
Security Fundamentals
Turtles, Clams, and Cyber Threat Actors: Shell Usage
The Socket Threat Research Team uncovers how threat actors weaponize shell techniques across npm, PyPI, and Go ecosystems to maintain persistence and exfiltrate data.
The microtime package provides high-resolution time in microseconds, which is useful for performance measurement and benchmarking in Node.js applications.
Get current time in microseconds
This feature allows you to get the current time in microseconds since the Unix epoch. It is useful for precise time measurements.
const microtime = require('microtime');
const currentTime = microtime.now();
console.log(currentTime);Get current time as an array
This feature returns the current time as an array with two elements: seconds and microseconds. It provides a structured way to access high-resolution time.
const microtime = require('microtime');
const timeArray = microtime.nowStruct();
console.log(timeArray);Get current time as a double
This feature returns the current time as a floating-point number representing seconds and fractions of a second. It is useful for calculations that require time in seconds.
const microtime = require('microtime');
const timeDouble = microtime.nowDouble();
console.log(timeDouble);The performance-now package provides a high-resolution timer that returns the current time in milliseconds with sub-millisecond precision. It is similar to microtime but uses milliseconds instead of microseconds, which may be sufficient for many applications.
The hrtime package is a Node.js built-in function that provides high-resolution real-time in nanoseconds. It is more precise than microtime and is suitable for applications requiring even finer time measurements.
Date.now() will only give you accuracy in milliseconds. This module calls
gettimeofday(2) to get the time in microseconds and provides it in a few
different formats. The same warning from that function applies:
The resolution of the system clock is hardware dependent, and the time may
be updated continuously or in ``ticks.''
As of version 3.0.0, this library is built using the N-API library. This should allow you to upgrade to newer versions of Node.js without having to reinstall / rebuild this library.
Version 3.0.0 and later also bundle prebuilt binaries for common systems in
the npm package itself. These will be used if the version of Node you are using
supports N-API (>= v6.14.2), otherwise the binary will be recompiled on install.
npm install microtime
Get the current time in microseconds as an integer.
Get the current time in seconds as a floating point number with microsecond
accuracy (similar to time.time() in Python and Time.now.to_f in Ruby).
Get the current time and return as a list with seconds and microseconds (matching the return value of gettimeofday(2)).
> var microtime = require('microtime')
> microtime.now()
1297448895297028
> microtime.nowDouble()
1297448897.600976
> microtime.nowStruct()
[ 1297448902, 753875 ]
Starting with version 0.1.3, there is a test script that tries to guess the clock resolution. You can run it with npm test microtime. Example output:
microtime.now() = 1298960083489806
microtime.nowDouble() = 1298960083.511521
microtime.nowStruct() = [ 1298960083, 511587 ]
Guessing clock resolution...
Clock resolution observed: 1us
FAQs
Get the current time in microseconds
The npm package microtime receives a total of 173,584 weekly downloads. As such, microtime popularity was classified as popular.
We found that microtime demonstrated a not healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

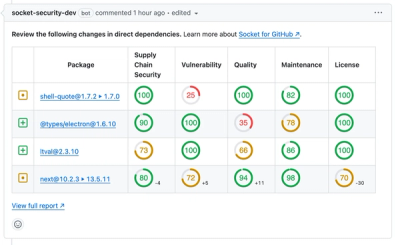
Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security Fundamentals
The Socket Threat Research Team uncovers how threat actors weaponize shell techniques across npm, PyPI, and Go ecosystems to maintain persistence and exfiltrate data.

Security News
At VulnCon 2025, NIST scrapped its NVD consortium plans, admitted it can't keep up with CVEs, and outlined automation efforts amid a mounting backlog.
Product
We redesigned our GitHub PR comments to deliver clear, actionable security insights without adding noise to your workflow.