distribus
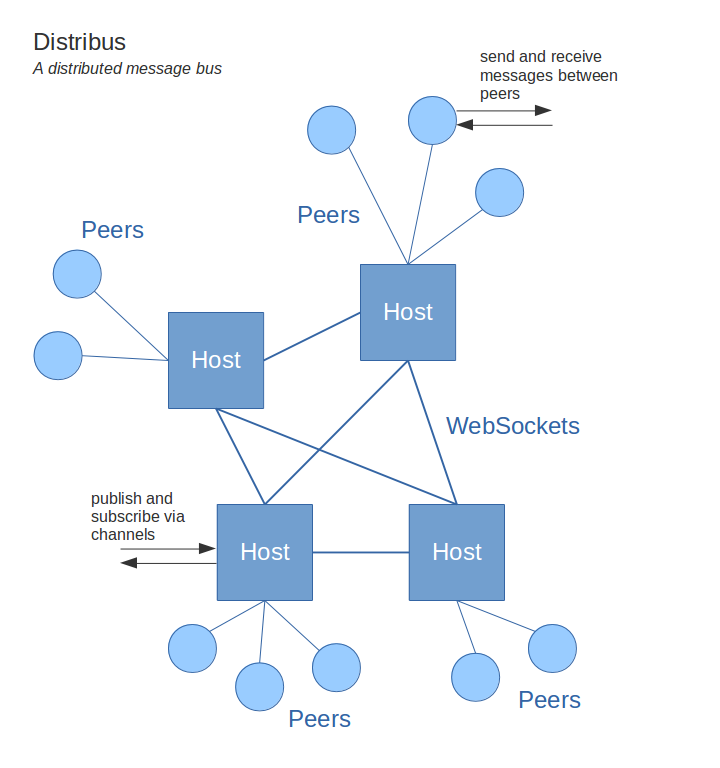
A scalable, distributed message bus for node.js and the browser. One or multiple
hosts are connected to each other in a peer-to-peer network. Peers can be
connected to any of the hosts in the network, and then send messages to each
other by their id.
Distribus scales up to hundreds of hosts and millions of peers.
Distribus can be used to:
- Send messages between individual peers
- Publish/subscribe to messages via channels
- Broadcast messages (not yet implemented)
Install
Install the library via npm:
npm install distribus
Use
Sending messages between peers
var distribus = require('distribus');
var host = new distribus.Host();
var peer1 = host.create('peer1');
var peer2 = host.create('peer2');
peer1.on('message', function (from, message) {
console.log('peer1 received a message from ' + from + ': ' + message);
peer1.send(from, 'Thanks for your message');
});
peer2.on('message', function (from, message) {
console.log('peer2 received a message from ' + from + ': ' + message);
});
peer2.send('peer1', 'Hi peer1!');
Publish and subscribe
var distribus = require('distribus');
var host = new distribus.Host();
host.subscribe('news', function (message) {
console.log('received message:', message);
});
host.publish('news', 'My first message!');
Multiple hosts
Create two files, host1.js and host2.js (see examples/multiple_hosts). Start them both with node.
host1.js
var distribus = require('distribus');
var PORT1 = 3000;
var HOST2_URL = 'ws://localhost:3001';
var host1 = new distribus.Host();
var peer1 = host1.create('peer1');
peer1.on('message', function (from, message) {
console.log('Received a message from ' + from + ': "' + message + '"');
if (message.indexOf('hello') === 0) {
peer1.send(from, 'hi ' + from);
}
});
host1.listen('localhost', PORT1)
.then(function () {
return host1.join(HOST2_URL);
})
.then(function () {
console.log('Connected to host2');
var message = 'hello peer2';
console.log('Sending a message to peer2: "' + message + '"');
peer1.send('peer2', message);
})
.catch(function (err) {
console.log('host2 is not running, please start host2.js as well');
});
host2.js
var distribus = require('../../index');
var PORT2 = 3001;
var HOST1_URL = 'ws://localhost:3000';
var host2 = new distribus.Host();
var peer2 = host2.create('peer2');
peer2.on('message', function (from, message) {
console.log('Received a message from ' + from + ': "' + message + '"');
if (message.indexOf('hello') === 0) {
peer2.send(from, 'hi ' + from);
}
});
host2.listen('localhost', PORT2)
.then(function () {
return host2.join(HOST1_URL);
})
.then(function () {
console.log('Connected to host1');
var message = "hello peer1";
console.log('Sending a message to peer1: "' + message + '"');
peer2.send('peer1', message);
})
.catch(function (err) {
console.log('host1 is not running, please start host1.js as well');
});
API
distribus
The distribus namespace contains the following prototypes:
distribus.Hostdistribus.Promise
Host
A Host can be created as
var host = new distribus.Host([options]);
The available options are listed under Host.config([options]).
