Product
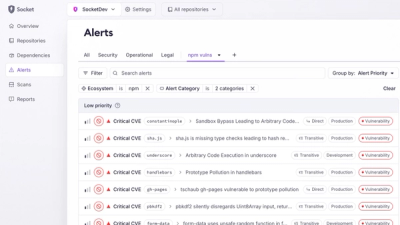
Introducing Custom Tabs for Org Alerts
Create and share saved alert views with custom tabs on the org alerts page, making it easier for teams to return to consistent, named filter sets.
passive-promise
Advanced tools
Promise that's resolvable from outside of executor context.
It comes with super light-weighted bundle with 0 dependencies.
This library exports the class named PassivePromise which works exactly like normal Promises, but can be resolved outside of promise executor context.
npm install passive-promise
or
yarn add passive-promise
The library supports pure ESM only and not exported as commonJS module syntax.
Just use exactly like normal promise, but returned promise (which is extended Promise class) also comes with the resolve() and reject() method in it, which you can use to force resolve or reject the promise from outside.
All the chain methods such as then, catch, finally works as expected, but remind that the both resolve, reject method of any chained PassivePromise instance will propagate to the root PassivePromise instance regardless of its depth.
import PassivePromise from 'passive-promise';
(async () => {
const foo = new PassivePromise((resolve, reject) => setTimeout(() => resolve(1), 1000));
console.log(await foo); // 1 after 1 sec
const bar = new PassivePromise((resolve, reject) => setTimeout(() => resolve(1), 1000));
bar.resolve(-1);
console.log(await bar); // -1 immedietly
const baz = new PassivePromise((resolve, reject) => setTimeout(() => resolve(1), 1000));
baz.reject(0) // Unhandled promise rejection.
})()
(async () => {
const foo = new PassivePromise(() => {})
.then((fulfilled) => console.log(fulfilled));
foo.resolve(1); // 1
const bar = new PassivePromise(() => {})
.then((fulfilled) => console.log(fulfilled))
.catch((errored) => console.log('Promise rejected!', errored));
bar.reject(-1); // Promise rejected! -1
const baz = new PassivePromise(() => {})
.then(
(fulfilled) => console.log(fulfilled),
(errored) => console.log('Promise rejected!', errored),
)
.finally(() => console.log('Finally.'));
baz.reject(-1) // Promise rejected! -1 Finally.
})()
import PassivePromise from 'passive-promise';
(async () => {
const chainedPromise = new PassivePromise(() => {})
.then((firstRes) => {
console.log('first.');
})
.then((secondRes) => {
console.log('second.');
})
.then((thirdRes) => {
console.log('third.');
});
chainedPromise.resolve(1);
await chainedPromise; // first. second. third.
const middleChain = new PassivePromise(() => {})
.then((firstRes) => {
console.log('first.');
})
.then((secondRes) => {
console.log('second.');
});
middleChain.then((thirdRes) => {
console.log('third.');
});
// Regardless of position of PassivePromise instance in the chained promises, they always resolve root promise in the chain.
middleChain.resolve(1);
await middleChain; // first. second. third.
// If you want to resolve the instance itself rather than root instance, use passiveResolve() and passiveReject() instead.
const anotherChain = new PassivePromise(() => {})
.then((firstRes) => {
console.log('first.');
})
.then((secondRes) => {
console.log('second.');
});
anotherChain.then((thirdRes) => {
console.log('third.');
});
// We want to directly resolve this promise rather than the whole promise chain here.
anotherChain.passiveResolve(1);
await anotherChain; // third.
})()
FAQs
Promise that's resolvable from outside of executor context.
We found that passive-promise demonstrated a not healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Product
Create and share saved alert views with custom tabs on the org alerts page, making it easier for teams to return to consistent, named filter sets.

Product
Socket’s Rust and Cargo support is now generally available, providing dependency analysis and supply chain visibility for Rust projects.

Security News
Chrome 144 introduces the Temporal API, a modern approach to date and time handling designed to fix long-standing issues with JavaScript’s Date object.