
Security News
ESLint Adds Official Support for Linting HTML
ESLint now supports HTML linting with 48 new rules, expanding its language plugin system to cover more of the modern web development stack.
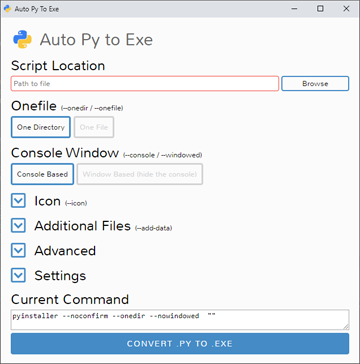
A .py to .exe converter using a simple graphical interface and PyInstaller in Python.
阅读中文版的 README ,点击 这里
Suomenkieliset käyttöohjeet löydät täältä
Türkçe Talimatları burada bulabilirsiniz.
دستور العمل های فارسی
한국어로 된 설명은 여기를 참고하세요.
Български README тук
Беларускамоўны README тут
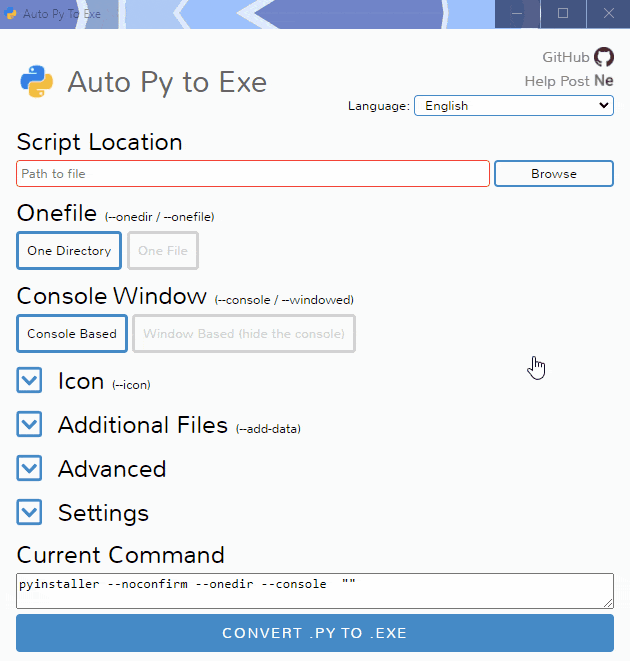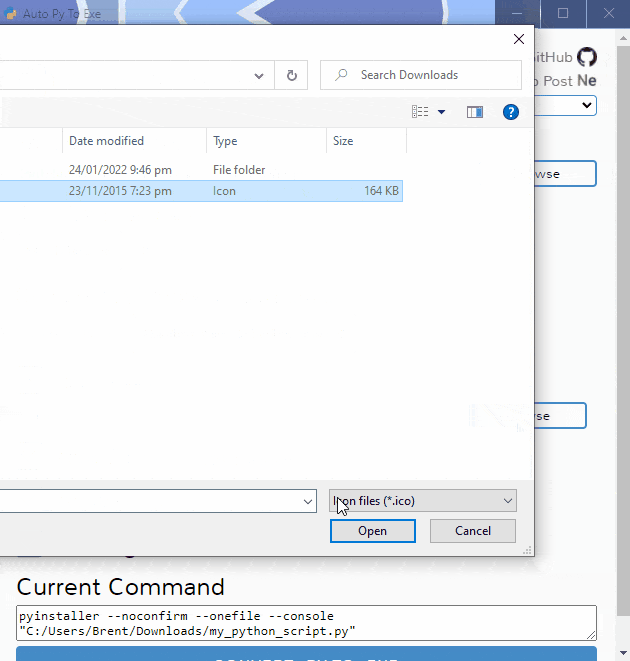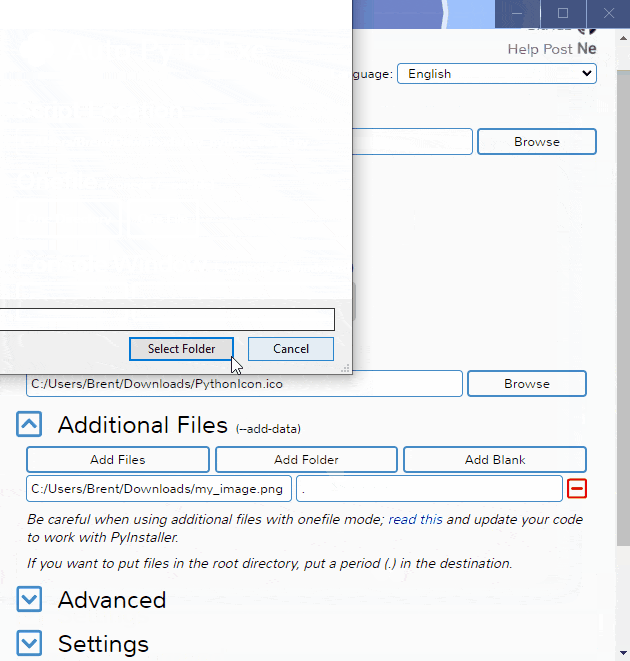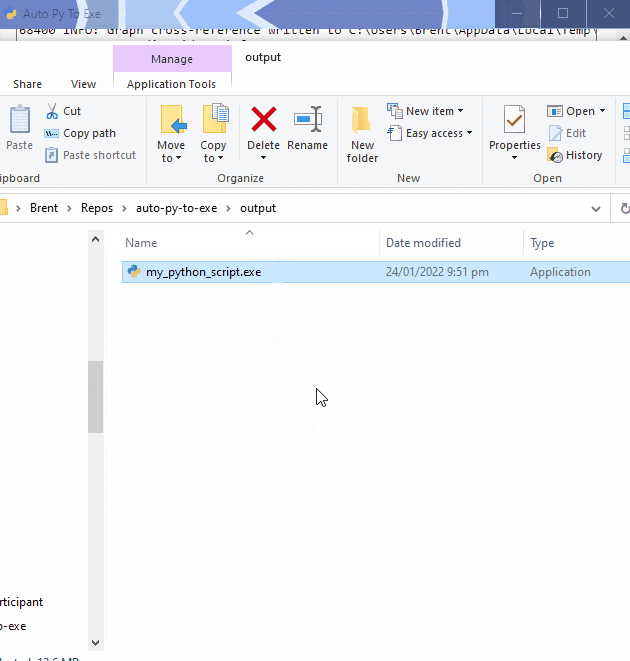
To have the interface displayed in the images, you will need Chrome. If Chrome is not installed or --default-browser is passed, the default browser will be used.
You can install this project using PyPI:
$ pip install auto-py-to-exe
Then to run it, execute the following in the terminal:
$ auto-py-to-exe
If you have more than one version of Python installed, you can use
python -m auto_py_to_exeinstead ofauto-py-to-exe.
$ git clone https://github.com/brentvollebregt/auto-py-to-exe.git
$ cd auto-py-to-exe
$ python setup.py install
Then to run it, execute the following in the terminal:
$ auto-py-to-exe
You can run this project locally by following these steps:
python -m pip install -r requirements.txtpython -m auto_py_to_exe to run the applicationEasy.
Use the help flag to get the usage: auto-py-to-exe --help
| Argument | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| filename | positional/optional | Pre-fill the "Script Location" field in the UI. |
| -db, --default-browser | optional | Open the UI using the default browser (which may be Chrome). Will not try to find Chrome. |
