Chrome Lens OCR
Library to use Google Lens OCR for free, via API used in Chromium. This doesn't require running a headless browser, and is much faster than using Puppeteer or similar.
It's set up to work without any options, there's no need to be authorized (no need for Google account!).
Installation
npm install chrome-lens-ocr
Usage
import Lens from 'chrome-lens-ocr';
import { inspect } from 'util';
const lens = new Lens();
const log = data => console.log(inspect(data, { depth: null, colors: true }));
lens.scanByFile('shrimple.png').then(log).catch(console.error);
lens.scanByBuffer(Buffer.from('...')).then(log).catch(console.error);
lens.scanByURL('https://lune.dimden.dev/7949f833fa42.png').then(log).catch(console.error);
All methods above return LensResult object (see docs below). In case error happened during the process, LensError will be thrown.
API
All of the classes are exported. Lens is the default export, and LensCore, LensResult, Segment, BoundingBox and LensError are named exports.
class Lens extends LensCore
constructor(options?: Object): Lens
Creates a new instance of Lens. options is optional.
scanByFile(path: String): Promise<LensResult>
Scans an image from a file.
scanByBuffer(buffer: Buffer): Promise<LensResult>
Scans an image from a buffer.
class LensCore
This is the core class, which is extended by Lens. You can use it if you want to use the library in environments that don't support Node.js APIs, as it doesn't include scanByFile and scanByBuffer methods. Keep in mind that Lens class extends LensCore, so all methods and properties of LensCore are available in Lens.
constructor(options?: Object, fetch?: Function): LensCore
Creates a new instance of LensCore. options is optional. fetch is function that will be used to send requests, by default it's fetch from global scope.
scanByURL(url: String): Promise<LensResult>
Fetches an image from a remote URL, and scans it.
scanByData(data: Uint8Array, mime: String, originalDimensions: Array): Promise<LensResult>
Scans an image from a Uint8Array. originalDimensions is array of [width, height] format. You must provide width and height of image before it was resized to get accurate pixel coordinates. You should only use this method if you're using the library in environments that don't support Node.js APIs, because it doesn't automatically resize images to less than 1000x1000 dimensions, like methods in Lens do.
updateOptions(options: Object): void
Updates the options for the instance.
fetch(options?: RequestInit & { endpoint: String } = {}, originalDimensions: Array): Promise<LensResult>
Internal method to send a request to the API. You can use it to send a custom request, but you'll have to handle the formdata and dimensions yourself. Original dimensions ([width, height]) are used to calculate pixel coordinates of the text. You should supply dimensions before any resizing (hence 'original') if you want to get correct coordinates for original image.
cookies
This property contains object with cookies that are set for the instance. You can use it to save and load cookies to avoid doing the consent process every time.
Options object
Options can be empty, or contain the following (default values):
{
chromeVersion: '124.0.6367.60',
userAgent: 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/124.0.0.0 Safari/537.36',
headers: {},
fetchOptions: {},
}
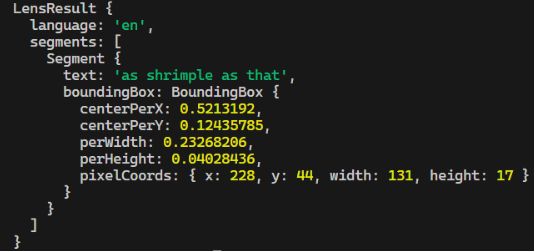
class LensResult
Instance of this class is is returned by all scan methods. It contains the following properties:
{
language: String,
segments: Array<Segment>
}
class Segment
Instance of this class is contained in LensResult's segments property. It contains the following properties:
{
text: String,
boundingBox: BoundingBox,
}
class BoundingBox
Instance of this class is contained in Segment's boundingBox property. It contains the following properties:
{
centerPerX: Number,
centerPerY: Number,
perWidth: Number,
perHeight: Number,
pixelCoords: {
x: Number,
y: Number,
width: Number,
height: Number,
}
}
class LensError extends Error
Instance of this class is thrown when an error happens during the process. It contains the following properties:
{
name: "LensError"
message: String,
code: String,
headers: HeadersList,
body: String,
}
Using proxy
By default, this library uses undici's fetch to make requests. You can use undici dispatcher to proxy requests. Here's an example:
import Lens from 'chrome-lens-ocr';
import { ProxyAgent } from 'undici';
const lens = new Lens({
fetchOptions: {
dispatcher: new ProxyAgent('http://user:pass@example.com:8080')
}
});
If you use core class with different fetch function, you can pass different options instead of dispatcher in fetchOptions (for example agent for node-fetch).
Using your cookies
You can use your own cookies to be authorized in Google. This is optional. Here's an example:
import Lens from 'chrome-lens-ocr';
const lens = new Lens({
headers: {
'cookie': '__Secure-ENID=17.SE=-dizH-; NID=511=---bcDwC4fo0--lgfi0n2-'
'cookie': {
'__Secure-ENID': {
name: '__Secure-ENID',
value: '17.SE=-dizH-',
expires: 1634025600,
},
'NID': {
name: 'NID',
value: '511=---bcDwC4fo0--lgfi0n2-',
expires: 1634025600,
}
}
}
});
Custom Sharex OCR
It's possible to use this package with Sharex to OCR images using Google Lens API, instead of bad default OCR in Sharex. Please refer to SHAREX.md for instructions.
CLI Usage
You may install this package globally by adding -g on install:
npm install -g chrome-lens-ocr
Doing this will allow you to use the OCR from a terminal.
Usage: chrome-lens-ocr [-d] ./path/to/image.png
-d Do not copy text to clipboard
Example:
chrome-lens-ocr ./shrimple.png
chrome-lens-ocr -d ./shrimple.png
chrome-lens-ocr -d https://lune.dimden.dev/7949f833fa42.png




