
Research
Malicious fezbox npm Package Steals Browser Passwords from Cookies via Innovative QR Code Steganographic Technique
A malicious package uses a QR code as steganography in an innovative technique.
colorful-logger
Advanced tools
A colorful logger for python3.
pip install colorful-logger
You can directly use the default logger. Colored logs will be printed on the terminal. The default logger level is warning.
from colorful_logger import logger
with logger:
logger.debug("default logger")
logger.info("default logger")
logger.warning("default logger")
logger.error("default logger")
logger needs to be executed inside a with statement, because this package uses QueueListener for log output. You need to call the start method before using logger to output logs, and call stop after you are done. I encapsulated these two methods inside the with statement. In most cases, there is no need to call start and stop separately.

You can also change the log level, save logs to a file, change the logger name, etc. Logs may not be printed to the terminal.
from colorful_logger import get_logger, DEBUG
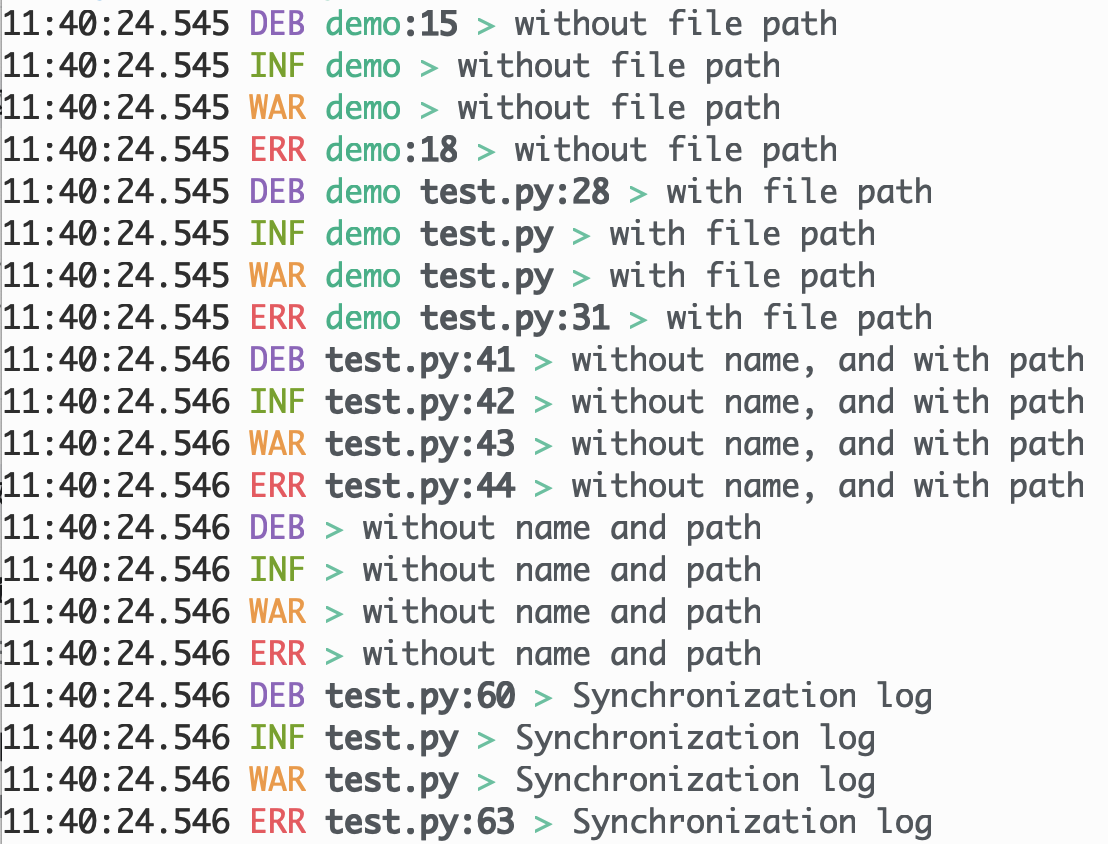
def demo_logger(to_file=False):
file = "test_%d.log"
l1 = get_logger(
"demo",
DEBUG,
add_file_path=False,
disable_line_number_filter=False,
file_path=file % 1 if to_file else None,
)
with l1:
l1.debug("without file path")
l1.info("without file path")
l1.warning("without file path")
l1.error("without file path")
l2 = get_logger(
"demo",
DEBUG,
add_file_path=True,
disable_line_number_filter=False,
file_path=file % 2 if to_file else None,
)
with l2:
l2.debug("with file path")
l2.info("with file path")
l2.warning("with file path")
l2.error("with file path")
l3 = get_logger(
None,
DEBUG,
add_file_path=True,
disable_line_number_filter=True,
file_path=file % 3 if to_file else None,
)
with l3:
l3.debug("without name, and with path")
l3.info("without name, and with path")
l3.warning("without name, and with path")
l3.error("without name, and with path")
l4 = get_logger(
None,
DEBUG,
add_file_path=False,
disable_line_number_filter=True,
file_path=file % 4 if to_file else None,
)
with l4:
l4.debug("without name and path")
l4.info("without name and path")
l4.warning("without name and path")
l4.error("without name and path")
l5 = get_logger(None, DEBUG, asynchronous=False)
l5.debug("Synchronization log")
l5.info("Synchronization log")
l5.warning("Synchronization log")
l5.error("Synchronization log")
There may be unexpected behavior when logging outside of the with statement.
Contents of the log file ./test.log (example, inconsistent with the image above):
