 DocStrange
DocStrange








🚀 Try DocStrange Online →
DocStrange
DocStrange converts documents to Markdown, JSON, CSV, and HTML quickly and accurately.
- Converts PDF, image, PPTX, DOCX, XLSX, and URL files.
- Formats tables into clean, LLM-optimized Markdown.
- Powered by an upgraded 7B model for higher accuracy and deeper document understanding.
- Extracts text from images and scanned documents with advanced OCR.
- Removes page artifacts for clean, readable output.
- Does structured extraction, given specific fields or a JSON schema.
- Includes a built-in, local Web UI for easy drag-and-drop conversion.
- Offers a free cloud API for instant processing or a 100% private, local mode.
- Works on GPU or CPU when running locally.
- Integrates with Claude Desktop via an MCP server for intelligent document navigation.
Processing Modes
☁️ Free Cloud Processing upto 10000 docs per month !
Extract documents data instantly with the cloud processing - no complex setup needed
🔒 Local Processing !
Use gpu mode for 100% local processing - no data sent anywhere, everything stays on your machine.
What's New
August 2025
- 🚀 Major Model Upgrade: The core model has been upgraded to 7B parameters, delivering significantly higher accuracy and deeper understanding of complex documents.
- 🖥️ Local Web Interface: Introducing a built-in, local GUI. Now you can convert documents with a simple drag-and-drop interface, 100% offline.
About
Convert and extract data from PDF, DOCX, images, and more into clean Markdown and structured JSON. Plus: Advanced table extraction, 100% local processing, and a built-in web UI.
DocStrange is a Python library for converting a wide range of document formats—including PDF, DOCX, PPTX, XLSX, and images — into clean, usable data. It produces LLM-optimized Markdown, structured JSON (with schema support), HTML, and CSV outputs, making it an ideal tool for preparing content for RAG pipelines and other AI applications.
The library offers both a powerful cloud API and a 100% private, offline mode that runs locally on your GPU. Developed by Nanonets, DocStrange is built on a powerful pipeline of OCR and layout detection models and currently requires Python >=3.8.
To report a bug or request a feature, please file an issue. To ask a question or request assistance, please use the discussions forum.
How DocStrange Differs
DocStrange focuses on end-to-end document understanding (OCR → layout → tables → clean Markdown or structured JSON) that you can run 100% locally. It is designed to deliver high-quality results from scans and photos without requiring the integration of multiple services.
- vs. Cloud AI Services (like AWS Textract):
DocStrange offers a completely private, local processing option and gives you full control over the conversion pipeline.
- vs. Orchestration Frameworks (like LangChain):
DocStrange is a ready-to-use parsing pipeline, not just a framework. It handles the complex OCR and layout analysis so you don't have to build it yourself.
- vs. Other Document Parsers:
DocStrange is specifically built for robust OCR on scans and phone photos, not just digitally-native PDFs.
When to Pick DocStrange
- You need a free cloud api to extract information in structured format (markdown, json, csv, html) from different document types
- You need local processing for privacy and compliance.
- You are working with scans, phone photos, or receipts where high-quality OCR is critical.
- You need a fast path to clean Markdown or structured JSON without training a model.
Examples
Try the live demo: Test DocStrange instantly in your browser with no installation required at docstrange.nanonets.com
See it in action:
Installation
Install the library using pip:
pip install docstrange
Quick Start
💡 New to DocStrange? Try the online demo first - no installation needed!
