
Security News
TC39 Advances 11 Proposals for Math Precision, Binary APIs, and More
TC39 advances 11 JavaScript proposals, with two moving to Stage 4, bringing better math, binary APIs, and more features one step closer to the ECMAScript spec.
EspressoDB is a Python framework designed to organize (relational) data without losing flexibility. Its objective is to be intuitive and fast.
More specifically, EspressoDB is built on top of the Object-Relational Mapping web framework Django and adds additional convenience functionalities to easily set up your project. Additionally, EspressoDB provides an extended framework of data consistency checks, giving users the freedom to define data tables and their relationships which uniquely mirror the underlying computation.
EspressoDB provides an easy to use database interface which helps you make educated decisions fast.
Once you have created your Python project (e.g., my_project) with EspressoDB
import numpy as np
from my_project.hamiltonian.models import Contact as ContactHamiltonian
# Ask the database for specific entries
hamiltonian = ContactHamiltonian.objects.filter(n_sites=20).first()
# Use class methods for an intuitive interface
## Print a formatted summary of the table entry
print(hamiltonian)
## Allocate an actual matrix for the given entry and use it in computations
eigs, vecs = np.linalg.eigh(hamiltonian.matrix)
models classes are regular classes in Python.
They can provide additional methods for convenience.
Also, they know how to talk to the database, e.g., you can query (read) and update (write) your data to a central database.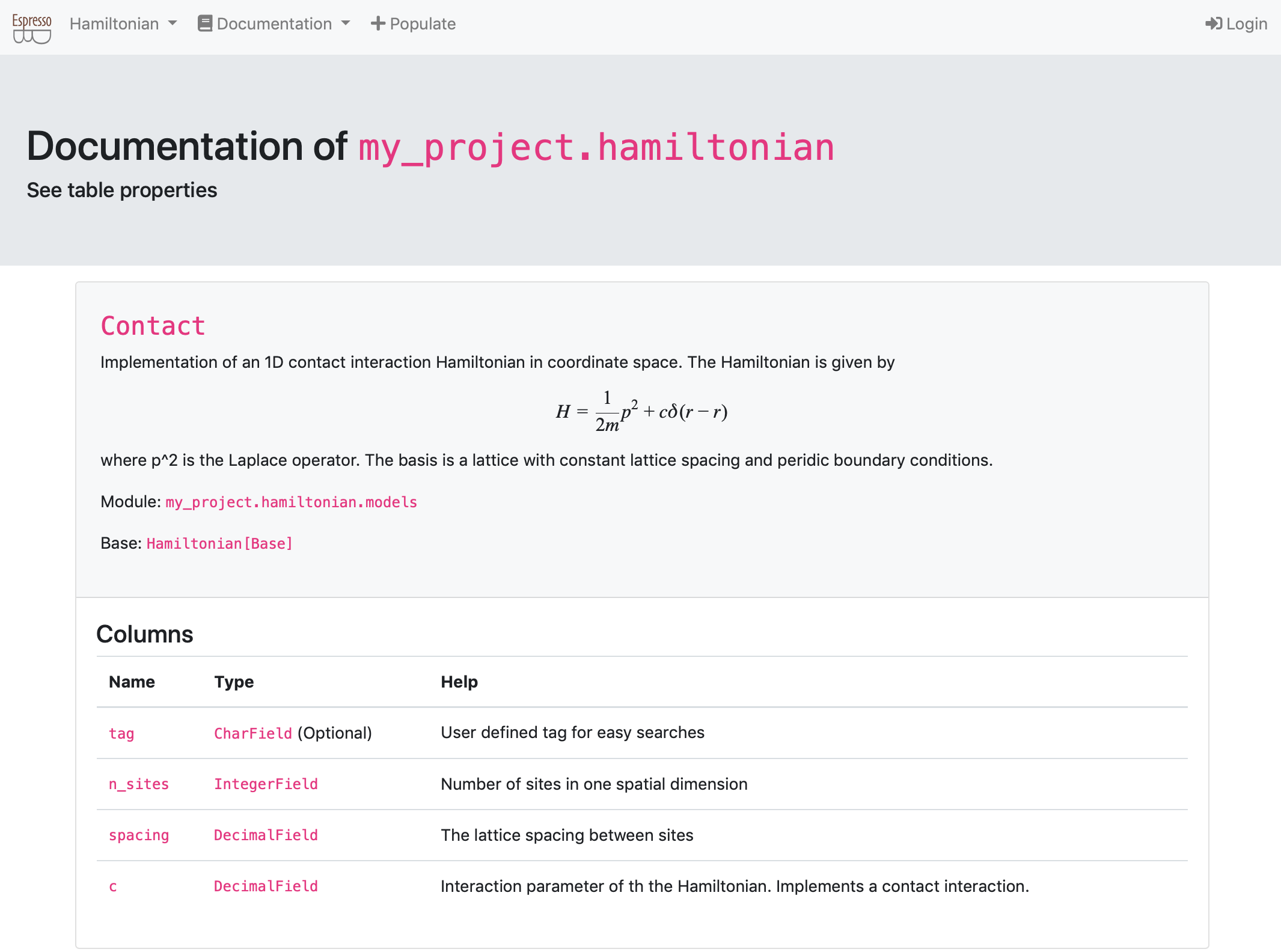 Because the web pages use a Python API as well, you can completely customize views with code you have already developed.
E.g., you can automate plots and display summaries in your browser.
If you want to, you can also make your web app public (with different layers of accessibility) and share results with others.
Because the web pages use a Python API as well, you can completely customize views with code you have already developed.
E.g., you can automate plots and display summaries in your browser.
If you want to, you can also make your web app public (with different layers of accessibility) and share results with others.See also the Documentation for more detailed usage instructions.
EspressoDB can be installed via pip:
pip install [--user] espressodb
Since EspressoDB is about creating projects, the tests are implemented for the example project. To run the tests, clone this repo, install the dependencies:
pip install .
pip install -r requirements-dev.txt
pip install -r example/my_project/requirements.txt
and run pytest (or the regular test) in example/my_project:
cd example/my_project
pytest [--cov=espressodb]
EspressoDB was developed when we created LatteDB -- a database for organizing Lattice Quantum Chromodynamics research. We intended to create a database for several purposes, e.g. to optimize the scheduling of architecture-dependent many-node jobs and to help in the eventual analysis process. For this reason, we started to abstract our thinking of how to organize physics objects.
It was the goal to have easily shareable and completely reproducible snapshots of our workflow while being flexible and not restricting ourselves too much -- in the end science is full of surprises. The challenges we encountered were:
The core module of LatteDB, EspressoDB, is trying to address those challenges.
Thanks for your interest in contributing! There are many ways to contribute to this project. Get started here.
BSD 3-Clause License. See also the LICENSE file.
FAQs
Science database interface using Django as the content manager.
We found that espressodb demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security News
TC39 advances 11 JavaScript proposals, with two moving to Stage 4, bringing better math, binary APIs, and more features one step closer to the ECMAScript spec.

Research
/Security News
A flawed sandbox in @nestjs/devtools-integration lets attackers run code on your machine via CSRF, leading to full Remote Code Execution (RCE).

Product
Customize license detection with Socket’s new license overlays: gain control, reduce noise, and handle edge cases with precision.