
Security News
curl Shuts Down Bug Bounty Program After Flood of AI Slop Reports
A surge of AI-generated vulnerability reports has pushed open source maintainers to rethink bug bounties and tighten security disclosure processes.
ts-patch-mongoose
Advanced tools
Patch history (audit log) & events plugin for mongoose
ts-patch-mongoose is a plugin for mongoose
I need to track changes of mongoose models and save them as patch history (audit log) in separate collection. Changes must also emit events that I can subscribe to and react in other parts of my application. I also want to omit some fields from patch history.
{
"node": "18.x || 20.x || 22.x",
"mongoose": ">=6.6.x || 7.x || 8.x",
}
npm install ts-patch-mongoose
pnpm add ts-patch-mongoose
yarn add ts-patch-mongoose
bun add ts-patch-mongoose
>=6.6.x || 7.x || 8.x to be installed as a peer dependency# For latest mongoose 6
npm install mongoose@6
pnpm add mongoose@6
yarn add mongoose@6
bun add mongoose@6
# For latest mongoose 7
npm install mongoose@7
pnpm add mongoose@7
yarn add mongoose@7
bun add mongoose@7
# For latest mongoose 8
npm install mongoose@8
pnpm add mongoose@8
yarn add mongoose@8
bun add mongoose@8
How to use it with express ts-express-tsx
Create your event constants events.ts
export const BOOK_CREATED = 'book-created'
export const BOOK_UPDATED = 'book-updated'
export const BOOK_DELETED = 'book-deleted'
Create your type Book in types.ts
import type { Types } from 'mongoose'
export type Book = {
title: string
description?: string
authorId: Types.ObjectId
createdAt?: Date
updatedAt?: Date
}
Setup your mongoose model Book.ts
import { Schema, model } from 'mongoose'
import type { HydratedDocument, Types } from 'mongoose'
import type { Book } from '../types'
import { patchHistoryPlugin, setPatchHistoryTTL } from 'ts-patch-mongoose'
import { BOOK_CREATED, BOOK_UPDATED, BOOK_DELETED } from '../constants/events'
// You can set patch history TTL in plain english or in milliseconds as you wish.
// This will determine how long you want to keep patch history.
// You don't need to use this global config in case you want to keep patch history forever.
// Execute this method after you connected to you database somewhere in your application.
setPatchHistoryTTL('1 month')
const BookSchema = new Schema<Book>({
name: {
title: String,
required: true
},
description: {
type: String,
},
authorId: {
type: Types.ObjectId,
required: true
}
}, { timestamps: true })
BookSchema.plugin(patchHistoryPlugin, {
// Provide your event constants to plugin
eventCreated: BOOK_CREATED,
eventUpdated: BOOK_UPDATED,
eventDeleted: BOOK_DELETED,
// You can omit some properties in case you don't want to save them to patch history
omit: ['__v', 'createdAt', 'updatedAt'],
// Addition options for patchHistoryPlugin plugin
// Everything bellow is optional and just shows you what you can do:
// Code bellow is abstract example, you can use any other way to get user, reason, metadata
// These three properties will be added to patch history document automatically and give you flexibility to track who, why and when made changes to your documents
getUser: async (doc: HydratedDocument<Book>) => {
// For example: get user from http context
// You should return an object, in case you want to save user to patch history
return httpContext.get('user') as Record<string, unknown>
},
// Reason of document (create/update/delete) like: 'Excel upload', 'Manual update', 'API call', etc.
getReason: async (doc: HydratedDocument<Book>) => {
// For example: get reason from http context, or any other place of your application
// You shout return a string, in case you want to save reason to patch history
return httpContext.get('reason') as string
},
// You can provide any information you want to save in along with patch history
getMetadata: async (doc: HydratedDocument<Book>) => {
// For example: get metadata from http context, or any other place of your application
// You should return an object, in case you want to save metadata to patch history
return httpContext.get('metadata') as Record<string, unknown>
},
// Do something before deleting documents
// This method will be executed before deleting document or documents and always returns a nonempty array of documents
preDelete: async (docs) => {
const bookIds = docs.map((doc) => doc._id)
await SomeOtherModel.deleteMany({ bookId: { $in: bookIds } })
},
// In case you just want to track changes in your models using events below.
// And don't want to save changes to patch history collection
patchHistoryDisabled: true,
})
const Book = model('Book', BookSchema)
export default Book
You can subscribe to events using patchEventEmitter anywhere in your application handlers/BookHandler.ts
import { patchEventEmitter } from 'ts-patch-mongoose'
import { BOOK_CREATED, BOOK_UPDATED, BOOK_DELETED } from '../constants/events'
patchEventEmitter.on(BOOK_CREATED, ({ doc }) => {
try {
console.log('Event - book created', doc)
// Do something with doc here
} catch (error) {
console.error(error)
}
})
patchEventEmitter.on(BOOK_UPDATED, ({ doc, oldDoc, patch }) => {
try {
console.log('Event - book updated', doc, oldDoc, patch)
// Do something with doc, oldDoc and patch here
} catch (error) {
console.error(error)
}
})
patchEventEmitter.on(BOOK_DELETED, ({ oldDoc }) => {
try {
console.log('Event - book deleted', oldDoc)
// Do something with doc here
} catch (error) {
console.error(error)
}
})
FAQs
Patch history & events for mongoose models
The npm package ts-patch-mongoose receives a total of 354 weekly downloads. As such, ts-patch-mongoose popularity was classified as not popular.
We found that ts-patch-mongoose demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security News
A surge of AI-generated vulnerability reports has pushed open source maintainers to rethink bug bounties and tighten security disclosure processes.
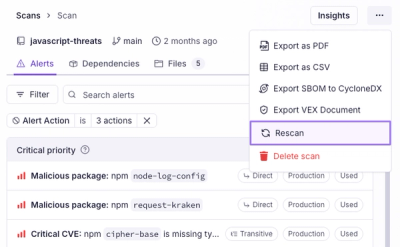
Product
Scan results now load faster and remain consistent over time, with stable URLs and on-demand rescans for fresh security data.
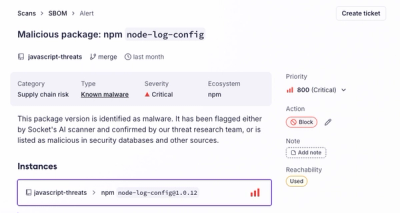
Product
Socket's new Alert Details page is designed to surface more context, with a clearer layout, reachability dependency chains, and structured review.