1. Convert any Document to LLM-Ready Markdown
This is the most common use case. Turn a complex PDF or DOCX file into clean, structured Markdown, perfect for RAG pipelines and other LLM applications.
from docstrange import DocumentExtractor
extractor = DocumentExtractor()
result = extractor.extract("document.pdf")
markdown = result.extract_markdown()
print(markdown)
2. Extract Structured Data as JSON
Go beyond plain text and extract all detected entities and content from your document into a structured JSON format.
from docstrange import DocumentExtractor
extractor = DocumentExtractor()
result = extractor.extract("document.pdf")
json_data = result.extract_data()
print(json_data)
3. Extract Specific Fields from a PDF or Invoice
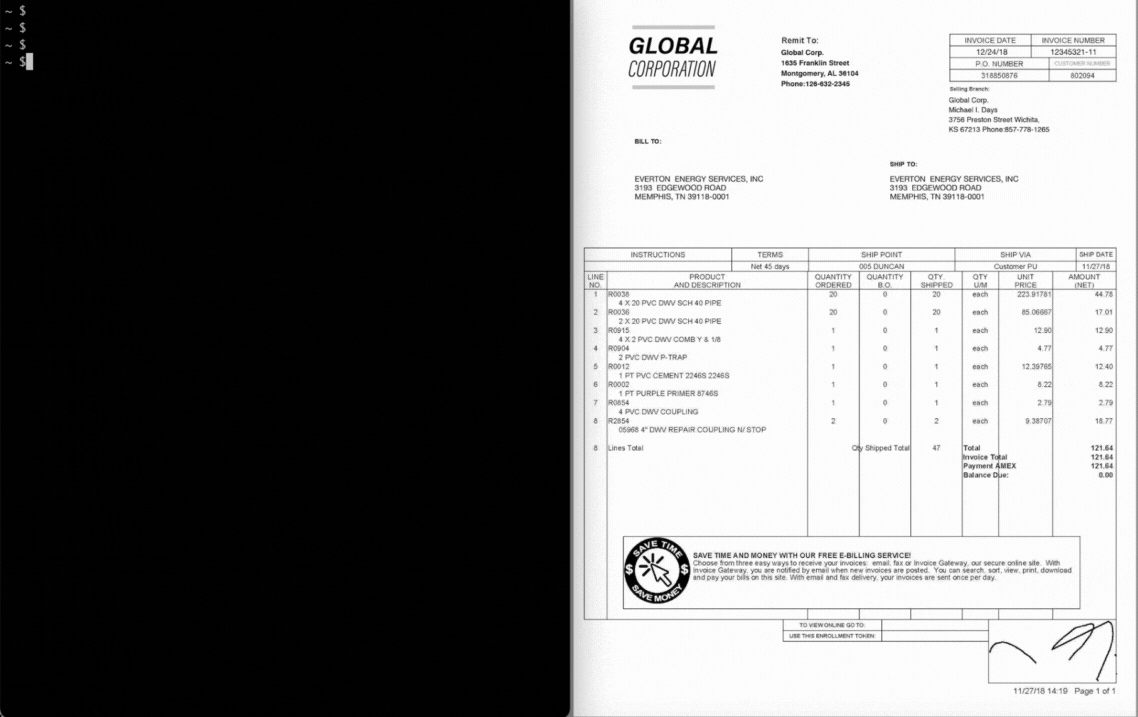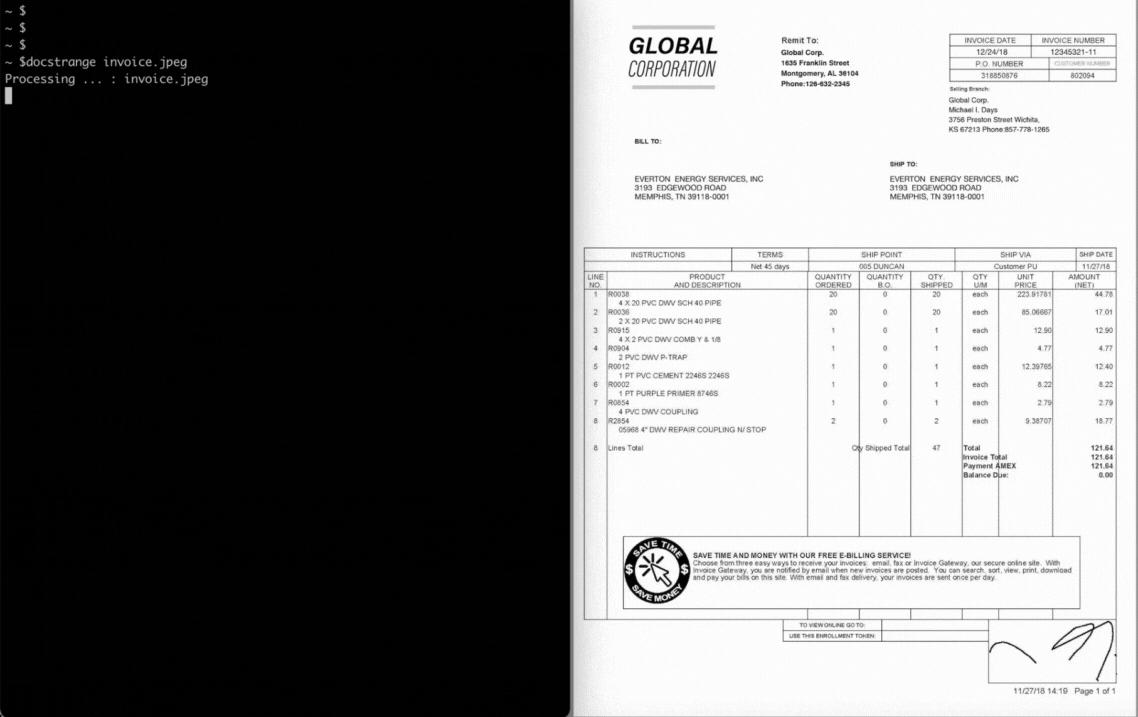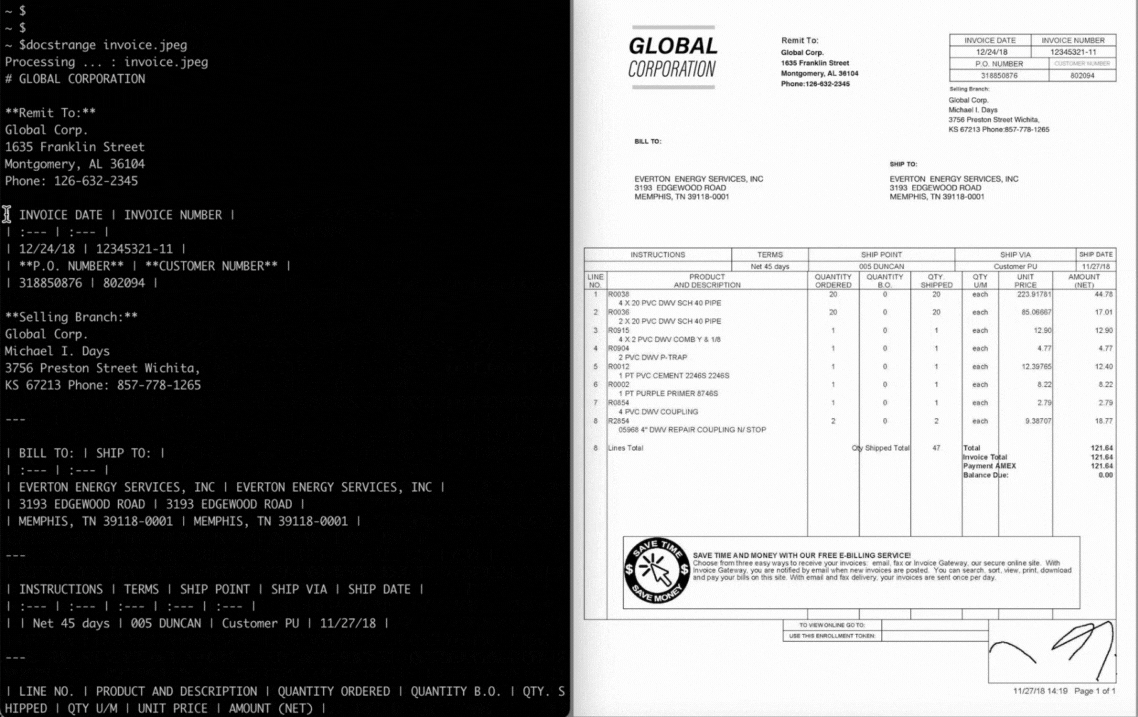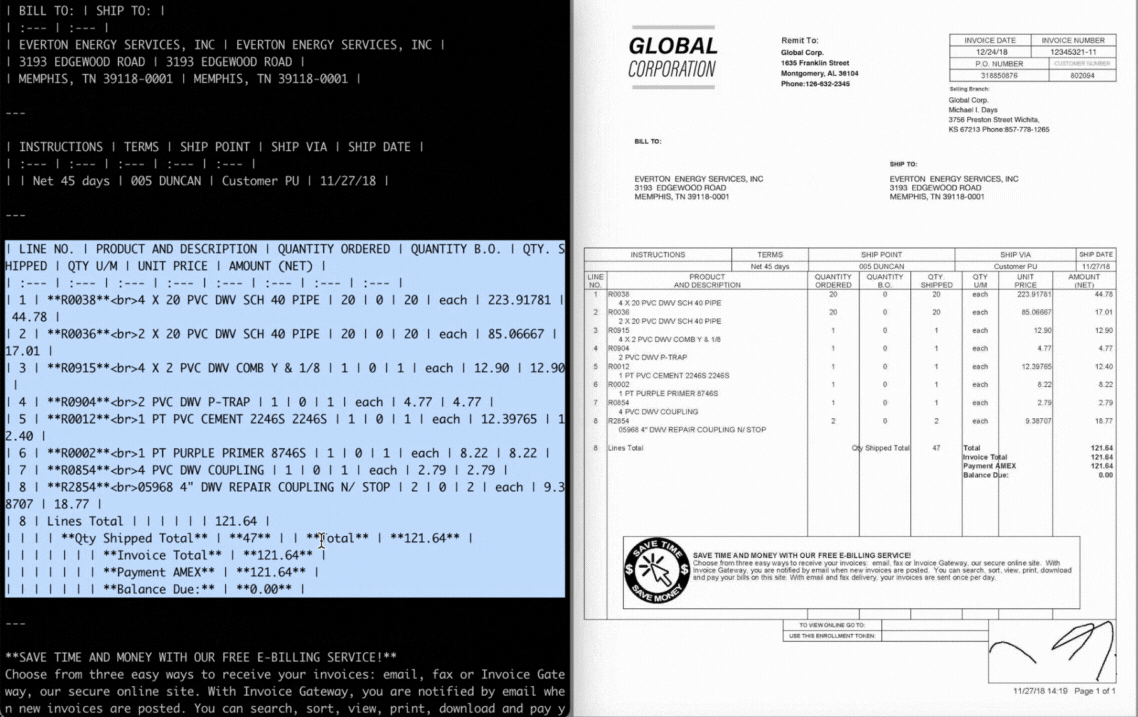
Target only the key-value data you need, such as extracting the invoice_number or total_amount directly from a document.
from docstrange import DocumentExtractor
extractor = DocumentExtractor()
result = extractor.extract("invoice.pdf")
fields = result.extract_data(specified_fields=[
"invoice_number", "total_amount", "vendor_name", "due_date"
])
print(fields)
4. Extract with Custom JSON Schema
Ensure the structure of your output by providing a custom JSON schema. This is ideal for getting reliable, nested data structures for applications that process contracts or complex forms.
from docstrange import DocumentExtractor
extractor = DocumentExtractor()
result = extractor.extract("contract.pdf")
schema = {
"contract_number": "string",
"parties": ["string"],
"total_value": "number",
"start_date": "string",
"terms": ["string"]
}
structured_data = result.extract_data(json_schema=schema)
print(structured_data)
Local Processing
For complete privacy and offline capability, run DocStrange entirely on your own machine using GPU processing.
extractor = DocumentExtractor(gpu=True)
Local Web Interface
💡 Want a GUI? Run the simple, drag-and-drop local web interface for private, offline document conversion.
For users who prefer a graphical interface, DocStrange includes a powerful, self-hosted web UI. This allows for easy drag-and-drop conversion of PDF, DOCX, and other files directly in your browser, with 100% private, offline processing on your own GPU. The interface automatically downloads required models on its first run.