| -nu, --no-ui | optional | Don't try to open the UI in a browser and simply print out the address where the application can be accessed. |
| -c [CONFIG], --config [CONFIG] | optional | Provide a configuration file (JSON) to pre-fill the UI. These can be generated in the settings tab. |
| -o [PATH], --output-dir [PATH] | optional | Set the default output directory. This can still be changed in the UI. |
| -bdo [FOLDER_PATH], --build-directory-override [FOLDER_PATH] | optional | Override the default build directory. Useful if you need to whitelist a folder to stop your antivirus from removing files. |
| -lang [LANGUAGE_CODE], --language [LANGUAGE_CODE] | optional | Hint the UI what language it should default to when opening. Language codes can be found in the table under "Translations" below. |
Instead of inserting the same data into the UI over and over again, you can export the current state by going to the "Configuration" section within the settings tab and exporting the config to a JSON file. This can then be imported into the UI again to re-populate all fields.
This JSON config export action does not save the output directory automatically as moving hosts could mean different directory structures. If you want to have the output directory in the JSON config, add the directory under nonPyinstallerOptions.outputDirectory in the JSON file (will need to create a new key).
The examples/ directory offers some examples of how to write your scripts and package them with auto-py-to-exe.
If you need something visual to help you get started, I made a video for the original release of this project; some things may be different but the same concepts still apply.
