
Security News
Meet Socket at Black Hat Europe and BSides London 2025
Socket is heading to London! Stop by our booth or schedule a meeting to see what we've been working on.
django-s3direct
Advanced tools
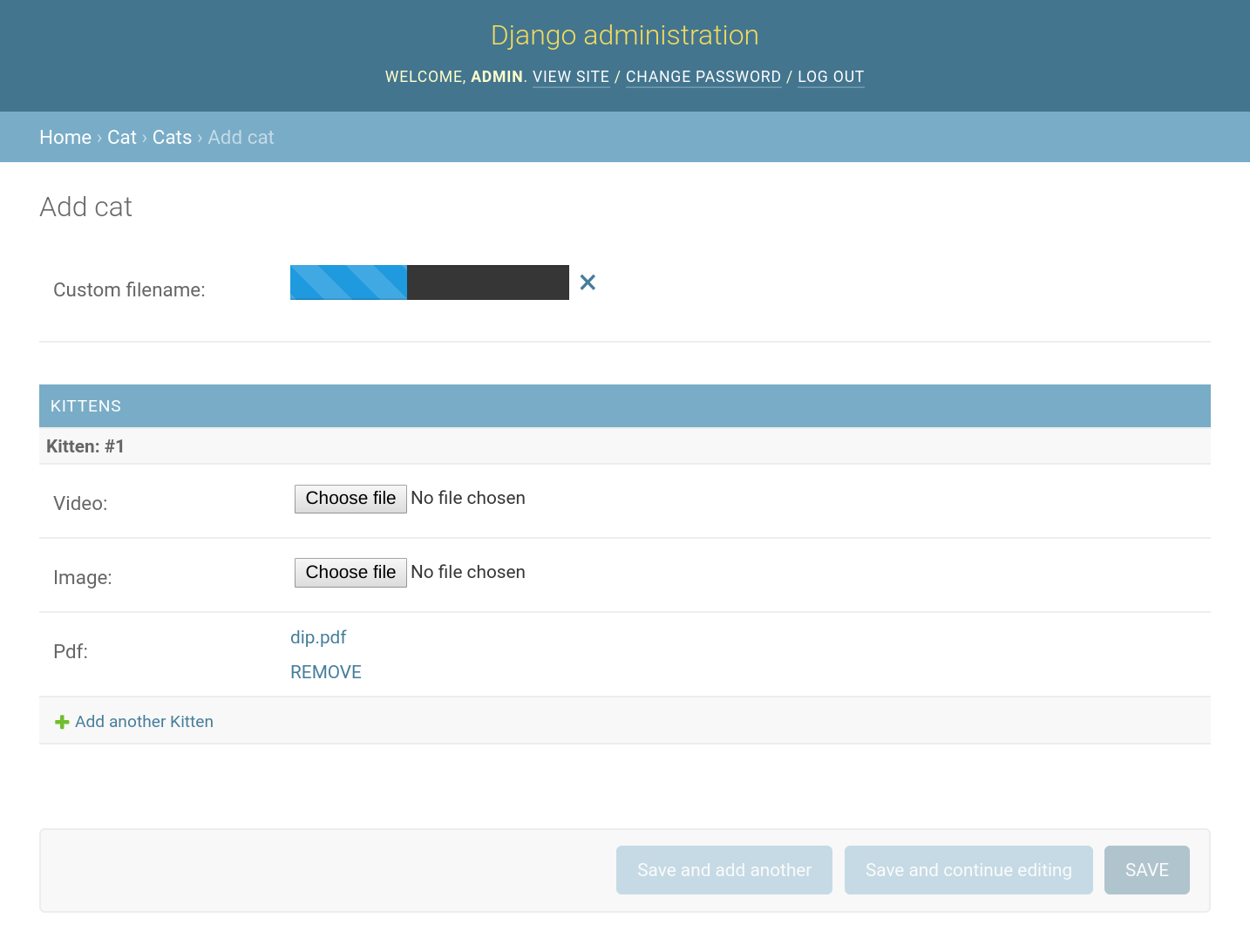
Install with Pip:
pip install django-s3direct
Generate access credentials and add them directly to your Django settings. If using Amazon S3 you'll also need to create an IAM policy which grants permission to upload to your bucket for your newly created credentials.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Action": [
"s3:AbortMultipartUpload",
"s3:GetObject",
"s3:ListMultipartUploadParts",
"s3:PutObject",
"s3:PutObjectAcl"
],
"Effect": "Allow",
"Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::YOUR_BUCKET_NAME/*"
}
]
}
Use the EC2 instance profile and its attached IAM role (AWS only)
Ensure the following trust policy is in place in addition to the policy
above. You'll also need the
boto3 package installed.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Service": "ec2.amazonaws.com"
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole"
}
]
}
Add a CORS policy to your bucket. Note the ETag header is important as it is used for multipart uploads. For more information see here.
[
{
"AllowedHeaders": ["*"],
"AllowedMethods": ["GET", "HEAD", "PUT", "POST", "DELETE"],
"AllowedOrigins": ["http://localhost:8080"],
"ExposeHeaders": ["ETag"],
"MaxAgeSeconds": 3000
}
]
INSTALLED_APPS = [
...
's3direct',
...
]
TEMPLATES = [{
...
