
Security Fundamentals
Turtles, Clams, and Cyber Threat Actors: Shell Usage
The Socket Threat Research Team uncovers how threat actors weaponize shell techniques across npm, PyPI, and Go ecosystems to maintain persistence and exfiltrate data.
Earth Science PRoblems for the Evaluation of Strategies, Solvers and Optimizers
Earth Science PRoblems for the Evaluation of Strategies, Solvers and Optimizers (Espresso) is a collection of datasets, and associated simulation codes, spanning a wide range of geoscience problems. Together they form a suite of real-world test problems that can be used to support the development, evaluation and benchmarking of a wide range of tools and algorithms for inference, inversion and optimisation. All problems are designed to share a common interface, so that changing from one test problem to another requires changing one line of code.
The Espresso project is a community effort - if you think it sounds useful, please consider contributing an example or two from your own research. The project is currently being coordinated by InLab, with support from the CoFI development team.
For more information, please visit our documentation (coming soon).
$ pip install cofi-espresso
Check Espresso documentation - installation page for details on dependencies and setting up with virtual environments.
Once installed, each test problem can be imported using the following command:
from cofi_espresso import <testproblem>
Replace <testproblem> with one of the following currently available problems:
GravityDensitySimpleRegressionXrayTomographyOnce a problem is imported, its main functions can be called using the same structure for each problem. For instance:
from cofi_espresso import GravityDensity
problem = GravityDensity(example_number=1)
model = problem.good_model
data = problem.data
pred = problem.forward(model)
fig_model = problem.plot_model(model)
fig_data = problem.plot_data(data, pred)
You can access related metadata programatically:
print(GravityDensity.problem_title)
print(GravityDensity.problem_short_description)
print(GravityDensity.author_names)
Other problem-specific parameters can be accessed through the problem instance. For instance:
print(problem.m)
print(problem.rec_coords)
Which additional values are set is highly problem-specific and we suggest to consult the Espresso Documentation on the problems.
Interested in contributing? Please check out our contributor's guide.
Espresso is a community driven project to create a large suite of forward simulations to enable researchers to get example data without the need to understand each individual problem in detail.
Licensing is done individually by each contributor. If a contributor wants to freely share their code example we recommend the MIT licence or a 2-clause BSD licence. To determine the licence of an existing Espresso problem, please consult the documentation section of that problem.
All the other core functions of Espresso written by InLab Espresso developer team are distributed under a 2-clause BSD licence. A copy of this licence is provided with distributions of the software.
FAQs
Earth Science PRoblems for the Evaluation of Strategies, Solvers and Optimizers
We found that cofi-espresso demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 3 open source maintainers collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

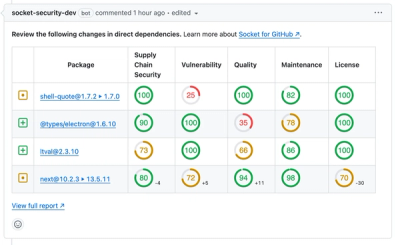
Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security Fundamentals
The Socket Threat Research Team uncovers how threat actors weaponize shell techniques across npm, PyPI, and Go ecosystems to maintain persistence and exfiltrate data.

Security News
At VulnCon 2025, NIST scrapped its NVD consortium plans, admitted it can't keep up with CVEs, and outlined automation efforts amid a mounting backlog.
Product
We redesigned our GitHub PR comments to deliver clear, actionable security insights without adding noise to your workflow.