
Security Fundamentals
Turtles, Clams, and Cyber Threat Actors: Shell Usage
The Socket Threat Research Team uncovers how threat actors weaponize shell techniques across npm, PyPI, and Go ecosystems to maintain persistence and exfiltrate data.
gatilegrid is compatible with python 2.7, 3.5, 3.6 and 3.7
$ pip install gatilegrid
Several tile grids are supported, namely 21781, 2056, 3857 and 4326. Here is an exemple using 21781.
For 4326, an additional parameter is available (tmsCompatible=True).
from gatilegrid import getTileGrid
from gatilegrid import GeoadminTileGridLV03 as GeoadminTileGrid
zoom = 18
tileCol = 6
tileRow = 7
# Get and initialize the grid (top-left and bottom-left are availble)
gagrid = getTileGrid(21781)(originCorner='top-left')
# With extent constraint
offset = 100000
gagridExtent = GeoadminTileGrid(extent=[gagrid.MINX + offset, gagrid.MINY + offset,
gagrid.MAXX - offset, gagrid.MAXY - offset])
bounds = [xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax] = gagrid.tileBounds(zoom, tileCol, tileRow)
print(bounds)
>>> [496800.0, 247600.0, 509600.0, 260400.0]
print(gagrid.tileAddressTemplate)
>>> {zoom}/{tileCol}/{tileRow}
topLeftCorner = [xmin, ymax]
tileAddress = [tileCol, tileRow] = gagrid.tileAddress(zoom, topLeftCorner)
print(tileAddress)
>>> [6, 7]
# Get the parent tiles
parentZoom = 1
gagrid.getParentTiles(zoom, tileCol, tileRow, parentZoom)
>>> [[1, 0, 0]]
# It also works if the point is within the tile
pointInTile = [topLeftCorner[0] + 200.0, topLeftCorner[1] - 200.0]
print(gagrid.tileAddress(zoom, pointInTile))
>>> [7, 6]
# Resolution in meters
print(gagrid.getResolution(zoom))
>>> 50.0
# Scale dpi dependent (defaults to 96)
print(gagrid.getScale(zoom, dpi=96.0))
>>> 188976.0
# Tile size in meters
print(gagrid.tileSize(zoom))
>>> 12800.0
# Number of tiles at zoom
print(gagrid.numberOfTilesAtZoom(zoom))
>>> 950
# Extent dependent
print(gagridExtent.numberOfTilesAtZoom(zoom))
>>> 253
# Get the closest zoom for a given resolution
print(gagrid.getClosestZoom(245))
>>> 16
# Get the ceiling zoom for a given resolution
print(gagrid.getCeilingZoom(245))
>>> 17
# Generate tilesSpec
minZoom = 16
maxZoom = zoom
tilesSpecGenerator = gagrid.iterGrid(minZoom, maxZoom)
for i, t in enumerate(tilesSpecGenerator):
(tileBounds, zoom, tileCol, tileRow) = t
print(t)
if i == 1:
break
>>> ([420000.0, 286000.0, 484000.0, 350000.0], 16, 0, 0)
>>> ([484000.0, 286000.0, 548000.0, 350000.0], 16, 1, 0)
# Extent dependent
tilesSpecGeneratorExtent = gagridExtent.iterGrid(minZoom, maxZoom)
for i, t in enumerate(tilesSpecGeneratorExtent):
(tileBounds, zoom, tileCol, tileRow) = t
print(t)
if i = 1:
break
>>> ([484000.0, 222000.0, 548000.0, 286000.0], 16, 1, 1)
>>> ([548000.0, 222000.0, 612000.0, 286000.0], 16, 2, 1)
This module also provides a simple grid API for grid cells addressing.
from gatilegrid import Grid
extent = [485349.96, 75250.055, 833849.959, 295950.054]
resolutionX = 100.0
resolutionY = -100.0
grid = Grid(extent, resolutionX, resolutionY)
# We use singed resolution to define the origin.
# Here the origin is at the top-left corner.
print(grid.origin)
>>> [485349.96, 295950.054]
# The Grid class defines a series of useful properties
print(grid.cellArea)
>>> 10000.0
print(grid.nbCellsX)
>>> 3485
print(grid.nbCellsY)
>>> 2207
print(grid.isTopLeft)
>>> True
print(grid.isBottomRight)
>>> False
[col, row] = grid.cellAddressFromPointCoordinate([500000, 100000])
print(col)
>>> 146
print(row)
>>> 1959
# Get the extent of the cell using its address
cellExtent = grid.cellExtent(col, row)
print(cellExtent)
>>> [499949.96, 99950.054, 500049.96, 100050.054]
# Get an address range using an extent
[minCol, minRow, maxCol, maxRow] = grid.getExtentAddress([500000, 100000, 550000, 150000])
print(minCol)
>>> 146
print(minRow)
>>> 1459
print(maxCol)
>>> 646
print(maxRow)
>>> 1959
source .venv/bin/activate
python setup.py test
Edit $HOME/.pypirc and add (username and password in keepass):
[distutils]
index-servers =
pypi
pypitest
[pypi]
repository=https://upload.pypi.org/legacy/
username=iwi***
password=
[pypitest]
repository=https://test.pypi.org/legacy/
username=iwi***
password=
Bump version in setup.py.
Build, check and upload the new module to the test repository:
pip install --upgrade twine wheel setuptools
python setup.py sdist bdist_wheel
twine upload --repository testpypi dist/*
Test local install from test repository.
pip install -i https://test.pypi.org/simple/ gatilegrid
If everything is ok, push the new version to the default repository.
twine upload --repository pypi dist/*
Test the newly created module.
Create a RELEASE in github.
FAQs
Popular tile grids and grids API for web mapping applications
We found that gatilegrid demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 4 open source maintainers collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security Fundamentals
The Socket Threat Research Team uncovers how threat actors weaponize shell techniques across npm, PyPI, and Go ecosystems to maintain persistence and exfiltrate data.

Security News
At VulnCon 2025, NIST scrapped its NVD consortium plans, admitted it can't keep up with CVEs, and outlined automation efforts amid a mounting backlog.
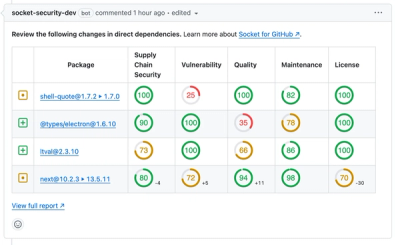
Product
We redesigned our GitHub PR comments to deliver clear, actionable security insights without adding noise to your workflow.