
Security Fundamentals
Turtles, Clams, and Cyber Threat Actors: Shell Usage
The Socket Threat Research Team uncovers how threat actors weaponize shell techniques across npm, PyPI, and Go ecosystems to maintain persistence and exfiltrate data.
nodejs-model-validator
Advanced tools
Model Validator for applications that need models with typings and validation without the help of typescript
Model generator is a simple model generator tool that enables you to create models with types and validators.
Run install command to install model-validator.
npm install model-validator
The module has differend exports. Best practice is to put these in differend variables.
let ModelValidatorModule = require('model-validator');
let ModelValidator = ModelValidatorModule().ModelValidator;
let Property = ModelValidatorModule().Property;
let Validators = ModelValidatorModule().Validators;
###Optional settings Include an object
let settings = {
/**
* name: debug
* default: false
* requires: Boolean
*/
debug: true
};
Edit the following line if you want to add settings:
let ModelValidator = ModelValidatorModule(settings).ModelValidator;
Create a class and extend it with the ModelValidator class. Create a constructor and then call super(<=StructureForYourModel=>).
class ExampleModel extends ModelValidator {
constructor() {
super(StructureForYourModel);
}
}
Model generator generates a model using a structure. A structure is how your model will be generated. A structure takes an array of type Property. Example structure:
const ExampleModelStructure = {
// array of all properties you want in your model
properties: [
new Property(
'UserEmail',// property name
undefined, // default value
String, // type
[Validators.Required, Validators.Email] // Array of validators
),
new Property(
'Test',
undefined,
Number,
[]
)
]
};
This module has an exported class Property. Property class can be used in the structure to define a property.
Property takes 4 arguments:
Properties are normal properties that automaticly run all validators and type checking. Use it like you would a normal property
Model.Property = "value"; // setting property runs all validators in the background
let model = Model.Property;
Validator is a check that needs to happen when a value is set on a property. Validators Need 2 Properties to work:
Here is a list of all validators that are available in the Validators array by default:
The generated model is bloated with properties and functions. Sometimes you need to return a model that is a clean javascript object without setters and getters. The getCleanModel is a function set on the generated model that returns the json model.
You can cast a json format into a Model using the exported member Cast. The function will throw error if it fails and return a model if it succeeds.
let Cast = require('./ModelValidatorModule').Cast;
let Model = <= Insert your model here =>
json = {
Prop1:1,
Prop2:'test',
}
Cast(json,Model)
let ModelValidatorModule = require('./ModelValidatorModule');
let ModelValidator = ModelValidatorModule.ModelValidator;
let Property = ModelValidatorModule.Property;
let Validators = ModelValidatorModule.Validators;
const ExampleModelStructure = {
properties: [
new Property(
'UserEmail',//property name
undefined, // default value
String, // type
[Validators.Required, Validators.Email] // Array of validators
),
new Property(
'Test',
undefined,
Number,
[]
)
]
};
class ExampleModel extends ModelValidator {
constructor() {
super(ExampleModelStructure);
}
}
FAQs
Model Validator for applications that need models with typings and validation without the help of typescript
The npm package nodejs-model-validator receives a total of 0 weekly downloads. As such, nodejs-model-validator popularity was classified as not popular.
We found that nodejs-model-validator demonstrated a not healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

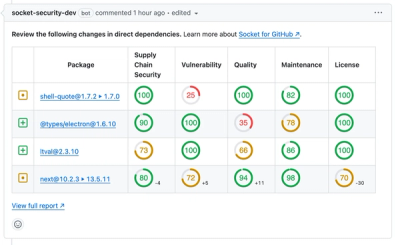
Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security Fundamentals
The Socket Threat Research Team uncovers how threat actors weaponize shell techniques across npm, PyPI, and Go ecosystems to maintain persistence and exfiltrate data.

Security News
At VulnCon 2025, NIST scrapped its NVD consortium plans, admitted it can't keep up with CVEs, and outlined automation efforts amid a mounting backlog.
Product
We redesigned our GitHub PR comments to deliver clear, actionable security insights without adding noise to your workflow.