
Product
Introducing Socket Firewall Enterprise: Flexible, Configurable Protection for Modern Package Ecosystems
Socket Firewall Enterprise is now available with flexible deployment, configurable policies, and expanded language support.
cemirutils
Advanced tools
Pythona yeni başlayanlar ve zaten kullananların yaptıkları işlerde vakit kazanmasını sağlayacak fonksiyon, metod, kütüphane ve dekoratörler...
cemirutils is a Python utility library designed to provide a range of commonly used functions, methods, libraries, and decorators to streamline development in Linux and Python environments.
pip install -U cemirutils
CemirUtilsLoopTimerloop: Decorator to measure loop execution time.check_loop: Context manager for loop timing.CemirUtilsConditionscondition_collector: Decorator to log the lines and conditions met during function execution.CemirUtilsFunctionNotificationnotify: Sends an email notification after the function execution.CemirUtilsHTTPget_methods: Returns available HTTP methods.get: Executes a GET request.post: Executes a POST request.put: Executes a PUT request.delete: Executes a DELETE request.patch: Executes a PATCH request.CemirUtilsDecoratorstimeit: Measures execution time.log: Logs function calls and results.retry: Retries a function upon failure.cache: Caches function results.cache_with_expiry: Caches results with an expiry time.deprecate: Marks a function as deprecated.debug: Logs detailed function calls.before_after: Executes actions before and after function calls.rate_limit: Limits function calls over a period.webhook_request: Sends a webhook request on function call.CemirUtilsEmailsend_email: Sends an email with optional attachments.IPGeolocationcreate_sqlite_db: Creates SQLite DB from CSV.get_ip_location: Retrieves IP location data.CemirPostgreSQLpsql_create_table: Creates a PostgreSQL table.psql_insert: Inserts data into a table.insert: Inserts data.read: Reads data from a table.update: Updates table data.delete: Deletes data from a table.CemirUtilsMethods for File Operations:
linux_ls: Lists files in a directory.linux_touch: Creates a new file.linux_gzip: Compresses a file.linux_cat: Displays file content.linux_cp: Copies a file.linux_mv: Moves a file.linux_rm: Deletes a file.linux_mkdir: Creates a new directory.linux_rmdir: Removes an empty directory.linux_cut: Cuts fields from a file.linux_find: Searches for files.linux_grep: Searches text in a file.Methods for List Operations:
list_head: Returns the first N elements.list_tail: Returns the last N elements.list_main: Returns the middle elements.list_unique_values: Returns unique values.list_sort_asc: Sorts the list in ascending order.list_sort_desc: Sorts the list in descending order.list_filter_greater_than: Filters values greater than a given number.list_filter_less_than: Filters values less than a given number.list_sum_values: Sums the values.list_average: Calculates the average.list_flatten: Flattens a nested list.list_multiply_by_scalar: Multiplies each element by a scalar.list_get_max_value: Returns the maximum value.list_get_frequency: Returns the frequency of a value.Methods for Dictionary Operations:
dict_get_keys: Returns the keys.dict_filter_by_key: Filters by key.dict_merge: Merges dictionaries.Methods for Time Operations:
time_days_between_dates: Returns days between dates.time_hours_minutes_seconds_between_times: Returns hours, minutes, and seconds between times.time_until_date: Returns time until a date.time_add_days_and_format: Adds days to a date and formats it.time_is_weekend: Checks if a date is a weekend.time_is_leap_year: Checks if a year is a leap year.time_days_in_month: Returns days in a month.time_next_weekday: Returns the next weekday.time_since: Returns the time since a date.time_business_days_between_dates: Returns business days between dates.This documentation provides an overview of the CemirUtils classes and their respective functions, offering a range of utilities for file operations, HTTP requests, email handling, PostgreSQL operations, and more.
