clock
Simple command-line time tracker based on a simple text file format.
Introduction
This simple utility uses a text file to store tasks with date/time information. Each time you start working on a task, a new line is created on the file with the current time and a description of the task you are starting to work on.
At the end of the day, or anytime, you can then generate reports and statistics based on the file.
File structure
The file structure is very simple and can be edited using the script or directly with your favorite text editor.
Here is an example file:
[2022-01-01]
10:00 Starting project X +projectX
11:23 Starting documentation of project X +projectX +doc
12:00 [Stop]
[2022-01-02]
08:05 Starting workday, checking emails +office +emails
09:00 Back on documentation +projectX +doc
10:00 [Stop]
Tags and ids
An entry in this file can be associated with tags if you start the tag with a + (+tag) or ID if you start with a . (.456).
Tags allow for powerful filtering and reporting. They are ordered, meaning that +project +doc is different from +doc +project (see reports and filters below).
IDs allow to track time of tasks from an external tool, such as Jira. Entries with an ID are automatically assigned a default tag (+jira).
Special tasks
The [Stop] task is used to stop the last task. It is not required if you switch tasks without taking a break.
Installation
The program is available as a python packge through Pypi, so you can download it using pip:
python -m pip install clock-tracking
Creating an alias
You can create a shortcut (alias) to make the package easier to be called from the command line. Follow the instructions below depending on your operating system.
Windows PowerShell
On Windows, you can use the script with PowerShell. To create an alias permenantly, open your profile.ps1 file (see Windows PowerShell Profiles) and add these lines:
function Invoke-Clock { python -m clock_tracking $args }
New-Alias -Name clock -Value Invoke-Clock
MacOS / Unix
Open your bash profile (see Bash Profiles) and add these lines:
alias clock="python -m clock_tracking"
Usage
Tracking tasks
Use the clock_tracking python package to run the program, i.e. python -m clock_tracking or directly the command alias (see above). In this documentation, we'll use the alias clock to call the python -m clock_tracking package.
You can add a new entry by adding the entry definition after the package name:
$ clock Definition of the prototype +myapp +proto
Added: 08:10 Definition of the prototype +myapp +proto
Duration Date Start Stop Tags Name IDs
00:00 2022-01-01 08:10 08:10 +myapp,+proto Definition of the prototype
To switch to a new task, just use the same command:
$ clock Switching to new task
Added: 09:02 Switching to a new task
Duration Date Start Stop Tags Name IDs
00:00 2022-01-01 08:10 08:10 Switching to a new task
This will automatically stop the last task and start a new one. When you have finished working, use the stop command:
$ clock stop
Added: 10:00 [Stop]
Reports
You can show reports/statistics with the show command:
$ clock show
All tasks are ordered by first tag by default. Several filters are available, see ./clock --help for the full documentation.
To show all the tasks with their details:
$ clock show --details
To filter by a tag:
$ clock show +tag
To filter by an ID:
$ clock show .345
Examples
Report by tags / projects:

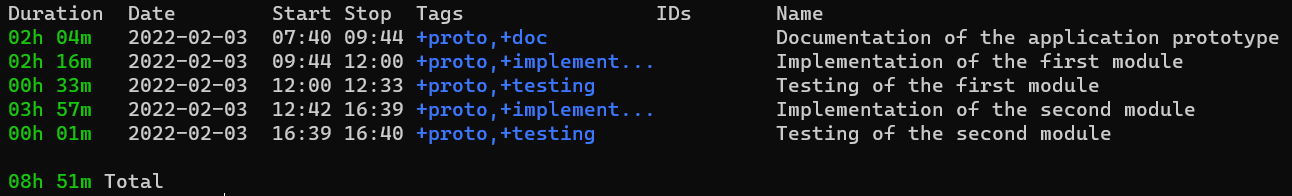
Show today's tasks details:
Documentation
usage: __main__.py [-h] [-f FILE] [--target HH:MM] [--target-per-day HH:MM] [-a HH:MM] [-t] [-w] [-s YYYY-mm-dd] [-e YYYY-mm-dd] [-l n] [-d]
[--categories] [--timeline]
command
Helps managing time tracking from the command-line
positional arguments:
command Command (add, edit, show). add: add a new entry. edit: edit current entry's description. show: show reports and statistics.
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
settings:
-f FILE, --file FILE Speficy the file to store time entries. Default is ~/clock.txt
--target HH:MM <show> Sets expected target time (format HH:MM) and computes the difference with actual times in the reports
--target-per-day HH:MM
<show> Sets expected target time per day (format HH:MM) and computes the difference with actual times in the reports
add:
-a HH:MM, --at HH:MM <add> Specify a time (format HH:MM) of a new entry
filters:
-t, --today <show> Show only entries from today
-w, --week <show> Show only entries from the current week
-s YYYY-mm-dd, --from YYYY-mm-dd
<show> Include entries with start date later or equal to given date (format YYYY-mm-dd)
-e YYYY-mm-dd, --to YYYY-mm-dd
<show> Include entries with start date earlier or equal to given date (format YYYY-mm-dd)
-l n, --last n <show> Show only the last n entries
reports:
-d, --details <show> Shows detailed report
--categories <show> Shows categories report (default)
--timeline <show> Shows issues on a timeline (only when --today is specified)





