ciscoconfparse2











Introduction: What is ciscoconfparse2?
Summary
ciscoconfparse2 is similar to an advanced grep and diff that
handles multi-vendor network configuration files (such as those from
Arista, Cisco, F5, Juniper, Palo Alto, etc); it is the next generation of
ciscoconfparse, which was the primary development package
from 2007 until 2023.
A ciscoconfparse2 example
Assume you have a bunch of interfaces in a configuration. How do you find which ones are shutdown?
One way is manually reading the whole Cisco IOS-XE configuration. Another option is ciscoconfparse2
>>> from ciscoconfparse2 import CiscoConfParse
>>>
>>> parse = CiscoConfParse("/path/to/config/file")
>>> intf_cmds = parse.find_parent_objects(["interface", "shutdown"])
>>>
>>> shut_intf_names = [" ".join(cmd.split()[1:]) for cmd in intf_cmds]
>>>
>>> shut_intf_names
['GigabitEthernet1/5', 'TenGigabitEthernet2/2', 'TenGigabitEthernet2/3']
>>>
Another ciscoconfparse2 example
Assume you have this IOS-XR bgp configuration:
router bgp 65534
bgp router-id 10.0.0.100
address-family ipv4 unicast
!
neighbor 10.0.0.37
remote-as 64000
route-policy EBGP_IN in
route-policy EBGP_OUT out
!
neighbor 10.0.0.1
remote-as 65534
update-source Loopback0
route-policy MANGLE_IN in
route-policy MANGLE_OUT out
next-hop-self
!
neighbor 10.0.0.34
remote-as 64000
route-policy EBGP_IN in
route-policy EBGP_OUT out
You can generate the list of EBGP peers pretty quickly with this script:
from ciscoconfparse2 import CiscoConfParse
parse = CiscoConfParse(
"/path/to/config/file"
)
branches = parse.find_object_branches(("router bgp", "neighbor", "remote-as"))
bgp_cmd = branches[0][0]
local_asn = bgp_cmd.split()[-1]
for branch in branches:
neighbor_addr = branch[1].split()[-1]
remote_asn = branch[2].split()[-1]
if local_asn != remote_asn:
print("EBGP NEIGHBOR", neighbor_addr)
When you run that, you'll see:
$ python example.py
EBGP NEIGHBOR 10.0.0.37
EBGP NEIGHBOR 10.0.0.34
$
There is a lot more possible; see the tutorial.
CLI Tool
ciscoconfparse2 distributes a CLI tool that will diff and grep various
network configuration or text files.
API Examples
The API examples are documented on the web
Why
ciscoconfparse2 is a Python library
that helps you quickly search for questions like these in your
router / switch / firewall / load-balancer / wireless text
configurations:
- What interfaces are shutdown?
- Which interfaces are in trunk mode?
- What address and subnet mask is assigned to each interface?
- Which interfaces are missing a critical command?
- Is this configuration missing a standard config line?
It can help you:
- Audit existing router / switch / firewall / wlc configurations
- Modify existing configurations
- Build new configurations
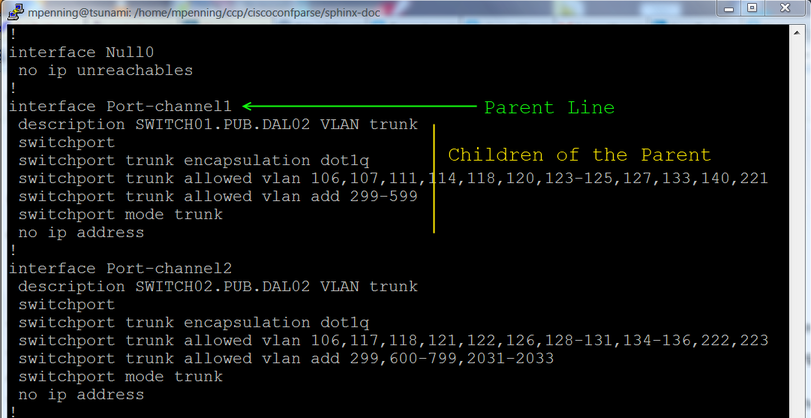
Speaking generally, the library examines a text network config and breaks
it into a set of linked parent / child relationships. You can perform
complex queries about these relationships.
What changed in ciscoconfparse2?
In late 2023, I started a rewrite because ciscoconfparse is too large
and has some defaults that I wish it didn't have. I froze
ciscoconfparse PYPI releases at version 1.9.52; there will be no
more ciscoconfparse PYPI releases.
What do you do? Upgrade to ciscoconfparse2!
Here's why, it:
- Includes a handy CLI command (including greps for mac addresses and IPv4 / IPv6 subnets)
- Streamlines the API towards a simpler user interface.
- Removes legacy and flawed methods from the original (this could be a breaking change for old scripts).
- Adds string methods to
BaseCfgLine() objects
- Defaults
ignore_blank_lines=False (this could be a breaking change for old scripts).
- Is better at handling multiple-child-level configurations (such as IOS XR and JunOS)
- Can search for parents and children using an arbitrary list of ancestors
- Adds the concept of change commits; this is a config-modification performance feature that ciscoconfparse lacks
- Adds an
auto_commit keyword, which defaults True
- Documents much more of the API
- Intentionally requires a different import statement to minimize confusion between the original and ciscoconfparse2
- Vasly improves Cisco IOS diffs
Cisco and Other Vendor-Specific factory parsers
Years ago, I introduced a beta-quality feature called factory, where
I built vendor-specific syntax parsers to extract values from Cisco and other
vendor configs.
This feature turned out to be a bad design decision; however, it's also much
more popular than I imagined.
Going forward I strongly discourage people from using factory features. There
will be no further development on vendor-specific factory parsers (such as
models_cisco.py).
I truly apologize for any disappointment.
Docs, Installation, and Dependencies
Installation and Downloads
Dependencies
Pre-requisites
The ciscoconfparse2 python package requires Python versions 3.10+.
What is the pythonic way of handling script credentials?
Other Resources
Are you releasing licensing besides GPLv3?
I will not. however, if it's truly a problem for your company, there are commercial solutions available (to include purchasing the project, or hiring me).
Bug Tracker and Support
- Please report any suggestions, bug reports, or annoyances with a github bug report.
- If you're having problems with general python issues, consider searching for a solution on Stack Overflow. If you can't find a solution for your problem or need more help, you can ask on Stack Overflow or reddit/r/Python.
- If you're having problems with your Cisco devices, you can contact:
License and Copyright
ciscoconfparse2 is licensed GPLv3
- Copyright (C) 2025 David Michael Pennington
The word "Cisco" is a registered trademark of Cisco Systems.
Author
ciscoconfparse2 was written by David Michael Pennington.









