Product
Introducing Custom Tabs for Org Alerts
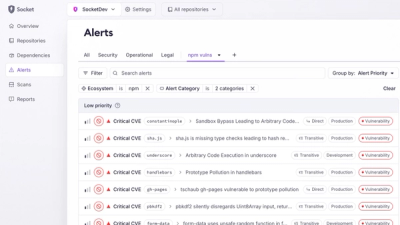
Create and share saved alert views with custom tabs on the org alerts page, making it easier for teams to return to consistent, named filter sets.
npme-auth-foo
Advanced tools
npmE launched with authorization that's tightly integrated with GitHub Enterprise:
This has been great for companies who use GHE, but overlooks people using other types authorization e.g., LDAP.
In prep for supporting a wider of variety auth-strategies, we're open-sourcing npmE's auth-plugin architecture.
Here's what you need to know to write a custom authentication strategy for npm Enterprise:
An auth-strategy is published as an npm module. Your package should contain the following files:
The index.js file is the file loaded by npmE, it should have the following content:
exports.Authenticator = require('./authenticator.js');
exports.Authorizer = require('./authorizer.js');
An authenticator handles the user's initial login:
npm login --scope=@myregistry --registry=http://my-npmee:8080
The authenticator need only expose the single method authenticate. Here's an example:
function FooAuthenticator() {}
FooAuthenticator.prototype.authenticate = function(credentials, cb) {};
module.exports = FooAuthenticator;
The authenticate method receives a credentials object, and a cb to execute once authentication is complete.
The credentials object contains the username, password, and email provided via npm login:
{
"body": {
"name": "foo",
"password": "bar",
"email": "ben@example.com"
}
}
This login information can then be validated against an arbitrary service, such as your company's LDAP server.
If the login fails, execute callback with an error object:
return cb(Error('invalid login'));
If a login is successful it's your responsibility to:
cb(null, {
token: 'foo-token',
user: {
email: credentials.body.email,
name: credentials.body.name
}
})
The token you issue should be a unique identifier which allows you to associate future installs and publications with the authenticated user. This is the value that will be stored in the user's .npmrc.
In the case of npme-auth-githb, a GitHub application-token is returned. This can be used to authorize future requests against the GitHub API.
An authorizer handels package installs and publications. To create an authorizer, simply implement the authorize method:
function FooAuthorizer(config) {};
FooAuthorizer.prototype.authorize = function(request, cb) {
};
module.exports = FooAuthorizer;
The authenticate method receives a request object and a cb to execute once authorization is complete.
The request object provided to authorize contains four important pieces of information:
request.path: a path representing the package authorization is being performed for.request.method: the type of request being authorized: GET for reads, PUT for publishes.request.body: the package.json contents (this is only sent for publishes).request.headers.authorization: contains the token issued by the authenticator.If an error occurs during authorization, cb should be executed with an error object:
return cb(Error('could not connect to LDAP'));
Otherwise cb should be executed with a true or false value, depending on whether or not authorization is successful:
return cb(null, true); // authorization was successful.
The information stored in request.body could potentially contain information that changes package permissions.
In the case of npme-auth-githb, we use the repository field in the package.json to determine who has write permissions for a package. After the initial package publication, the contents of request.body should not be trusted. Instead, you should use request.path to fetch the last version of the package that was published:
FooAuthorizer.prototype.loadPackageJson = function(request, cb) {
request.get(this.frontDoorHost + request.path.split('?')[0] + '?sharedFetchSecret=' + this.sharedFetchSecret, {
json: true
}, function(err, response, package) {
if (err) return cb(err);
else return cb(null, response, package);
});
};
npme-auth-[my-plugin-name].{
"args": {
"--authentication-method": "foo",
"--authorization-method": "foo",
"--session-handler": "redis"
}
}
cd /etc/npme; npm install npme-auth-foo.npme generate-scripts; npme restart.The example code used in this post is taken from the npme-auth-foo auth-strategy.
For a more thorough working example, check out the npme-auth-github auth strategy. This is default auth approach currently used by npm Enterprise.
That's all you need to know to start writing your own auth-plugins for npm Enterprise!
I can't wait to see what people come up with.
FAQs
An example auth-strategy for npm Enterprise.
We found that npme-auth-foo demonstrated a not healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Product
Create and share saved alert views with custom tabs on the org alerts page, making it easier for teams to return to consistent, named filter sets.

Product
Socket’s Rust and Cargo support is now generally available, providing dependency analysis and supply chain visibility for Rust projects.

Security News
Chrome 144 introduces the Temporal API, a modern approach to date and time handling designed to fix long-standing issues with JavaScript’s Date object.