
Research
2025 Report: Destructive Malware in Open Source Packages
Destructive malware is rising across open source registries, using delays and kill switches to wipe code, break builds, and disrupt CI/CD.
bisslog-schema
Advanced tools
It is a lightweight framework to organize and document the key elements of a distributed system, focusing on its use cases and service design. It structures the metadata without exposing any underlying technical or implementation-specific details.
bisslog-schema-py is a lightweight framework to organize and document the key elements of a distributed system, focusing on its use cases and service design.
It structures the metadata without exposing any underlying technical or implementation-specific details.
The goal is to design and document a distributed system from a service-centric perspective, emphasizing business use cases and their criticality, while remaining technology-agnostic.
You can install bisslog-schema using pip:
pip install bisslog_schema
For YAML support, you may also need to install PyYAML:
pip install bisslog_schema[yaml]
or
pip install pyyaml
Here is an example of how to define a service and its use cases using YAML:
---
name: "webhook receiver"
type: "microservice"
description: "Receives events from external platforms and converts them into company events for internal processing"
service_type: "functional"
team: "code-infrastructure"
tags:
service: "webhook-receptor"
use_cases:
addEventAdmitted:
name: "add event type admitted to platform"
description: "Updates adding event type admitted to platform if not exists, otherwise updates"
triggers:
- type: "http"
options:
route: "/webhook/event-type-admitted/{uid}"
apigw: "internal"
authenticator: "employee"
method: "post"
mapper:
path_query.uid: uid
body: data
headers.user: creator
external_interactions:
- keyname: "marketing_division"
type_interaction: "database"
operation: "get_last_sales_from_client"
# More use cases...
Note: The criticality field can use either named levels (e.g., "high") or direct numeric values (e.g., 90).
Validate metadata files through the command line, ensuring they conform to the expected schema.
bisslog_schema analyze_metadata service.yaml --format-file yaml
--path: Specify the path to the metadata file. If not provided, it will search in the default locations.--format-file: Specify the format of the metadata file. Supported formats are yaml and json. Default is yaml.--encoding: File encoding (default: utf-8)--min-warnings: Minimum warning percentage (optional)You can load service definitions from YAML or JSON files using the read_service_metadata function.
It automatically searches for metadata files in predefined locations if a path is not provided.
You can specify the path to the metadata file as an argument or as an environment variable in SERVICE_METADATA_PATH.
from bisslog_schema import read_service_metadata
service_info = read_service_metadata()
print(service_info.name)
for use_case_keyname, use_case in service_info.use_cases.items():
print(f"{use_case.keyname}: {use_case.name}")
The ServiceInfo class models a service in the system.
Each service can define:
name: Service namedescription: Brief explanation of the service's responsibilitytype: Logical category (e.g., "microservice", "library")service_type: Service type (e.g., "functional", "technical")team: Responsible teamtags: Arbitrary metadata tags for classificationuse_cases: List of UseCaseInfo objects representing the service's use casesService metadata can be loaded dynamically from external YAML or JSON files.
Service Definition Example:
The following example illustrates a service definition with its use cases and external interactions:
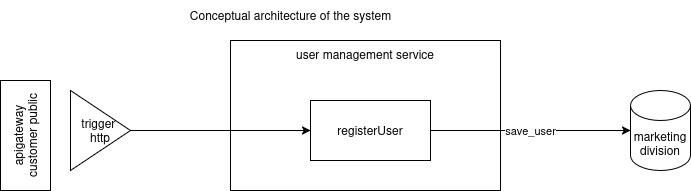
This is the YAML representation of the service definition:
---
name: "user management"
type: "microservice"
description: "Handles creation, update, and retrieval of user accounts in the system"
service_type: "functional"
team: "identity-platform"
tags:
service: "user-management"
use_cases:
registerUser:
name: "register user"
description: "Registers or creates a new user in the system"
actor: "end user"
criticality: "high"
type: "create functional data"
triggers:
- type: "http"
options:
route: "/user"
method: "post"
apigw: "customer-public"
mapper:
body: user_data
external_interactions:
- keyname: users_division
type_interaction: "database"
operation: "create_user"
tags:
accessibility: "public"
The UseCaseInfo class represents a use case belonging to a service, with the following fields:
keyname: Unique identifier for the use case.name: Human-readable name.description: A detailed description of what the use case does.actor: The entity (user, system, platform) that initiates the use case.type: Logical operation type (e.g., "create", "read", "update", "delete").criticality: Business importance of the use case, represented as a CriticalityEnum.tags: Metadata tags for further classification.triggers: List of TriggerInfo entries defining how the use case is triggered.external_interactions: List of ExternalInteraction Represents any external systems or APIs this use case depends on or interacts with.Triggers define how a use case is initiated.
Available trigger types (enumerated by TriggerEnum) include:
HTTP: HTTP request initiation.WebSocket: WebSocket-based interaction.Consumer: Event-driven trigger (e.g., queues).Schedule: Time-based scheduled triggers.Each trigger may have associated options (e.g., route, method, authenticator).
The ExternalInteraction class represents an external interaction in the system, such as database access or external service calls.
keyname: Unique identifier for the interaction. For example, marketing_division.type_interaction: String representing the type of interaction (optional). For example, database.operation: Specific operation or action being performed (optional). For example, get_last_sales_from_client.type_interaction_standard: Standardized type of interaction resolved from type_interaction using aliases (optional).Example of External Interaction:
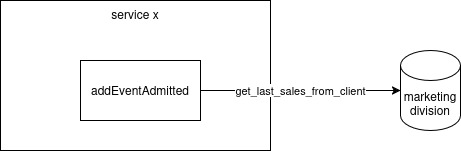
use_cases:
addEventAdmitted:
external_interactions:
- keyname: "marketing_division"
type_interaction: "database"
operation: "get_last_sales_from_client"
CriticalityEnum provides a standardized set of criticality levels for use cases:
| Level | Value |
|---|---|
| NONE | 0 |
| VERY_LOW | 10 |
| LOW | 20 |
| MEDIUM | 50 |
| HIGH | 70 |
| VERY_HIGH | 90 |
| CRITICAL | 100 |
This scale helps prioritize use cases based on their business or operational impact.
Technology-agnostic: Focus on service and use case modeling, independent of the underlying implementation.
Organized metadata: Centralizes your distributed system documentation.
Extensible: Easily expandable with new fields and trigger types.
Integration-friendly: Can be used for CI/CD validation or automated documentation generation.
To Run test with coverage
coverage run --source=bisslog_schema -m pytest tests/
To generate report
coverage html && open htmlcov/index.html
This project is licensed under the MIT License. See the LICENSE file for details.
FAQs
It is a lightweight framework to organize and document the key elements of a distributed system, focusing on its use cases and service design. It structures the metadata without exposing any underlying technical or implementation-specific details.
We found that bisslog-schema demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Research
Destructive malware is rising across open source registries, using delays and kill switches to wipe code, break builds, and disrupt CI/CD.

Security News
Socket CTO Ahmad Nassri shares practical AI coding techniques, tools, and team workflows, plus what still feels noisy and why shipping remains human-led.

Research
/Security News
A five-month operation turned 27 npm packages into durable hosting for browser-run lures that mimic document-sharing portals and Microsoft sign-in, targeting 25 organizations across manufacturing, industrial automation, plastics, and healthcare for credential theft.