Product
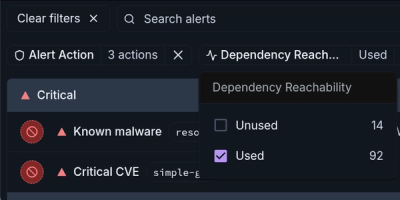
Introducing Module Reachability: Focus on the Vulnerabilities That Matter
Module Reachability filters out unreachable CVEs so you can focus on vulnerabilities that actually matter to your application.
express-error-catcher
Advanced tools
express-error-catcherexpress-error-catcher is a robust npm package engineered to streamline error handling in Node.js Express applications. It provides an elegant solution for managing async/await errors, reducing boilerplate code, and enhancing the maintainability of your applications.
Integrating express-error-catcher into your project is straightforward. Use the following npm command to install the package:
npm install express-error-catcher
To leverage express-error-catcher in your Express application, follow these steps:
Begin by importing the necessary functions and middleware from the express-error-catcher package.
import express from "express";
import { asyncErrorHandler, error, Response, Error } from "express-error-catcher";
Apply the error-handling middleware with optional configuration parameters to customize its behavior.
const app = express();
app.use(error({
defaultErrorMessage: "Internal server error", // Sets a default error message for uncaught errors.
defaultStatusCode: 500, // Defines the default HTTP status code for errors.
log: "dev" // Chooses the logging format: "dev" for detailed logs, "prod" for concise logs.
}));
Use the asyncErrorHandler function to wrap your asynchronous route handlers. This ensures that any errors are automatically caught and passed to the error-handling middleware.
app.get(
"/name",
asyncErrorHandler((req, res) => {
// Intentionally throwing an error
throw Error("Error while retrieving name", 500);
// Returning a successful response
return Response("Successfully retrieved name", { name: "Daisy" }, 200);
})
);
Finally, start your Express server as usual:
const PORT = process.env.PORT || 3000;
app.listen(PORT, () => {
console.log(`Server is running on port ${PORT}`);
});
The error middleware provides a range of configuration options to tailor error handling to your application’s requirements.
defaultErrorMessage: A string specifying the default message to return when an error is unhandled.defaultStatusCode: An integer representing the default HTTP status code to use when responding to unhandled errors.log: A string determining the log format. Options include:
"dev": Detailed log output for development, including error messages and file paths."pretty": A more readable format compared to dev, with enhanced formatting for better human readability. Example."production": Simplified log output for production environments, focusing on error messages only.dev)In development mode, express-error-catcher provides detailed logs that include the error message, file path, and line number, presented in a table format for easy reading:
<------------------------------->
ERROR => Internal Server Error
FILE => /path/to/file.js:16:11
<------------------------------->
pretty)In development mode, express-error-catcher offers detailed logs in a table format that includes the error message and file path. This format enhances readability and helps quickly identify issues:
┌─────────┬─────────────────────────┬────────────────────────────────┐
│ (index) │ Message │ File │
├─────────┼─────────────────────────┼────────────────────────────────┤
│ 0 │ 'Internal Server Error' │ '/path/to/file.js:16:11' │
└─────────┴─────────────────────────┴────────────────────────────────┘
production)In production mode, logs are minimized to reduce noise and focus on essential information:
<------------------------------->
ERROR => Internal Server Error
<------------------------------->
express-error-catcher allows you to define and handle custom errors with specific messages and status codes, providing fine-grained control over error management.
throw Error("Custom error message", 400);
When an operation completes successfully, the response is structured as follows:
return new Response("Success.", { data: "Welcome daisy.." }, 200);
The corresponding JSON output will be:
{
"code": 200,
"success": true,
"status": "OK",
"message": "Success.",
"data": "Welcome daisy.."
}
If an error occurs during processing, an error is thrown with the following structure:
throw new Error("Daisy already exists.", 400);
The corresponding JSON output will be:
{
"success": false,
"code": 400,
"status": "Bad Request",
"message": "Daisy already exists."
}
You can also include additional data in the error response for more context:
throw new Error("Daisy already exists.", 400, { details: "Validation failed" });
{
"success": false,
"code": 400,
"status": "Bad Request",
"message": "Daisy already exists.",
"data": {
"details": "Validation failed"
}
}
The package is designed to integrate seamlessly with other Express middleware, allowing you to create a cohesive error-handling strategy across your application.
FAQs
async error handler
The npm package express-error-catcher receives a total of 52 weekly downloads. As such, express-error-catcher popularity was classified as not popular.
We found that express-error-catcher demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 0 open source maintainers collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Product
Module Reachability filters out unreachable CVEs so you can focus on vulnerabilities that actually matter to your application.

Company News
Socket is bringing best-in-class reachability analysis into the platform — cutting false positives, accelerating triage, and cementing our place as the leader in software supply chain security.
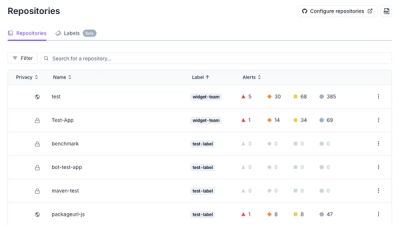
Product
Socket is introducing a new way to organize repositories and apply repository-specific security policies.