Research
Using Trusted Protocols Against You: Gmail as a C2 Mechanism
Socket uncovers malicious packages on PyPI using Gmail's SMTP protocol for command and control (C2) to exfiltrate data and execute commands.
jsii-diff
Advanced tools
jsii-diff compares two jsii assemblies for compatibility.
In the future, it will be able to do generic comparisons. But for now it will compare assemblies for API compatibility, and exit with a non-zero exit code if any stable or deprecated APIs have had incompatible changes.
API items that have no stability are treated as stable.
To treat unmarked API items as experimental, pass the --default-experimental flag.
To compare two JSII packages:
jsii-diff <old> [new]
Packages can be identified by either:
.jsii file.npm:[<package>[@version]], in
which case the indicated version is downloaded and used. If @version is
left out, the latest version will be used. If package is left out,
the assembly name of .jsii in the current directory will be used.To compare current package against latest published NPM release:
jsii-diff npm:<package>
By default only incompatible changes to stable or deprecated APIs are treated as errors and will fail the command.
Changes to experimental or external APIs emit a warning.
Change this behavior with the --error-on flag:
jsii-diff npm:<package> --error-on=all
The following --error-on groups are available:
--error-on | Stabilities that cause an ERROR |
|---|---|
prod (default) | stable, deprecated |
non-experimental | stable, deprecated, external |
all | stable, deprecated, experimental, external |
jsii-diff will assert that code written against version A of a library will still typecheck when compiled against version B of that library. It does this by verifying the following properties:
Strengthening a type refers to excluding more possible values. Changing
a field from optional to required, or changing a type from any to
string are examples of strengthening.
As the opposite of strengthening, weakening refers to allowing more
possible values. Changing a field from required to optional, or
changing a type to a superclass or interface are examples of weakening.
An API can change in the following way without breaking its consumer:
Structs (interfaces consisting completely of readonly properties) are
treated as bags of data. Their API compatibility will be evaluated depending
on whether they appear in input or output position of operations.
jsii-diff will check the evolution of structs against their position in an operation, similar to other types. Input structs may be weakened, and output structs may be strengthened.
Classes and non-struct interface types are considered "reference types". By default we treat them as being the result of a function call:
This means their evolution falls under the rules of "strengthening": they may only add fields, never take any away or make them optional.
@subclassableSome classes or interfaces may be intended to be implemented by consumers.
Those should be marked with the docstring tag @subclassable.
This will effectively cause changes against those types to be checked against the rules for weakening as well (i.e., no new (abstract) fields or members added). This is necessary because otherwise any existing implementor of that interface would be broken, since they wouldn't be implementing the new abstract members yet.
@subclassable is not the default since most interfaces are not intended
for subclassing, but treating them as such would limit the evolvability of
libraries too much.
See BREAKING_CHANGES.md for more information.
jsii-diff is distributed under the Apache License, Version 2.0.
FAQs
Assembly comparison for jsii
The npm package jsii-diff receives a total of 22,683 weekly downloads. As such, jsii-diff popularity was classified as popular.
We found that jsii-diff demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 4 open source maintainers collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Research
Socket uncovers malicious packages on PyPI using Gmail's SMTP protocol for command and control (C2) to exfiltrate data and execute commands.
Product
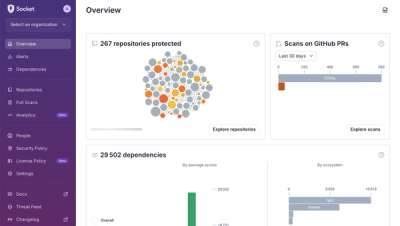
We redesigned Socket's first logged-in page to display rich and insightful visualizations about your repositories protected against supply chain threats.

Product
Automatically fix and test dependency updates with socket fix—a new CLI tool that turns CVE alerts into safe, automated upgrades.