
Security News
curl Shuts Down Bug Bounty Program After Flood of AI Slop Reports
A surge of AI-generated vulnerability reports has pushed open source maintainers to rethink bug bounties and tighten security disclosure processes.
dbldatagen
Advanced tools
dbldatagen)The dbldatagen Databricks Labs project is a Python library for generating synthetic data within the Databricks
environment using Spark. The generated data may be used for testing, benchmarking, demos, and many
other uses.
It operates by defining a data generation specification in code that controls how the synthetic data is generated. The specification may incorporate the use of existing schemas or create data in an ad-hoc fashion.
It has no dependencies on any libraries that are not already installed in the Databricks runtime, and you can use it from Scala, R or other languages by defining a view over the generated data.
It supports:
hash of the underlying values or the values themselves)Details of these features can be found in the online documentation - online documentation.
Please refer to the online documentation for details of use and many examples.
Release notes and details of the latest changes for this specific release can be found in the GitHub repository here
Use pip install dbldatagen to install the PyPi package.
Within a Databricks notebook, invoke the following in a notebook cell
%pip install dbldatagen
The Pip install command can be invoked within a Databricks notebook, a Delta Live Tables pipeline and even works on the Databricks community edition.
The documentation installation notes contains details of installation using alternative mechanisms.
The Databricks Labs Data Generator framework can be used with Pyspark 3.1.2 and Python 3.8 or later. These are compatible with the Databricks runtime 10.4 LTS and later releases. For full Unity Catalog support, we recommend using Databricks runtime 13.2 or later (Databricks 13.3 LTS or above preferred)
For full library compatibility for a specific Databricks Spark release, see the Databricks release notes for library compatibility
When using the Databricks Labs Data Generator on "Unity Catalog" enabled Databricks environments,
the Data Generator requires the use of Single User or No Isolation Shared access modes when using Databricks
runtimes prior to release 13.2. This is because some needed features are not available in Shared
mode (for example, use of 3rd party libraries, use of Python UDFs) in these releases.
Depending on settings, the Custom access mode may be supported.
The use of Unity Catalog Shared access mode is supported in Databricks runtimes from Databricks runtime release 13.2
onwards.
See the following documentation for more information:
To use the data generator, install the library using the %pip install method or install the Python wheel directly
in your environment.
Once the library has been installed, you can use it to generate a data frame composed of synthetic data.
The easiest way to use the data generator is to use one of the standard datasets which can be further customized for your use case.
import dbldatagen as dg
df = dg.Datasets(spark, "basic/user").get(rows=1000_000).build()
num_rows=df.count()
You can also define fully custom data sets using the DataGenerator class.
For example
import dbldatagen as dg
from pyspark.sql.types import IntegerType, FloatType, StringType
column_count = 10
data_rows = 1000 * 1000
df_spec = (dg.DataGenerator(spark, name="test_data_set1", rows=data_rows,
partitions=4)
.withIdOutput()
.withColumn("r", FloatType(),
expr="floor(rand() * 350) * (86400 + 3600)",
numColumns=column_count)
.withColumn("code1", IntegerType(), minValue=100, maxValue=200)
.withColumn("code2", IntegerType(), minValue=0, maxValue=10)
.withColumn("code3", StringType(), values=['a', 'b', 'c'])
.withColumn("code4", StringType(), values=['a', 'b', 'c'],
random=True)
.withColumn("code5", StringType(), values=['a', 'b', 'c'],
random=True, weights=[9, 1, 1])
)
df = df_spec.build()
num_rows=df.count()
Refer to the online documentation for further examples.
The GitHub repository also contains further examples in the examples directory.
The dbldatagen package is intended to be compatible with recent LTS versions of the Databricks runtime, including
older LTS versions at least from 10.4 LTS and later. It also aims to be compatible with Delta Live Table runtimes,
including current and preview.
While we don't specifically drop support for older runtimes, changes in Pyspark APIs or
APIs from dependent packages such as numpy, pandas, pyarrow, and pyparsing make cause issues with older
runtimes.
By design, installing dbldatagen does not install releases of dependent packages in order
to preserve the curated set of packages pre-installed in any Databricks runtime environment.
When building on local environments, the build process uses the Pipfile and requirements files to determine
the package versions for releases and unit tests.
Please note that all projects released under Databricks Labs
are provided for your exploration only, and are not formally supported by Databricks with Service Level Agreements
(SLAs). They are provided AS-IS, and we do not make any guarantees of any kind. Please do not submit a support ticket
relating to any issues arising from the use of these projects.
Any issues discovered through the use of this project should be filed as issues on the GitHub Repo.
They will be reviewed as time permits, but there are no formal SLAs for support.
Issues with the application? Found a bug? Have a great idea for an addition? Feel free to file an issue.
FAQs
Databricks Labs - PySpark Synthetic Data Generator
We found that dbldatagen demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security News
A surge of AI-generated vulnerability reports has pushed open source maintainers to rethink bug bounties and tighten security disclosure processes.
Product
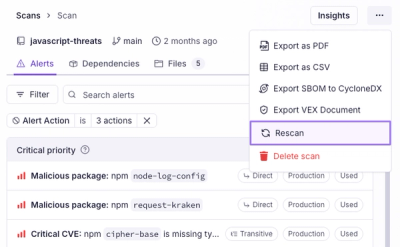
Scan results now load faster and remain consistent over time, with stable URLs and on-demand rescans for fresh security data.
Product
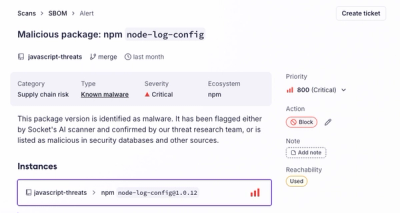
Socket's new Alert Details page is designed to surface more context, with a clearer layout, reachability dependency chains, and structured review.