
Security News
CISA Rebuffs Funding Concerns as CVE Foundation Draws Criticism
CISA denies CVE funding issues amid backlash over a new CVE foundation formed by board members, raising concerns about transparency and program governance.
Efficient Evolutionary Scale Modeling: Efficient and simplified implementation of protein language model for inference and training.
Efficient implementation of the ESM family of models: ESM1b, ESM1v, ESM2, ESMC.


Download the appropriate version of pytorch and install it.
pip install flash-attn --no-build-isolation
pip install esm-efficient
from esme import ESM
model = ESM.from_pretrained('esmc') # or 'esm1b', 'esm1v', 'esm2', 'esm2_8m', ...
This will download the model weights from the HuggingFace model hub and load the model. See doc from getting started.
Predict the log probabilities of a sequence of tokens using the model.
import torch
from esme import ESM2
from esme.alphabet import tokenize
# create load the model
model = ESM2.from_pretrained("{model}.safetensors", device=0)
tokens = tokenize(['MEEPQSDPSVEPPLSQESTFSLDLWK', 'MADQLTEEQIAEFKEAFSLFDKDG'])
tokens = tokens.to(0)
# predict logits
logits = model(tokens)
# logits.shape = (2, seq_len, embed_size)
# predict log probabilities
log_probs = model.predict_log_prob(tokens)
# log_probs.shape = (2, seq_len, embed_size)
from esme.alphabet import tokenize_unpad
# tokenize without padding (more efficient avoids calculating with padding)
tokens, indices, cu_lens, max_len = tokenize_unpad(['MEEPQSDPSVEPPLSQETFSDLWK', 'MADQLTEEQIAEFKEAFSLFDKDG'])
tokens = tokens.to(0)
cu_lens = cu_lens.to(0)
log_probs = model.predict_log_prob(tokens, (cu_lens, max_len))
# log_probs.shape = (seq_len_protein1 + seq_len_protein2, embed_size)
from esme.variant import predict_mask_margin
seq = 'MEEPQSDPSVEPPLSQETFSDLWK'
df = predict_mask_margin(model, seq)
# ... pd.DataFrame({
# ... 'variant': ['M1A', 'M1C', ..., 'P16Y'],
# ... 'score': [-0.1, -0.2, ..., -0.3]
# ... }).set_index('variant')
# only add will be trained by default
model.add_lora(rank=16, layers=('query', 'key', 'value'), adapter_names=['adapter1', 'adapter2'])
# mark only lora as trainable called by default when adding lora
model.mark_only_lora_as_trainable()
# save the model with the lora weights
model.save_lora('<path>.safetensors', adapter_names=['adapter1'])
# load the model with the lora weights
model.load_lora('<path>.safetensors')
model = ESM2.from_pretrained('8M.safetensors', quantization='4bit', device=0)
Activation checkpointing of each transformer layer:
model = ESM2.from_pretrained('8M.safetensors', checkpointing=True)
We provide pytorch lightning trainer for training the model. The following code trains the model with the masked language model objective:
from esme import ESM2
from esme.data import MaskedFastaTokenDataModule
from esme.trainer import MaskedPLM
trainer = MaskedPLM(model) # pytorch lightning trainer
datamodule = MaskedFastaTokenDataModule(
train_fasta='train.fasta',
val_fasta='val.fasta',
token_per_batch=50_000,
) # data module for training
trainer.fit(datamodule)
The model weights can be downloaded from the HuggingFace: https://huggingface.co/mhcelik/esm-efficient/tree/main
To perform the evaluation reported in the paper, run the following command:
snakemake -n --use-conda
This will download the data, train the models, and evaluate them. The results will be saved in the results directory.
See the workflow/Snakefile for more details.
To generate a specific figures in the paper, run the following command:
snakemake reports/paper_figures/figure-2.pdf -n --use-conda
Manuscript for the efficient implementation: https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2024.10.22.619563v1
@article {Celik2024.10.22.619563,
author = {Celik, Muhammed Hasan and Xie, Xiaohui},
title = {Efficient Inference, Training, and Fine-tuning of Protein Language Models},
elocation-id = {2024.10.22.619563},
year = {2024},
doi = {10.1101/2024.10.22.619563},
publisher = {Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory},
URL = {https://www.biorxiv.org/content/early/2024/10/25/2024.10.22.619563},
eprint = {https://www.biorxiv.org/content/early/2024/10/25/2024.10.22.619563.full.pdf},
journal = {bioRxiv}
}
Also, cite original ESM papers for the related model: https://github.com/facebookresearch/esm
This code implements ESM models from scratch and is licensed under the MIT License. Refer to the esm and fair-esm repositories for the licenses for the model weights.
FAQs
Efficient Evolutionary Scale Modeling: Efficient and simplified implementation of protein language model for inference and training.
We found that esm-efficient demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security News
CISA denies CVE funding issues amid backlash over a new CVE foundation formed by board members, raising concerns about transparency and program governance.
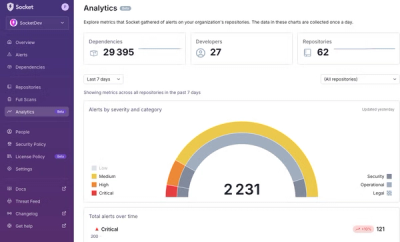
Product
We’re excited to announce a powerful new capability in Socket: historical data and enhanced analytics.
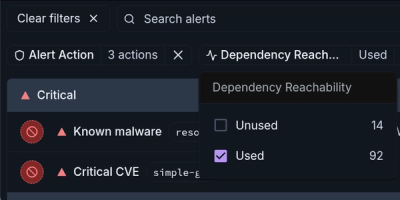
Product
Module Reachability filters out unreachable CVEs so you can focus on vulnerabilities that actually matter to your application.