
Security News
rv Is a New Rust-Powered Ruby Version Manager Inspired by Python's uv
Ruby maintainers from Bundler and rbenv teams are building rv to bring Python uv's speed and unified tooling approach to Ruby development.
multi-agent-orchestrator
Advanced tools
[DEPRECATED] This package has been renamed to 'agent-squad'. Please use 'npm install agent-squad' instead. Multi-Agent Orchestrator framework
|
⚠️ IMPORTANT: This package has been renamed to agent-squad. Please use npm install agent-squad instead.See: https://www.npmjs.com/package/agent-squad |
Flexible and powerful framework for managing multiple AI agents and handling complex conversations.






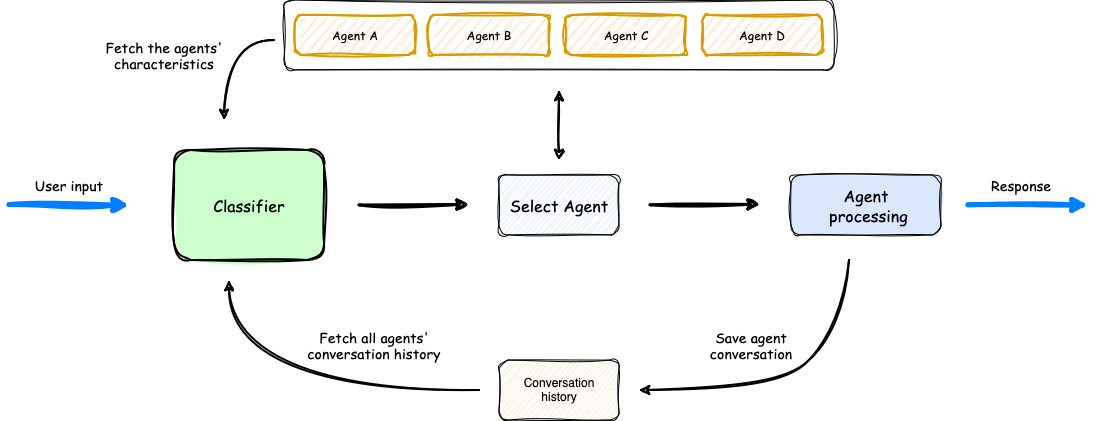
The Multi-Agent Orchestrator is a flexible framework for managing multiple AI agents and handling complex conversations. It intelligently routes queries and maintains context across interactions.
The system offers pre-built components for quick deployment, while also allowing easy integration of custom agents and conversation messages storage solutions.
This adaptability makes it suitable for a wide range of applications, from simple chatbots to sophisticated AI systems, accommodating diverse requirements and scaling efficiently.
To quickly get a feel for the Multi-Agent Orchestrator, we've provided a Demo App with a few basic agents. This interactive demo showcases the orchestrator's capabilities in a user-friendly interface. To learn more about setting up and running the demo app, please refer to our Demo App section.
In the screen recording below, we demonstrate an extended version of the demo app that uses 6 specialized agents:
Watch as the system seamlessly switches context between diverse topics, from booking flights to checking weather, solving math problems, and providing health information. Notice how the appropriate agent is selected for each query, maintaining coherence even with brief follow-up inputs.
The demo highlights the system's ability to handle complex, multi-turn conversations while preserving context and leveraging specialized agents across various domains.

Check out our documentation for comprehensive guides on setting up and using the Multi-Agent Orchestrator!
npm install multi-agent-orchestrator
The following example demonstrates how to use the Multi-Agent Orchestrator with two different types of agents: a Bedrock LLM Agent with Converse API support and a Lex Bot Agent. This showcases the flexibility of the system in integrating various AI services.
import { MultiAgentOrchestrator, BedrockLLMAgent, LexBotAgent } from "multi-agent-orchestrator";
const orchestrator = new MultiAgentOrchestrator();
// Add a Bedrock LLM Agent with Converse API support
orchestrator.addAgent(
new BedrockLLMAgent({
name: "Tech Agent",
description:
"Specializes in technology areas including software development, hardware, AI, cybersecurity, blockchain, cloud computing, emerging tech innovations, and pricing/costs related to technology products and services.",
streaming: true
})
);
// Add a Lex Bot Agent for handling travel-related queries
orchestrator.addAgent(
new LexBotAgent({
name: "Travel Agent",
description: "Helps users book and manage their flight reservations",
botId: process.env.LEX_BOT_ID,
botAliasId: process.env.LEX_BOT_ALIAS_ID,
localeId: "en_US",
})
);
// Example usage
const response = await orchestrator.routeRequest(
"I want to book a flight",
'user123',
'session456'
);
// Handle the response (streaming or non-streaming)
if (response.streaming == true) {
console.log("\n** RESPONSE STREAMING ** \n");
// Send metadata immediately
console.log(`> Agent ID: ${response.metadata.agentId}`);
console.log(`> Agent Name: ${response.metadata.agentName}`);
console.log(`> User Input: ${response.metadata.userInput}`);
console.log(`> User ID: ${response.metadata.userId}`);
console.log(`> Session ID: ${response.metadata.sessionId}`);
console.log(
`> Additional Parameters:`,
response.metadata.additionalParams
);
console.log(`\n> Response: `);
// Stream the content
for await (const chunk of response.output) {
if (typeof chunk === "string") {
process.stdout.write(chunk);
} else {
console.error("Received unexpected chunk type:", typeof chunk);
}
}
} else {
// Handle non-streaming response (AgentProcessingResult)
console.log("\n** RESPONSE ** \n");
console.log(`> Agent ID: ${response.metadata.agentId}`);
console.log(`> Agent Name: ${response.metadata.agentName}`);
console.log(`> User Input: ${response.metadata.userInput}`);
console.log(`> User ID: ${response.metadata.userId}`);
console.log(`> Session ID: ${response.metadata.sessionId}`);
console.log(
`> Additional Parameters:`,
response.metadata.additionalParams
);
console.log(`\n> Response: ${response.output}`);
}
This example showcases:
We welcome contributions! Please see our Contributing Guide for more details.
This project is licensed under the Apache 2.0 licence - see the LICENSE file for details.
This project uses the JetBrainsMono NF font, licensed under the SIL Open Font License 1.1. For full license details, see FONT-LICENSE.md.
FAQs
[DEPRECATED] This package has been renamed to 'agent-squad'. Please use 'npm install agent-squad' instead. Multi-Agent Orchestrator framework
The npm package multi-agent-orchestrator receives a total of 70 weekly downloads. As such, multi-agent-orchestrator popularity was classified as not popular.
We found that multi-agent-orchestrator demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security News
Ruby maintainers from Bundler and rbenv teams are building rv to bring Python uv's speed and unified tooling approach to Ruby development.

Security News
Following last week’s supply chain attack, Nx published findings on the GitHub Actions exploit and moved npm publishing to Trusted Publishers.

Security News
AGENTS.md is a fast-growing open format giving AI coding agents a shared, predictable way to understand project setup, style, and workflows.