How to get started?
- Install with web dependencies:
pip install "docstrange[web]"
docstrange web
python -m docstrange.web_app
python -c "from docstrange.web_app import run_web_app; run_web_app()"
- Open your browser: Navigate to
http://localhost:8000 (or the port shown in the terminal)
Features of DocStrange's Local Web Interface:
- 🖱️ Drag & Drop Interface: Simply drag files onto the upload area.
- 📁 Multiple File Types: Supports PDF, DOCX, XLSX, PPTX, images, and more.
- ⚙️ Processing Modes: Choose between Cloud and Local GPU processing.
- 📊 Multiple Output Formats: Get Markdown, HTML, JSON, CSV, and Flat JSON.
- 🔒 Privacy Options: Choose between cloud processing (default) or local GPU processing.
- 📱 Responsive Design: Works on desktop, tablet, and mobile
Supported File Types:
- Documents: PDF, DOCX, DOC, PPTX, PPT
- Spreadsheets: XLSX, XLS, CSV
- Images: PNG, JPG, JPEG, TIFF, BMP
- Web: HTML, HTM
- Text: TXT
Processing Modes:
- Cloud processing: For instant, zero-setup conversion, you can head over to docstrange.nanonets.com — no setup (default)
- Local GPU: Fastest local processing, requires CUDA support
Output Formats:
- Markdown: Clean, structured text perfect for documentation
- HTML: Formatted output with styling and layout
- CSV: Table data in spreadsheet format
- Flat JSON: Simplified JSON structure
- Specific Fields: Specific information from documents
Advanced Usage:
docstrange web --port 8080
python -c "from docstrange.web_app import run_web_app; run_web_app(port=8080)"
python -c "from docstrange.web_app import run_web_app; run_web_app(debug=True)"
- Run on a Custom Host (to make it accessible on your local network):
python -c "from docstrange.web_app import run_web_app; run_web_app(host='0.0.0.0')"
Troubleshooting
docstrange web --port 8001
- The interface automatically detects GPU availability
- GPU option will be disabled if CUDA is not available
- Error will be thrown
- Models are downloaded automatically on first startup
- Check your internet connection during initial setup
- Download progress is shown in the terminal
pip install -e ".[web]"
pip install Flask
Cloud Alternative
Need cloud processing? Use the official DocStrange Cloud service: 🔗 docstrange.nanonets.com
Usage and Features
You can use DocStrange in three main ways: as a simple Web Interface, as a flexible Python Library, or as a powerful Command Line Interface (CLI). This section provides a summary of the library's key capabilities, followed by detailed guides and examples for each method.
- Convert Multiple File Types
DocStrange natively handles a wide variety of formats, returning the most appropriate output for each.
from docstrange import DocumentExtractor
extractor = DocumentExtractor()
pdf_result = extractor.extract("report.pdf")
print(pdf_result.extract_markdown())
docx_result = extractor.extract("document.docx")
print(docx_result.extract_data())
excel_result = extractor.extract("data.xlsx")
print(excel_result.extract_csv())
pptx_result = extractor.extract("slides.pptx")
print(pptx_result.extract_html())
image_result = extractor.extract("screenshot.png")
print(image_result.extract_text())
url_result = extractor.extract("https://example.com")
print(url_result.extract_markdown())
b. Extract Tables to CSV
Easily extracts all tables from a document into a clean CSV format.
result = extractor.extract("financial_report.pdf")
csv_data = result.extract_csv()
print(csv_data)
c. Extract Specific Fields & Structured Data
You can go beyond simple conversion and extract data in the exact structure you require. There are two ways to do this. You can either target and pull only the key-value data you need or ensure the structure of your output by providing a custom JSON schema.