Check out CONTRIBUTING.md to see guidelines on how to contribute. This outlines what to do if you have a new feature, a change, translation update or have found an issue with auto-py-to-exe.
If you're having issues with the packaged executable or using this tool in general, I recommend you read my blog post on common issues when using auto-py-to-exe. This post covers things you should know about packaging Python scripts and fixes for things that commonly go wrong.
If you believe you've found an issue with this tool, please follow the "Reporting an Issue" section in CONTRIBUTING.md.
| Language | Translator | Translated |
|---|---|---|
| Arabic (العربية) | Tayeb-Ali | UI |
| Belarusian (Беларуская) | Zmicier21 | UI and README |
| Brazilian Portuguese (Português Brasileiro) | marleyas, reneoliveirajr | UI |
| Bulgarian (Български) | kbkozlev | UI and README |
| Chinese Simplified (简体中文) | jiangzhe11 | UI and README |
| Chinese Traditional (繁體中文) | startgo | UI |
| Czech (Čeština) | Matto58 | UI |
| Dutch (Nederlands) | barremans | UI |
| English | - | UI and README |
| Finnish (Suomen kieli) | ZapX5 | UI and README |
| French (Français) | flaviedesp | UI |
| German (Deutsch) | hebens, ackhh | UI |
| Greek (Ελληνικά) | sofronas | UI |
| Hebrew (עברית) | ronbentata | UI and README |
| Hindi (हिन्दी) | triach-rold | UI and README |
| Hungarian (Magyar) | synexdev01 | UI |
| Indonesian (Bahasa Indonesia) | MarvinZhong | UI |
| Italian (Italiano) | itsEmax64 | UI |
| Japanese (日本語) | NattyanTV | UI |
| Korean (한국어) | jhk1090 | UI and README |
| Persian (فارسی) | DrunkLeen, Ar.dst | UI and README |
| Polish (Polski) | Akuczaku | UI |
| Russian (Русский) | Oleg | UI |
| Serbian | rina | UI |
