
Security News
curl Shuts Down Bug Bounty Program After Flood of AI Slop Reports
A surge of AI-generated vulnerability reports has pushed open source maintainers to rethink bug bounties and tighten security disclosure processes.
Single file write-once database that is valid JSON with efficient random access on bigger datasets
Single file write-once database that is valid JSON with efficient random access on bigger datasets
npm install jsonkv
const jsonkv = require('jsonkv')
// First create a database (all data will be stored in ./db.json as valid JSON)
const ws = jsonkv.createWriteStream('db.json')
// Write a ton of data to it
for (var i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
ws.write({
key: i,
value: `this is a value: ${i}`
})
}
ws.end(function () {
// our jsonkv is now fully written and cannot be updated again.
// to query it make an instance
const db = jsonkv('db.json')
db.get(42, function (err, doc) {
console.log(doc) // prints {key: 42, value: 'this is a value: 42'}
})
})
ws = jsonkv.createWriteStream(filename, [opts])Create a new database by writing data to the input stream.
All data should be objects and include a sortable primary key. Per default the property key is used. If you want to use another property pass your own sort function as in options.
const ws = jsonkv.createWriteStream('db.json')
ws.write({
key: 'hello', // per default key is used as the primary key
world: true
})
The data will be stored temporarily as {filename}.tmp and will then be indexed and stored in filename as a valid JSON file where all the data is stored sorted in a values array with some whitespace padding to make lookups efficient.
The indexing procedure is memory efficient so should be able to handle large datasets as input.
When the stream emits finish the database is safe to use.
db = jsonkv(filename, [opts])After writing data to a database file you can query by making a database instance.
If you used an optional sort function when writing your data you should pass that here as well.
db.get(key, callback)Lookup a key. Return the value if found and null otherwise.
rs = db.createReadStream([opts])Make a readable stream that traverses the database in sorted order.
Options include:
{
gt: key, // only keys > than key
gte: key, // only keys >= than key
lt: key, // only keys < than key
lte: key // only keys <= than key
}
ite = db.iterate([opts])Same as above but returns a nanoiterator instance instead of a stream
MIT
FAQs
Single file write-once database that is valid JSON with efficient random access on bigger datasets
We found that jsonkv demonstrated a not healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security News
A surge of AI-generated vulnerability reports has pushed open source maintainers to rethink bug bounties and tighten security disclosure processes.
Product
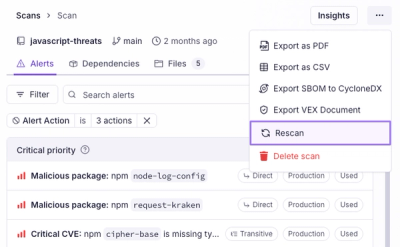
Scan results now load faster and remain consistent over time, with stable URLs and on-demand rescans for fresh security data.
Product
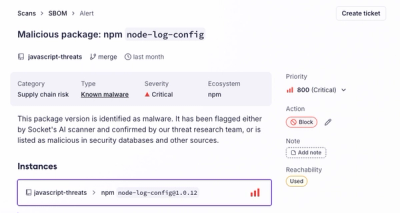
Socket's new Alert Details page is designed to surface more context, with a clearer layout, reachability dependency chains, and structured review.