result = extractor.extract("invoice.pdf")
extracted = result.extract_data(specified_fields=[
"invoice_number",
"total_amount",
"vendor_name",
"due_date"
])
schema = {
"invoice_number": "string",
"total_amount": "number",
"vendor_name": "string",
"line_items": [{
"description": "string",
"amount": "number"
}]
}
structured = result.extract_data(json_schema=schema)
d. Cloud Mode Usage Examples:
Use DocStrange's cloud mode to extract precise, structured data from various documents by either specifying a list of fields to find or enforcing a custom JSON schema for the output. Authenticate with DocStrange login or a free API key to get 10,000 documents/month.
from docstrange import DocumentExtractor
extractor = DocumentExtractor()
extractor = DocumentExtractor()
extractor = DocumentExtractor(api_key="your_api_key_here")
result = extractor.extract("invoice.pdf")
invoice_fields = result.extract_data(specified_fields=[
"invoice_number",
"total_amount",
"vendor_name",
"due_date",
"items_count"
])
print("Extracted Invoice Fields:")
print(invoice_fields)
invoice_schema = {
"invoice_number": "string",
"total_amount": "number",
"vendor_name": "string",
"billing_address": {
"street": "string",
"city": "string",
"zip_code": "string"
},
"line_items": [{
"description": "string",
"quantity": "number",
"unit_price": "number",
"total": "number"
}],
"taxes": {
"tax_rate": "number",
"tax_amount": "number"
}
}
structured_invoice = result.extract_data(json_schema=invoice_schema)
print("Structured Invoice Data:")
print(structured_invoice)
receipt = extractor.extract("receipt.jpg")
receipt_data = receipt.extract_data(specified_fields=[
"merchant_name", "total_amount", "date", "payment_method"
])
contract = extractor.extract("contract.pdf")
contract_schema = {
"parties": [{
"name": "string",
"role": "string"
}],
"contract_value": "number",
"start_date": "string",
"end_date": "string",
"key_terms": ["string"]
}
contract_data = contract.extract_data(json_schema=contract_schema)
e. Chain with LLM
The clean Markdown output is perfect for use in Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) and other LLM workflows.
document_text = extractor.extract("research_paper.pdf").extract_markdown()
response = your_llm_client.chat(
messages=[{
"role": "user",
"content": f"Summarize this research paper:\n\n{document_text}"
}]
)
Key Capabilities
- 🌐 Universal Input: Process a wide range of formats, including PDF, DOCX, PPTX, XLSX, images, and URLs.
- 🔒 Dual Processing Modes: Choose between a cloud API for instant processing or 100% private, local processing on your own CPU or GPU.
- 🤖 Intelligent Extraction: Extract specific fields or enforce a nested JSON schema to get structured data output.
- 🖼️ Advanced OCR: Handle scanned documents and images with an OCR pipeline that includes multiple engine fallbacks.
- 📊 Table & Structure Recognition: Accurately extract tables and preserve document structure, producing clean, LLM-optimized output.
- 🖥️ Built-in Web UI: Use the built-in drag-and-drop web interface for easy local conversions.
How It Works
DocStrange uses a multi-stage process to create structured output from documents.
- Ingestion: It natively handles various file formats, including PDF, DOCX, PPTX, images, and URLs.
- Layout Detection: The library identifies the structure of the document, such as headers, paragraphs, lists, and tables, to preserve the original reading order.
- OCR & Text Extraction: It employs advanced OCR for scanned documents and directly extracts text from digital files.
- Formatting & Cleaning: The extracted content is converted into clean, LLM-optimized Markdown and other formats, removing page artifacts.
- Structured Extraction (Optional): If a schema or specific fields are provided, DocStrange uses an LLM to populate the desired JSON structure.
Cloud API Tiers and Rate Limits
DocStrange offers free cloud processing with different tiers to ensure fair usage.
- 🔐 Authenticated Access (Recommended)
- Rate Limit: 10,000 documents/month.
- Setup: A single command:
docstrange login.
- Benefits: Links to your Google account for a significantly higher free limit.
- 🔑 API Key Access (Alternative)
- Rate Limit: 10,000 documents/month.
- Setup: Get a free API key from docstrange.nanonets.com.