[90m10:09:33.146[0m [35mDEB[0m [36mdemo[0m[1m:26[0m [96m-[0m without file path
[90m10:09:33.146[0m [32mINF[0m [36mdemo[0m [96m-[0m without file path
[90m10:09:33.146[0m [33mWAR[0m [36mdemo[0m [96m-[0m without file path
[90m10:09:33.146[0m [91mERR[0m [36mdemo[0m[1m:29[0m [96m-[0m without file path
The log file does not contain color logs by default.
To save color logs to a file, set file_colorful to True. In this example, color logs are saved.
The only purpose of the color log file is to view logs in real-time in the terminal:
tail -f test.log
# or
cat test.log
Get-Content -Path -Wait test.log
If you don't want to log asynchronously, you can create a synchronous logger by passing asynchronous=False. In the example above, l5 is a synchronous logger. When using a synchronous logger, you don't need to wrap the logs in a with statement.
After defining a logger, I want to use all the parameters of this logger except for name to output logs. You need to use the child_logger method to generate a child logger. The child logger needs to be executed inside the with statement of the parent logger:
from colorful_logger import get_logger, DEBUG
# parent logger
logger = get_logger(name="sample_logger", level=DEBUG, file_path="./test.log")
with logger:
logger.error("parent error")
l1 = logger.child("l1")
l1.error("l1 error")
l1.fatal("l1 fatal")
The child logger is the same as the parent logger except for the name. It will not log third-party libraries.
Executing the child logger inside the with statement of the parent logger does not mean it has to be called directly inside the with. It can be executed inside a function in the with statement:
# log.py
from colorful_logger import get_logger, DEBUG
logger = get_logger(name="sample_logger", level=DEBUG, file_path="./test.log")
# main.py
from log import logger
from other_file import test
with logger:
test()
# other_file.py
test_logger = logger.child("test_logger")
def test():
test_logger.error("test error")
FAQs
A colorful logger for python3.
We found that colorful-logger demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Research
A malicious package uses a QR code as steganography in an innovative technique.

Research
/Security News
Socket identified 80 fake candidates targeting engineering roles, including suspected North Korean operators, exposing the new reality of hiring as a security function.

Application Security
/Research
/Security News
Socket detected multiple compromised CrowdStrike npm packages, continuing the "Shai-Hulud" supply chain attack that has now impacted nearly 500 packages.