
const WITH_EXIF_JPG = await fs.readFile('with-exif.jpg')
const imageOutputWebp = await new Transformer(WITH_EXIF)
.rotate()
.resize(450 / 2)
.webp(75)
console.timeEnd('@napi-rs/image webp')
writeFileSync('output-exif.image.webp', imageOutputWebp)

grayscale/**
* Return a grayscale version of this image.
* Returns `Luma` images in most cases. However, for `f32` images,
* this will return a greyscale `Rgb/Rgba` image instead.
*/
grayscale(): this
invertInvert the colors of this image.
invert(): this
resize/**
* Resize this image using the specified filter algorithm.
* The image is scaled to the maximum possible size that fits
* within the bounds specified by `width` and `height`.
*/
resize(width: number, height?: number | undefined | null, filterType?: ResizeFilterType | undefined | null): this
export enum ResizeFilterType {
/** Nearest Neighbor */
Nearest = 0,
/** Linear Filter */
Triangle = 1,
/** Cubic Filter */
CatmullRom = 2,
/** Gaussian Filter */
Gaussian = 3,
/** Lanczos with window 3 */
Lanczos3 = 4
}
overlay/**
* Overlay an image at a given coordinate (x, y)
*/
overlay(onTop: Buffer, x: number, y: number): this
import { writeFileSync } from 'fs'
import { Transformer } from '@napi-rs/image'
const imageOutputPng = await new Transformer(PNG).overlay(PNG, 200, 200).png()
writeFileSync('output-overlay-png.png', imageOutputPng)
ResizeFilterType:
To test the different sampling filters on a real example, you can find two
examples called
scaledown
and
scaleup
in the examples directory of the crate source code.
Here is a 3.58 MiB test image that has been scaled down to 300x225 px:
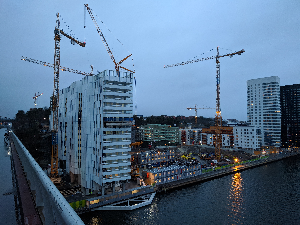




Speed
Time required to create each of the examples above, tested on an Intel i7-4770 CPU with Rust 1.37 in release mode:
| Nearest | 31 ms |
|---|---|
| Triangle | 414 ms |
| CatmullRom | 817 ms |
| Gaussian | 1180 ms |
| Lanczos3 | 1170 ms |
blurPerforms a Gaussian blur on this image.
sigma` is a measure of how much to blur by.
blur(sigma: number): this
unsharpenPerforms an unsharpen mask on this image.
sigmais the amount to blur the image by.
thresholdis a control of how much to sharpen.See https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Unsharp_masking#Digital_unsharp_masking
unsharpen(sigma: number, threshold: number): this
filter3x3Filters this image with the specified 3x3 kernel. Error will thrown if the kernel length is not 9.
filter3x3(kernel: Array<number>): this
adjustContrastAdjust the contrast of this image.
contrastis the amount to adjust the contrast by.
Negative values decrease the contrast and positive values increase the contrast.
adjustContrast(contrast: number): this
brightenBrighten the pixels of this image.
valueis the amount to brighten each pixel by.
Negative values decrease the brightness and positive values increase it.
brighten(brightness: number): this
huerotateHue rotate the supplied image.
valueis the degrees to rotate each pixel by. 0 and 360 do nothing, the rest rotates by the given degree value. just like the css webkit filter hue-rotate(180)
huerotate(hue: number): this
Lossless optimize PNG powered by oxipng.
PNGLosslessOptions
export interface PNGLosslessOptions {
/**
* Attempt to fix errors when decoding the input file rather than returning an Err.
* Default: `false`
*/
fixErrors?: boolean | undefined | null
/**
* Write to output even if there was no improvement in compression.
* Default: `false`
*/
force?: boolean | undefined | null
/** Which filters to try on the file (0-5) */
filter?: Array<number> | undefined | null
/**
* Whether to attempt bit depth reduction
* Default: `true`
*/
bitDepthReduction?: boolean | undefined | null
/**
* Whether to attempt color type reduction
* Default: `true`
*/
colorTypeReduction?: boolean | undefined | null
/**
* Whether to attempt palette reduction
* Default: `true`
*/
paletteReduction?: boolean | undefined | null
/**
* Whether to attempt grayscale reduction
* Default: `true`
*/
grayscaleReduction?: boolean | undefined | null
/**
* Whether to perform IDAT recoding
* If any type of reduction is performed, IDAT recoding will be performed regardless of this setting
* Default: `true`
*/
idatRecoding?: boolean | undefined | null
/** Whether to remove ***All non-critical headers*** on PNG */
strip?: boolean | undefined | null
/** Whether to use heuristics to pick the best filter and compression */
useHeuristics?: boolean | undefined | null
}
export function losslessCompressPng(
input: Buffer,
options?: PNGLosslessOptions | undefined | null,
signal?: AbortSignal | undefined | null,
): Promise<Buffer>
export function losslessCompressPngSync(input: Buffer, options?: PNGLosslessOptions | undefined | null): Buffer
Powered by pngquant, converts RGBA images to palette-based 8-bit indexed images, including alpha component.
PngQuantOptions:
export interface PngQuantOptions {
/** default is 70 */
minQuality?: number | undefined | null
/** default is 99 */
maxQuality?: number | undefined | null
/**
* 1- 10
* Faster speeds generate images of lower quality, but may be useful for real-time generation of images.
* default: 5
*/
speed?: number | undefined | null
/**
* Number of least significant bits to ignore.
* Useful for generating palettes for VGA, 15-bit textures, or other retro platforms.
*/
posterization?: number | undefined | null
}
export function pngQuantize(
input: Buffer,
options?: PngQuantOptions | undefined | null,
signal?: AbortSignal | undefined | null,
): Promise<Buffer>
export function pngQuantizeSync(input: Buffer, options?: PngQuantOptions | undefined | null): Buffer
Lossy and Lossless JPEG compression powered by mozjpeg.
JpegCompressOptions:
export interface JpegCompressOptions {
/** Output quality, default is 100 (lossless) */
quality?: number | undefined | null
/**
* If true, it will use MozJPEG’s scan optimization. Makes progressive image files smaller.
* Default is `true`
*/
optimizeScans?: boolean | undefined | null
}
export function compressJpeg(
input: Buffer,
options?: JpegCompressOptions | undefined | null,
signal?: AbortSignal | undefined | null,
): Promise<Buffer>
export function compressJpegSync(input: Buffer, options?: JpegCompressOptions | undefined | null): Buffer
See Credits
FAQs
Image processing library
The npm package @napi-rs/image receives a total of 18,683 weekly downloads. As such, @napi-rs/image popularity was classified as popular.
We found that @napi-rs/image demonstrated a not healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released a year ago. It has 2 open source maintainers collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Research
A deceptive PyPI package posing as an Instagram growth tool collects user credentials and sends them to third-party bot services.

Product
Socket now supports pylock.toml, enabling secure, reproducible Python builds with advanced scanning and full alignment with PEP 751's new standard.

Security News
Research
Socket uncovered two npm packages that register hidden HTTP endpoints to delete all files on command.