| Slovak (Slovenčina) | mostypc123 | UI |
| Spanish (Español) | enriiquee | UI |
| Spanish Latam (Español Latam) | Matyrela | UI |
| Thai (ภาษาไทย) | teerut26 | UI (partial) |
| Turkish (Türkçe) | mcagriaksoy | UI and README |
| Ukrainian (Українська) | AndrejGorodnij | UI |
| Vietnamese (Tiếng Việt) | 7777Hecker | UI |
Want to add a translation for another language? follow the "Add or Update a Translation" section in CONTRIBUTING.md.
As of PyInstaller v4.0 released on Aug 9 2020, Python 2.7 is no longer supported; although you can still use this tool with Python 2.7 by installing an older version of PyInstaller. PyInstaller v3.6 was the last version that supported Python 2.7; to install this, first uninstall any existing versions of PyInstaller and then execute python -m pip install pyinstaller==3.6.
Tests are located in tests/ and are run using pytest:
$ pip install pytest
$ pip install -e .
$ pytest
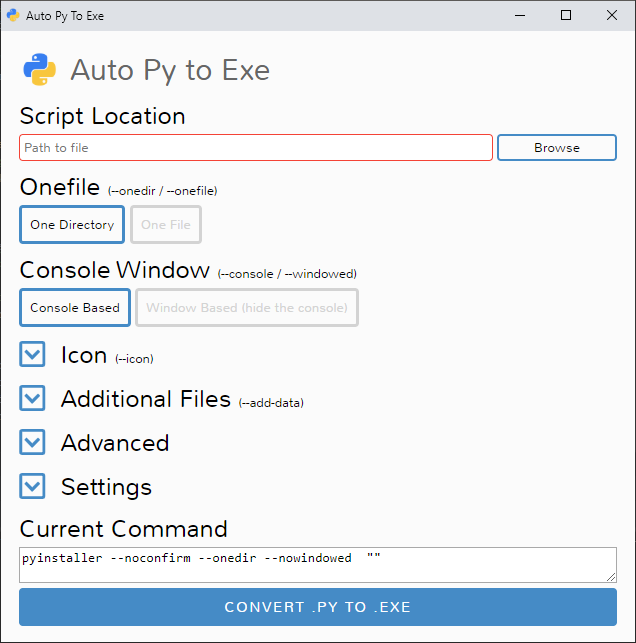 | 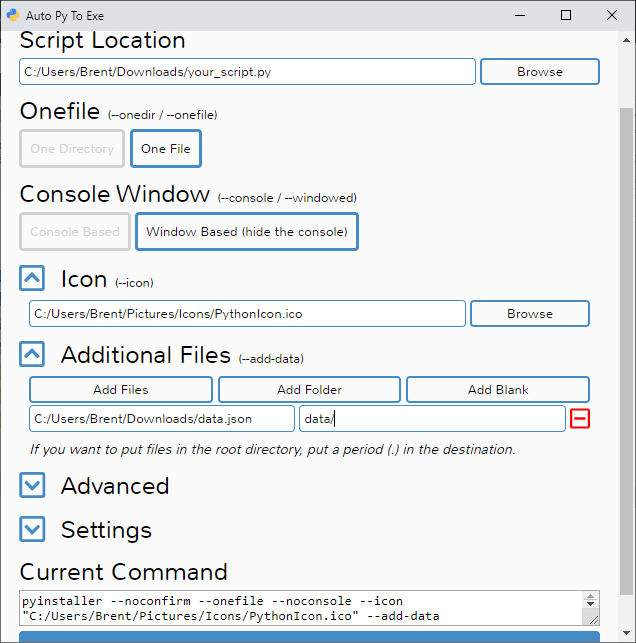 |
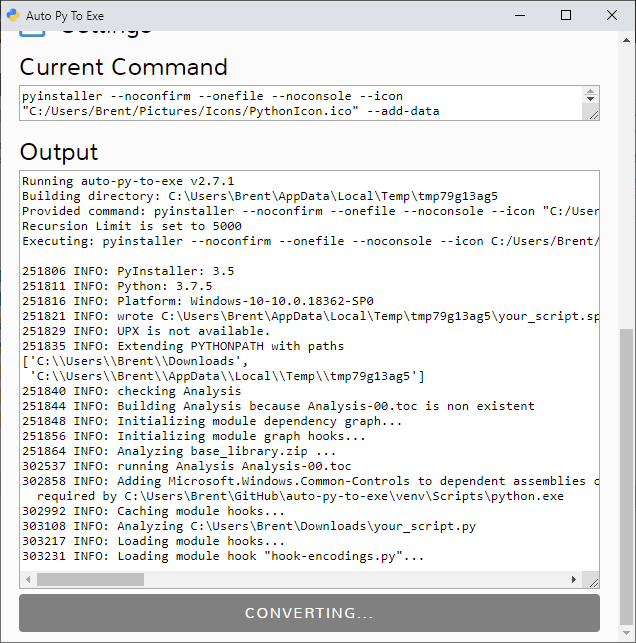 | 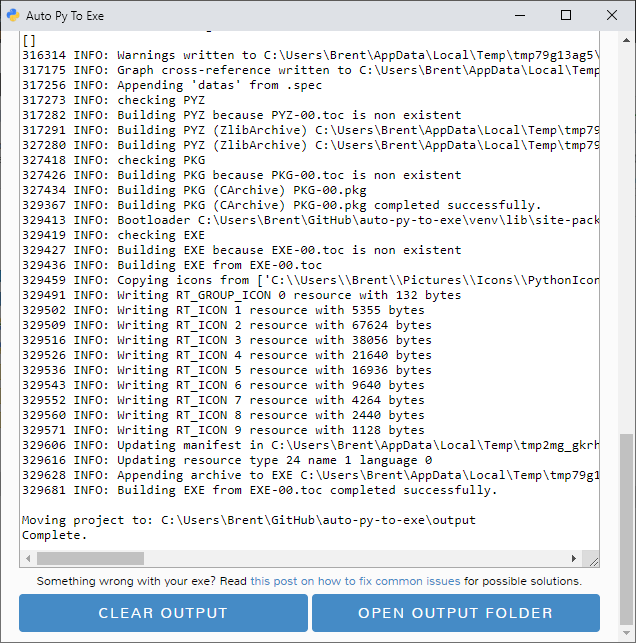 |
FAQs
Converts .py to .exe using a simple graphical interface.
We found that auto-py-to-exe demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security News
ESLint now supports HTML linting with 48 new rules, expanding its language plugin system to cover more of the modern web development stack.

Security News
CISA is discontinuing official RSS support for KEV and cybersecurity alerts, shifting updates to email and social media, disrupting automation workflows.

Security News
The MCP community is launching an official registry to standardize AI tool discovery and let agents dynamically find and install MCP servers.