
Security News
Insecure Agents Podcast: Certified Patches, Supply Chain Security, and AI Agents
Socket CEO Feross Aboukhadijeh joins Insecure Agents to discuss CVE remediation and why supply chain attacks require a different security approach.
For diffing ordered trees
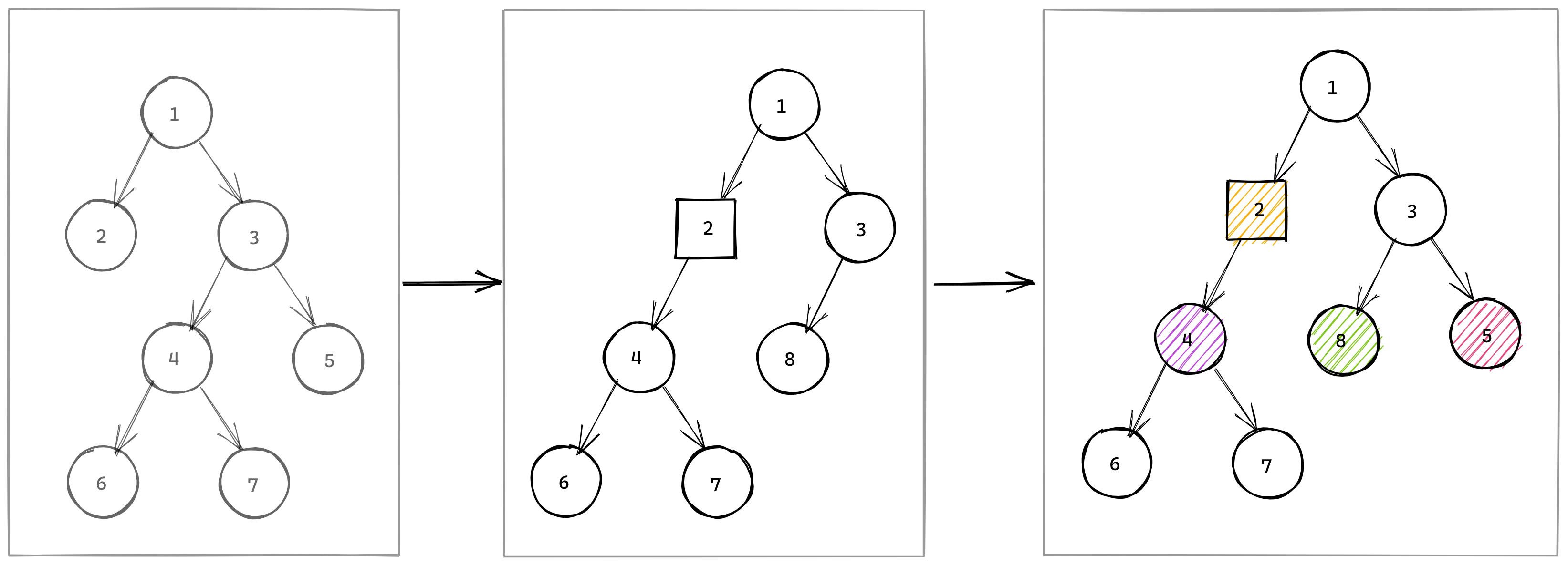
A single diffTrees function is exported:
declare function diffTrees<TValue>(
treeA: TreeNode<{ value: TValue }>,
treeB: TreeNode<{ value: TValue }>
): DiffTree<TValue>;
It takes two trees of type TreeNode:
type TreeNode<TValues> = {
id: string;
children: TreeNode<TValues>[];
} & TValues;
And produces a single tree of type DiffTree which is an array containing one or two DiffTreeNodes. The second DiffTreeNode is included if the root of the tree was deleted.
type DiffTree<TValue> =
| [DiffTreeNode<TValue>]
| [DiffTreeNode<TValue>, DiffTreeNode<TValue>];
type DiffTreeNode<TValue> = Omit<TreeNode<{ value: TValue }>, 'children'> & {
change: Change;
children: DiffTreeNode<TValue>[];
};
Where a Change is:
type Change =
| [ChangeType.Unchanged]
| [ChangeType.Inserted]
| [ChangeType.Deleted]
| [ChangeType.Updated]
| [ChangeType.Moved]
| [ChangeType.Moved, ChangeType.Updated];
ChangeType.Unchanged denotes unchanged nodes.ChangeType.Inserted denotes new nodes.ChangeType.Deleted denotes deleted nodes.ChangeType.Updated denotes nodes where the value changed.ChangeType.Moved denotes nodes that moved to another subtree or changed place within the same subtree.The value in a TreeNode can is generic. If the value has changed, the DiffTreeNode is annotated with ChangeType.Updated. By default, values are compared using strict equality (===). To change how values are compared, add a custom valueEquality function to the optional options object:
declare function diffTrees<TValue>(
treeA: TreeNode<{ value: TValue }>,
treeB: TreeNode<{ value: TValue }>,
options?: {
valueEquality: (a: TValue, b: TValue) => boolean;
}
): DiffTreeNode<TValue>;
diffTrees(
{ id: '1', value: 'a', children: [] },
{ id: '1', value: 'a', children: [] }
);
// =>
[
{
id: '1',
value: 'a',
children: [],
change: [ChangeType.Unchanged],
},
];
diffTrees(
{ id: '1', value: 'a', children: [] },
{ id: '2', value: 'b', children: [] }
);
// =>
[
{
id: '2',
value: 'b',
children: [],
change: [ChangeType.Inserted],
},
{
id: '1',
value: '1',
children: [],
change: [ChangeType.Deleted],
},
];
diffTrees(
{ id: '1', value: 'a', children: [] },
{ id: '1', value: 'a', children: [{ id: '2', value: 'b', children: [] }] }
);
// =>
[
{
id: '1',
value: 'a',
change: [ChangeType.Unchanged],
children: [
{ id: '2', value: 'b', change: [ChangeType.Inserted], children: [] },
],
},
];
diffTrees(
{
id: '1',
value: 'a',
children: [
{ id: '2', value: 'b', children: [] },
{ id: '3', value: 'c', children: [] },
],
},
{
id: '1',
value: 'a',
children: [
{ id: '3', value: 'c2', children: [] },
{ id: '2', value: 'b', children: [] },
],
}
);
// =>
[
{
id: '1',
value: 'a',
change: [ChangeType.Unchanged],
children: [
{
id: '3',
value: 'c2',
change: [ChangeType.Moved, ChangeType.Updated],
children: [],
},
{
id: '2',
value: 'b',
change: [ChangeType.Moved],
children: [],
},
],
},
];
FAQs
For diffing ordered trees
We found that diff-trees demonstrated a not healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security News
Socket CEO Feross Aboukhadijeh joins Insecure Agents to discuss CVE remediation and why supply chain attacks require a different security approach.

Security News
Tailwind Labs laid off 75% of its engineering team after revenue dropped 80%, as LLMs redirect traffic away from documentation where developers discover paid products.

Security News
The planned feature introduces a review step before releases go live, following the Shai-Hulud attacks and a rocky migration off classic tokens that disrupted maintainer workflows.