
Security News
npm Adopts OIDC for Trusted Publishing in CI/CD Workflows
npm now supports Trusted Publishing with OIDC, enabling secure package publishing directly from CI/CD workflows without relying on long-lived tokens.
celery-node
Advanced tools
Celery client / worker for in node.js
This project focuses on implementing task queue using celery protocol in node.js influenced by node-celery
Task queue is a mechanism to distribute or dispatch "tasks" or "jobs" across "workers" or "machines" for executing them asynchronously.
Common use cases of task queue:
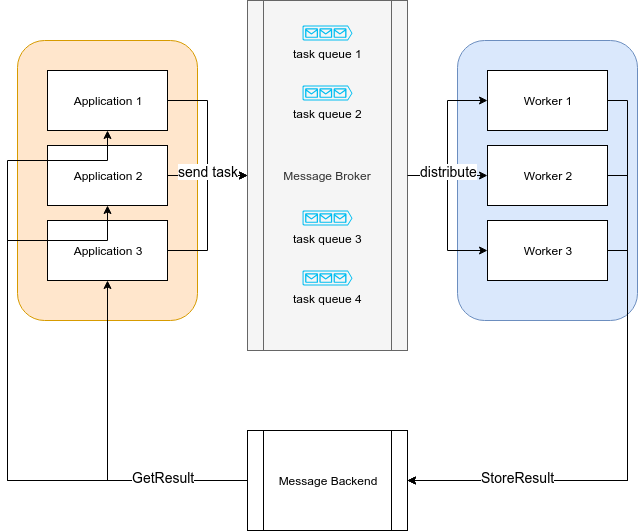
Applications, also called as "Producers", "Publishers" register logical blocks of code as "tasks".
Workers, also called "Consumers" consume these "task" and optionally store any results to a "message backend".
The broker (task queue) receives tasks encapsulated as messages from "producers" and routes them to "consumers".
But managing messages is not as simple as storing them in a data sotre as aqueue.
Suppose that a number of messages sent and dispatched by large number of producers and workers.
We have to consider below.
Celery is a one of most famous task queue open source software. A Celery system can consist of multiple workers and brokers, giving way to high availability and horizontal scaling.
The features of celery is
Celery is written in Python, but the protocol can be implemneted in any languages. There's gocelery for Go and like gocelery, here's celery.node.
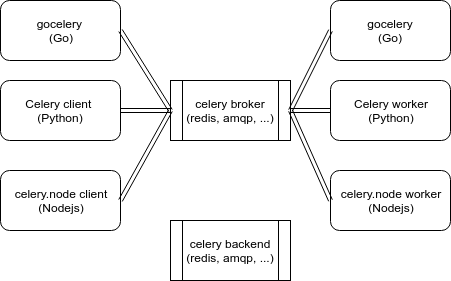
We usually make programs using different languages because of the specific features of each language and sometimes the programs should be communicated with each others by task-queueing, such as python web application with go worker or nodejs worker for better performance.
We can make the programs distribute the tasks to processes written in different languages super easily by using celery, gocelery, and celery.node.
Also, you can use celery.node as pure nodejs task queue.
celery protocol reference
Celery.node now supports Celery Message Protocol Version 1 and Version 2.
client.conf.TASK_PROTOCOL = 1; // 1 or 2. default is 2.
$ npm install celery-node
const celery = require('celery-node');
const client = celery.createClient(
"amqp://",
"amqp://"
);
const task = client.createTask("tasks.add");
const result = task.applyAsync([1, 2]);
result.get().then(data => {
console.log(data);
client.disconnect();
});
from celery import Celery
app = Celery('tasks',
broker='amqp://',
backend='amqp://'
)
@app.task
def add(x, y):
return x + y
if __name__ == '__main__':
result = add.apply_async((1, 2), serializer='json')
print(result.get())
const celery = require('celery-node');
const worker = celery.createWorker(
"amqp://",
"amqp://"
);
worker.register("tasks.add", (a, b) => a + b);
worker.start();
from celery import Celery
app = Celery('tasks',
broker='amqp://',
backend='amqp://'
)
@app.task
def add(x, y):
return x + y
$ celery worker -A tasks --loglevel=INFO
Ensure you already installed nodejs, npm, and docker-compose
# Generate dist/ directory, tutorial files depend on it
$ npm run dist
# start a docker container rabbitmq in the background
$ docker-compose -f examples/docker-compose.yml up -d rabbit
# run celery.node client with rabbitmq
$ node examples/tutorial/client.js
# run celery.node worker with rabbitmq
# when you run worker, you can see the result printed out from client
$ node examples/tutorial/worker.js
# stop and remove containers
$ docker-compose -f examples/docker-compose.yml down
Before contributing, please read contributing.md
Let's make this project more awesome!
FAQs
celery written in nodejs
The npm package celery-node receives a total of 8,230 weekly downloads. As such, celery-node popularity was classified as popular.
We found that celery-node demonstrated a not healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security News
npm now supports Trusted Publishing with OIDC, enabling secure package publishing directly from CI/CD workflows without relying on long-lived tokens.

Research
/Security News
A RubyGems malware campaign used 60 malicious packages posing as automation tools to steal credentials from social media and marketing tool users.

Security News
The CNA Scorecard ranks CVE issuers by data completeness, revealing major gaps in patch info and software identifiers across thousands of vulnerabilities.