'APP_DIRS': True,
...
}]
# AWS
# If these are set to None, the EC2 instance profile and IAM role are used.
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID = 'your-aws-access-key-id'
AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY = 'your-aws-secret-access-key'
# Bucket name
AWS_STORAGE_BUCKET_NAME = 'your-aws-s3-bucket-name'
# The region of your bucket, more info:
# http://docs.aws.amazon.com/general/latest/gr/rande.html#s3_region
AWS_S3_REGION_NAME = 'eu-west-1'
# The endpoint of your bucket, more info:
# http://docs.aws.amazon.com/general/latest/gr/rande.html#s3_region
AWS_S3_ENDPOINT_URL = 'https://s3.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com'
S3DIRECT_DESTINATIONS = {
'example_destination': {
# "key" [required] The location to upload file
# 1. String: folder path to upload to
# 2. Function: generate folder path + filename using a function
'key': 'uploads/images',
# "auth" [optional] Limit to specfic Django users
# Function: ACL function
'auth': lambda u: u.is_staff,
# "allowed" [optional] Limit to specific mime types
# List: list of mime types
'allowed': ['image/jpeg', 'image/png', 'video/mp4'],
# "bucket" [optional] Bucket if different from AWS_STORAGE_BUCKET_NAME
# String: bucket name
'bucket': 'custom-bucket',
# "endpoint" [optional] Endpoint if different from AWS_S3_ENDPOINT_URL
# String: endpoint URL
'endpoint': 'custom-endpoint',
# "region" [optional] Region if different from AWS_S3_REGION_NAME
# String: region name
'region': 'custom-region', # Default is 'AWS_S3_REGION_NAME'
# "acl" [optional] Custom ACL for object, default is 'public-read'
# String: ACL
'acl': 'private',
# "cache_control" [optional] Custom cache control header
# String: header
'cache_control': 'max-age=2592000',
# "content_disposition" [optional] Custom content disposition header
# String: header
'content_disposition': lambda x: 'attachment; filename="{}"'.format(x),
# "content_length_range" [optional] Limit file size
# Tuple: (from, to) in bytes
'content_length_range': (5000, 20000000),
# "server_side_encryption" [optional] Use serverside encryption
# String: encrytion standard
'server_side_encryption': 'AES256',
# "allow_existence_optimization" [optional] Checks to see if file already exists,
# returns the URL to the object if so (no upload)
# Boolean: True, False
'allow_existence_optimization': False,
},
'example_destination_two': {
'key': lambda filename, args: args + '/' + filename,
'key_args': 'uploads/images',
}
}
urlpatterns = [
...
url(r'^s3direct/', include('s3direct.urls')),
...
]
Run python manage.py collectstatic if required.
from django.db import models
from s3direct.fields import S3DirectField
class Example(models.Model):
video = S3DirectField(dest='example_destination')
from django import forms
from s3direct.widgets import S3DirectWidget
class S3DirectUploadForm(forms.Form):
images = forms.URLField(widget=S3DirectWidget(dest='example_destination'))
*Optional. You can modify the HTML of the widget by overiding template s3direct/templates/s3direct-widget.tpl
from django.views.generic import FormView
from .forms import S3DirectUploadForm
class MyView(FormView):
template_name = 'form.html'
form_class = S3DirectUploadForm
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title>s3direct</title>
{{ form.media }}
</head>
<body>
<form action="" method="post">{% csrf_token %} {{ form.as_p }}</form>
</body>
</html>
Examples of both approaches can be found in the examples folder. To run them:
$ git clone git@github.com:bradleyg/django-s3direct.git
$ cd django-s3direct
$ python setup.py install
$ cd example
# Add config to your environment
export AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID='…'
export AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY='…'
export AWS_STORAGE_BUCKET_NAME='…'
export AWS_S3_REGION_NAME='…'
export AWS_S3_ENDPOINT_URL='…'
$ python manage.py migrate
$ python manage.py createsuperuser
$ python manage.py runserver
Visit http://localhost:8080/admin to view the admin widget and
http://localhost:8080/form to view the custom form widget.
$ git clone git@github.com:bradleyg/django-s3direct.git
$ cd django-s3direct
# Add your AWS keys/details to .env file and export
$ cp .env-dist .env
# Frontend deps
$ npm i
# Install locally
$ python setup.py develop
# Run examples
$ python example/manage.py migrate
$ python example/manage.py createsuperuser
$ python example/manage.py runserver 0.0.0.0:8080
# Run tests
$ npm run test
# Run frontend bundler and Django server
$ npm run dev
# Watch and build frontend (dev)
$ npm run watch
# Build frontend (prod)
$ npm run build
# Format python // PEP8
$ npm run yapf
# Upload to PYPI
$ npm run pypi
FAQs
Add direct uploads to S3 functionality with a progress bar to file input fields.
We found that django-s3direct demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security News
Socket is heading to London! Stop by our booth or schedule a meeting to see what we've been working on.

Security News
OWASP’s 2025 Top 10 introduces Software Supply Chain Failures as a new category, reflecting rising concern over dependency and build system risks.

Research
/Security News
Socket researchers discovered nine malicious NuGet packages that use time-delayed payloads to crash applications and corrupt industrial control systems.