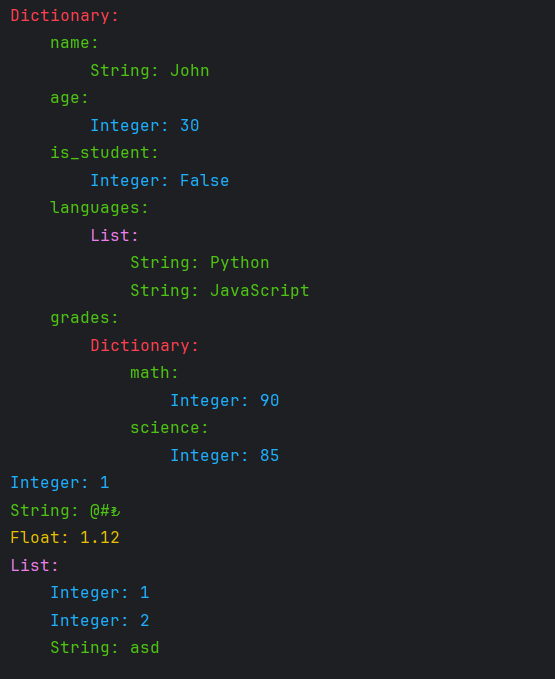
from cemirutils import cprint
data = {
"name": "John",
"age": 30,
"is_student": False,
"languages": ["Python", "JavaScript"],
"grades": {
"math": 90,
"science": 85
}
}
cprint(data)
cprint(1)
cprint("@#₺")
cprint(1.12)
cprint([1,2,"asd"])
from cemirutils import crange
# Kullanım örneği / Example usage
for i in crange(1, '99-105', 'c,e,m,i,r'):
print(i)
# Output:
# 1
# 99
# 100
# 101
# 102
# 103
# 104
# 105
# c
# e
# m
# i
# r
import time
from cemirutils import CemirUtilsLoopTimer
timer = CemirUtilsLoopTimer()
@timer.loop
def example_function():
with timer.check_loop():
for _ in range(10):
time.sleep(0.1)
with timer.check_loop():
count = 0
while count < 3:
count += 1
time.sleep(count)
with timer.check_loop():
for _ in range(5):
time.sleep(0.1)
example_function()
# Output:
# String: ------------------
# String: Loop 1 (For at line 4): 1.09 seconds
# String: Loop 2 (While at line 9): 6.04 seconds
# String: Loop 3 (For at line 15): 0.54 seconds
# String: Total execution time of 'example_function': 7.68 seconds
# String: ------------------
from cemirutils import CemirUtilsConditions
cemir_utils = CemirUtilsConditions()
@cemir_utils.condition_collector
def test_function(x, y, z):
if x > 15:
# print("x is greater than 15")
pass
elif x < 15 and y > 10:
# print("x is less than 15 and y is greater than 10")
pass
else:
# print("x is not within the expected range or y is not greater than 10")
pass
if y == 20:
# print("y is exactly 20")
pass
elif y >= 15:
# print("y is greater than or equal to 15")
pass
else:
# print("y is less than 15")
pass
if z == "hello":
# print("z is 'hello'")
pass
elif z == "world":
# print("z is 'world'")
pass
else:
# print("z is something else")
pass
if x == 10:
# print("x is 10")
pass
elif x >= 10:
# print("x is greater than or equal to 10")
pass
else:
# print("x is less than 10")
pass
if y % 2 == 0:
# print("y is even")
pass
else:
# print("y is odd")
pass
if z.startswith("hq"):
# print("z starts with 'h'")
pass
elif z.startswith("w"):
# print("z starts with 'w'")
pass
else:
# print("z starts with another letter")
pass
test_function(10, 20, "hello")
# Output:
# x is less than 15 and y is greater than 10
# y is exactly 20
# z is 'hello'
# x is 10
# y is even
# z starts with another letter
# Line 10: elif x < 15 and y > 10:
# Line 15: if y == 20:
# Line 22: if z == "hello":
# Line 29: if x == 10:
# Line 36: if y % 2 == 0:
# Line 45: else:
from cemirutils import CemirUtilsFunctionNotification
utils = CemirUtilsFunctionNotification(
smtp_server="mail.makdos.com",
smtp_port=587,
smtp_user="notify@makdos.com",
smtp_password="nope"
)
@utils.notify(to_email="musluyuksektepe@gmail.com", subject="Function Called")
def important_action():
return {"status": "Important action completed."}
# SMTP server must be working
important_action()
from cemirutils import CemirUtilsHTTP
http = CemirUtilsHTTP()
# Show methods name
print(http.get_methods())
get_response = http.get("https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/1", verify_ssl=True)
print("GET Response:", get_response)
# POST
post_data = {"title": "foo", "body": "bar", "userId": 1}
post_response = http.post("https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts", data=post_data, verify_ssl=True)
print("POST Response:", post_response)
# PUT
put_data = {"title": "foo", "body": "bar", "userId": 1}
put_response = http.put("https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/1", data=put_data, verify_ssl=True)
print("PUT Response:", put_response)
# DELETE
delete_response = http.delete("https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/1", verify_ssl=True)
print("DELETE Response:", delete_response)
# PATCH
patch_data = {"title": "foo"}
patch_response = http.patch("https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/1", data=patch_data, verify_ssl=True)
print("PATCH Response:", patch_response)
import time
from datetime import datetime
from cemirutils import CemirUtilsDecorators
@CemirUtilsDecorators.timeit
@CemirUtilsDecorators.log
def timeit_log(x, y):
time.sleep(1)
return x + y
timeit_log(3, 5)
# Output:
# Calling function 'timeit_log' with arguments (3, 5) and keyword arguments {}
# Function 'timeit_log' returned 8
# Function 'timeit_log' took 1.0018 seconds
@CemirUtilsDecorators.retry(retries=5, delay=2)
def may_fail_function():
if time.time() % 2 < 1:
raise ValueError("Random failure!")