A Host has the following methods:
Host.close(): Promise.<Host, Error>
Close the hosts web server socket. Returns the host itself.Host.config([options]): Object
Apply configuration options to the host, and/or retrieve the current
configuration. Available options:
reconnectTimeout
Timeout in milliseconds for giving up reconnecting. 300000 ms (5 minutes)
by default.reconnectDelay
Initial delay in milliseconds for trying to reconnect. For consecutive
reconnect trials, the delay decays with a factor reconnectDecay.
The initial delay is 1000 ms (1 second) by default.reconnectDecay
Decay for the reconnect delay. 2 by default.
Host.create(id: string) : Peer
Create a new Peer.
Throws an error when a peer with the same id already exists on this host.
Does not check whether this id exists on any remote host (use Host.find(id)
to validate this before creating a peer, or even better, use a uuid to
prevent id collisions).Host.find(id: string): Promise.<string, Error>
Find the host where the peer with given id is located. Rejects with an error
when the peer is not found. Returns null when the peer is located on a host
without url.Host.get(id: string) : Peer
Get a local Peer by its id. Returns null if the peer does not exist.Host.join(address: string, port: number): Promise.<Host, Error>
Join another host, the hosts will form a network. Peers located on the
joined host can be contacted.Host.listen(address: string, port: number): Promise.<Host, Error>
Start listening on a web socket server. Returns the host it self once
the server is started.Host.publish(channel: string, message: *)
Publish a message on a specific channel. All subscribers of the channel (on
all connected hosts) will receive the message.Host.remove(peer: Peer | string)
Remove a peer from the host.Host.subscribe(channel: string, callback: function)
Subscribe to a channel. The callback is called as callback(message).Host.unsubscribe(channel: string, callback: function)
Unsubscribe from a channel.
Peer
A Peer can send and receive messages. A Peer can be created by a Host.
var host = new distribus.Host();
host.create('peer1')
.then(function (peer) {
console.log(peer.id + ' created');
})
.catch(function (err) {
console.log(err);
});
A Peer has the following functions:
-
Peer.on(event, callback)
Listen for an event. Available events:
'message'. Receive a message. Syntax:
Peer.on('message', function (from : String, message: *) {...})
-
Peer.send(to: String, message: *) : Promise.<null, Error>
Send a message to an other peer. The message must be valid JSON.
Roadmap
- Implement broadcasting.
- Implement wildcards to address a group of peers
- Implement wildcards to subscribe to a group of channels.
- Create a bundle of the library for use in the browser.
- Add support for Hosts and Peers in a client environment like a browser.
A Host on a client can be connected to a Host on a server, which then serves
as a proxy to route messages to peers located on the client.
- Improve performance and optimize memory usage.
- Implement support for WebRTC to connect clients.
Related
Test
To execute tests for the library, install the project dependencies once:
npm install
Then, the tests can be executed:
npm test
To test code coverage of the tests:
npm run coverage
To see the coverage results, open the generated report in your browser:
./coverage/lcov-report/index.html
License
Copyright (C) 2014 Jos de Jong wjosdejong@gmail.com
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
limitations under the License.