- Usage: Pass the API key when initializing the library.
extractor = DocumentExtractor()
extractor = DocumentExtractor()
extractor = DocumentExtractor(api_key="your_api_key_here")
💡 Tip: Start with the anonymous free tier to test functionality, then authenticate with docstrange login for the full 10,000 documents/month limit.
Command Line Interface (CLI)
💡 Prefer a GUI? Try the web interface for drag-and-drop document conversion!
For automation, scripting, and batch processing, you can use DocStrange directly from your terminal.
Authentication Commands
docstrange login
docstrange --login
docstrange login --reauth
docstrange --logout
Document Processing
docstrange document.pdf
docstrange document.pdf
docstrange document.pdf --api-key YOUR_API_KEY
docstrange document.pdf --gpu-mode
docstrange document.pdf --output json
docstrange document.pdf --output html
docstrange document.pdf --output csv
docstrange invoice.pdf --output json --extract-fields invoice_number total_amount
docstrange document.pdf --output json --json-schema schema.json
docstrange *.pdf --output markdown
docstrange document.pdf --output-file result.md
docstrange invoice.pdf --output json --extract-fields invoice_number vendor_name total_amount due_date line_items
docstrange receipt.jpg --output json --extract-fields merchant_name total_amount date payment_method
docstrange contract.pdf --output json --extract-fields parties contract_value start_date end_date
docstrange invoice.pdf --output json --json-schema invoice_schema.json
docstrange contract.pdf --output json --json-schema contract_schema.json
docstrange document.pdf --output json --extract-fields title author date summary
docstrange document.pdf --api-key YOUR_API_KEY --output json --extract-fields title author date summary
Example schema.json file:
{
"invoice_number": "string",
"total_amount": "number",
"vendor_name": "string",
"billing_address": {
"street": "string",
"city": "string",
"zip_code": "string"
},
"line_items": [{
"description": "string",
"quantity": "number",
"unit_price": "number"
}]
}
API Reference for library
This section details the main classes and methods for programmatic use.
DocumentExtractor(
api_key: str = None,
model: str = None,
cpu: bool = False,
gpu: bool = False
)
b. ConversionResult Methods
result.extract_markdown() -> str
result.extract_data(
specified_fields: List[str] = None,
json_schema: Dict = None
) -> Dict
result.extract_html() -> str
result.extract_csv() -> str
result.extract_text() -> str
🤖 MCP Server for Claude Desktop (Local Development)
The DocStrange repository includes an optional MCP (Model Context Protocol) server for local development that enables intelligent document processing in Claude Desktop with token-aware navigation.
Note: The MCP server is designed for local development and is not included in the PyPI package. Clone the repository to use it locally.
Features
- Smart Token Counting: Automatically counts tokens and recommends processing strategy
- Hierarchical Navigation: Navigate documents by structure when they exceed context limits
- Intelligent Chunking: Automatically splits large documents into token-limited chunks
- Advanced Search: Search within documents and get contextual results
Local Setup
git clone https://github.com/nanonets/docstrange.git
cd docstrange
- Install in development mode:
pip install -e ".[dev]"
- Add to your Claude Desktop config (
~/Library/Application Support/Claude/claude_desktop_config.json):
{
"mcpServers": {
"docstrange": {
"command": "python3",
"args": ["/path/to/docstrange/mcp_server_module/server.py"]
}
}
}
For detailed setup and usage, see mcp_server_module/README.md
The Nanonets Ecosystem
DocStrange is a powerful open-source library developed and maintained by the team at Nanonets. The full Nanonets platform is an AI-driven solution for automating end-to-end document processing for businesses. The platform allows technical and non-technical teams to build complete automated document workflows.
This is an actively developed open-source project, and we welcome your feedback and contributions.
- Discussions: For questions, ideas, and to show what you've built, please visit our GitHub Discussions.
- Issues: For bug reports and feature requests, please open an Issue.
- Email: For private inquiries, you can reach us at support@nanonets.com.
⭐ Star this repo if you find it helpful! Your support helps us improve the library.
License: This project is licensed under the MIT License.


 DocStrange
DocStrange