return "Success"
may_fail_function()
# Output:
# Attempt 1 failed: Random failure!
# Attempt 2 failed: Random failure!
# Attempt 3 failed: Random failure!
# Attempt 4 failed: Random failure!
# Attempt 5 failed: Random failure!
# Function 'may_fail_function' failed after 5 attempts
@CemirUtilsDecorators.cache
def slow_function(x):
time.sleep(2) # Performing a time-consuming operation.
return x * x
print(slow_function(4))
print(slow_function(4)) # This time, result will be fetched from cache
# Output:
# 16
# Returning cached result for slow_function with args (4,) and kwargs {}
# 16
@CemirUtilsDecorators.cache_with_expiry(expiry_time=5)
def cached_function(x):
time.sleep(3) # Performing a time-consuming operation as an example.
return x * x
print(datetime.now(), cached_function(4))
time.sleep(1)
print(datetime.now(), cached_function(4)) # Time has expired, so it will be recalculated
# Output:
# 2024-06-17 13:02:29.906200 16
# Returning cached result for cached_function with args (4,) and kwargs {}
# 2024-06-17 13:02:33.920453 16
@CemirUtilsDecorators.deprecate("Please use new_function instead.")
def old_function(x, y):
return x + y
old_function(3, 5)
# Output:
# WARNING: old_function is deprecated. Please use new_function instead.
@CemirUtilsDecorators.debug
def add_numbers(a, b):
return a + b
add_numbers(3, 5)
# Output:
# DEBUG: Calling function 'add_numbers' with arguments (3, 5) and keyword arguments {}
# DEBUG: Function 'add_numbers' returned 8
@CemirUtilsDecorators.before_after
def test_beforeafter(data):
print(f"1 Performing database operation with data: {data}")
return "2 Success"
print(test_beforeafter("Muslu Y."))
# Output:
# Starting transaction
# 1 Performing database operation with data: Muslu Y.
# Committing transaction
# 2 Success
# max_call = Specifies how many times a function can be called within a certain period of time.
# period = For example, when set to period=10, the function can be called 5 times within a 10-second period.
@CemirUtilsDecorators.rate_limit(max_calls=5, period=10)
def limited_function():
return {"status": "ok"}
# Test the rate-limited function
try:
print(datetime.now(), limited_function())
print(datetime.now(), limited_function())
print(datetime.now(), limited_function())
time.sleep(4)
print(datetime.now(), limited_function()) # This call should succeed
print(datetime.now(), limited_function())
print(datetime.now(), limited_function())
print(datetime.now(), limited_function()) # This call should raise a rate limit error
except RuntimeError as e:
print(e)
#Output:
# 2024-06-17 13:19:42.270686 {'status': 'ok'}
# 2024-06-17 13:19:42.270686 {'status': 'ok'}
# 2024-06-17 13:19:42.270686 {'status': 'ok'}
# 2024-06-17 13:19:46.281105 {'status': 'ok'}
# 2024-06-17 13:19:46.281105 {'status': 'ok'}
# Rate limit exceeded
utils = CemirUtilsDecorators()
@utils.webhook_request(url="https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts", headers={"x-sent-by": "CemirUtils", "user-agent": "CemirUtils"})
def send_webhook():
return {'message': 'Webhook request'}
print(send_webhook())
@CemirUtilsDecorators.webhook_request(url="https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts", headers={"x-sent-by": "CemirUtils", "user-agent": "CemirUtils"})
def send_webhook():
return {'message': 'Webhook request'}
print(send_webhook())
from cemirutils import CemirUtilsEmail
# Kullanım
email_util = CemirUtilsEmail(
smtp_host="smtp.gmail.com",
smtp_port=465,
smtp_user="musluyuksektepe@gmail.com",
smtp_pass="nopass",
smtp_ssl=True
)
email_util.send_email(
to_email="cememir2017@gmail.com",
subject="Test Subject",
body_html="<html><body><h1>This is a test email in HTML.</h1></body></html>",
attachments=["2024.pdf", "not_found.log"],
zip_files=False # ZIP if files are exist
)
from cemirutils import IPGeolocation
ip_geolocator = IPGeolocation()
## CSV -> SQLite
# ip_geolocator.create_sqlite_db()
#
ip_address = "121.0.11.0"
location_info = ip_geolocator.get_ip_location(ip_address, force_download=False)
print(location_info)
from datetime import datetime
from cemirutils import CemirPostgreSQL
utils = CemirPostgreSQL(dbname='test_db3', dbhost='127.0.0.1', dbuser='postgres', dbpassword='', dbport=5435, dbcreate_db_if_not_exists=True)
# print(utils.psql_create_table('test_table_flat', 'id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY, name VARCHAR(100), surname VARCHAR(100)'))
# print(utils.psql_create_table('test_table_json', 'id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY, dates DATE, content JSONB'))
# print(utils.psql_insert('test_table_flat', ('id', 'name', 'surname'), (3, 'Muslu', 'Yüksektepe'), get_id=True))
print(utils.insert('test_table_json', ('id', 'dates', 'content'), (2, datetime.now(), {"age": 40, "city": "İzmir"}), get_id=True))
print(utils.read('test_table_json'))
print(utils.update('test_table_json', {'dates': datetime.now(), 'content': '{"age": 40, "city": "Sivas"}'}, 'id = 1', get_id=True))
print(utils.read('test_table_json'))
asd = utils.read(table_name='test_table_json', columns="content", condition="content ->> 'age' = '40'")
# asd = utils.read(table_name='test_table_json', columns="content", condition="content ->> 'age' like '%4%'")
print(type(asd), asd)
# asdd = Dict2Dot(asd[0])
# print(type(asd), asdd.id)
print(utils.delete('test_table_json', 'id = 1'))
print(utils.read('test_table_json'))
from cemirutils import CemirUtils
utils = CemirUtils()
# Sample usage of file operations
files = utils.linux_ls(path=".")
print(files)
utils.linux_touch(file_name="new_file.txt")
utils.linux_gzip(file_name="file.txt")
content = utils.linux_cat(file_name="file.txt")
print(content)
utils.linux_cp(src="file.txt", dest="copy_file.txt")
utils.linux_mv(src="file.txt", dest="moved_file.txt")
utils.linux_rm(file_name="file.txt")
utils.linux_mkdir(dir_name="new_dir")
utils.linux_rmdir(dir_name="new_dir")
utils.linux_cut(file_name="file.txt", delimiter=" ", fields=[1, 2])
utils.linux_find(path=".", name="*.txt")
utils.linux_grep(file_name="file.txt", pattern="search_text")
from cemirutils import CemirUtils
data_list = [3, 1, 4, 1, 5, 9, 2, 6, 5, 3, 5]
cem = CemirUtils(data_list)
print(data_list)
print(cem.list_head(2)) # Prints the first 2 elements of the list.
print(cem.list_tail(4)) # Prints the last 4 elements of the list.
print(cem.list_main()) # Prints the middle elements of the list.
print(cem.list_unique_values()) # Prints the unique elements of the list.
print(cem.list_sort_asc()) # Prints the list in ascending order.
print(cem.list_sort_desc()) # Prints the list in descending order.
print(cem.list_filter_greater_than(5)) # Prints values greater than 5: [9, 6]
print(cem.list_filter_less_than(4)) # Prints values less than 4: [3, 1, 1, 2, 3]
print(cem.list_sum_values()) # Prints the sum of values: 44
print(cem.list_average()) # Prints the average of values: 4.0
data = [{'a': 1}, {'b': 2}, {'a': 3}, {"name": "sivas", "age": 10}]
cemd = CemirUtils(data)
print(cemd.dict_get_keys())
print(cemd.dict_filter_by_key('name'))
print(cemd.dict_merge({'a': 1}, {'b': 2}))
from cemirutils import CemirUtils
utils = CemirUtils(None)
print(utils.time_days_between_dates("2024-05-01", "2024-05-25")) # 24
print(utils.time_hours_minutes_seconds_between_times("08:30:00", "15:45:30")) # (7, 15, 30)
print(utils.time_until_date("2024-05-27 23:59:59")) # Remaining days, hours, minutes, seconds
print(utils.time_add_days_and_format("2024-05-01", 30)) # "2024-05-31 (Friday)"
print(utils.time_is_weekend("2024-05-25")) # True
print(utils.time_is_leap_year(2024)) # True
print(utils.time_days_in_month(2024, 2)) # 29
print(utils.time_next_weekday("2024-05-25", 0)) # 2024-05-27
print(utils.time_since("2022-01-01 00:00:00")) # (2, 4, 24, 14, 30, 15)
print(utils.time_business_days_between_dates("2024-05-01", "2024-05-25")) # 17
CemirUtils library. Each function is shown with a clear, working example to illustrate its usage.FAQs
Pythona yeni başlayanlar ve zaten kullananların yaptıkları işlerde vakit kazanmasını sağlayacak fonksiyon, metod, kütüphane ve dekoratörler...
We found that cemirutils demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 3 open source maintainers collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Product
Socket Firewall Enterprise is now available with flexible deployment, configurable policies, and expanded language support.

Security News
Open source dashboard CNAPulse tracks CVE Numbering Authorities’ publishing activity, highlighting trends and transparency across the CVE ecosystem.

Product
Detect malware, unsafe data flows, and license issues in GitHub Actions with Socket’s new workflow scanning support.