
Research
/Security News
Critical Vulnerability in NestJS Devtools: Localhost RCE via Sandbox Escape
A flawed sandbox in @nestjs/devtools-integration lets attackers run code on your machine via CSRF, leading to full Remote Code Execution (RCE).
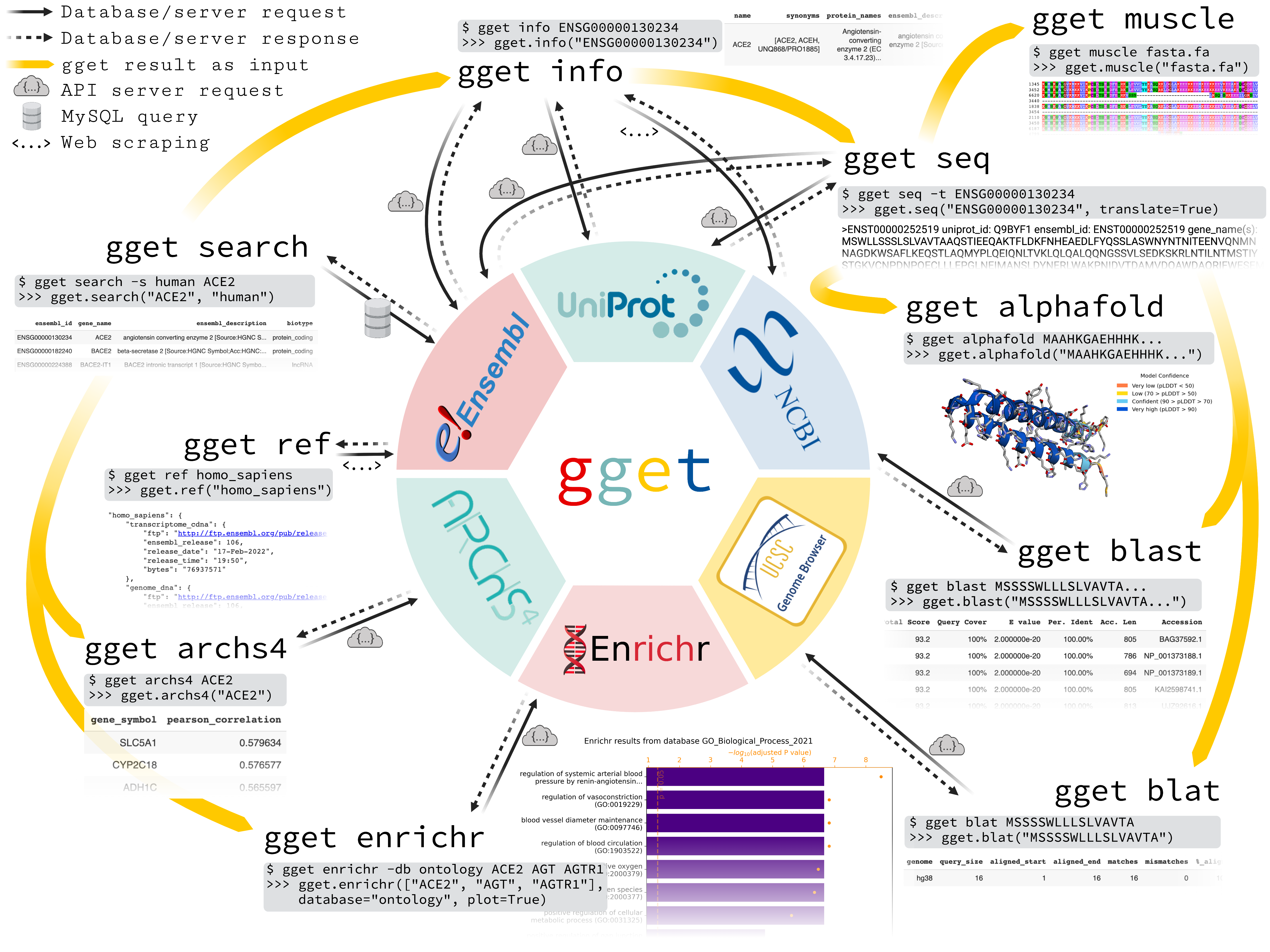
gget is a free, open-source command-line tool and Python package that enables efficient querying of genomic databases. gget consists of a collection of separate but interoperable modules, each designed to facilitate one type of database querying in a single line of code.
If you use gget in a publication, please cite*:
Luebbert, L., & Pachter, L. (2023). Efficient querying of genomic reference databases with gget. Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btac836
Read the article here: https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btac836
uv pip install gget
or
pip install --upgrade gget
For use in Jupyter Lab / Google Colab:
# Python
import gget
Command line:
# Fetch all Homo sapiens reference and annotation FTPs from the latest Ensembl release
$ gget ref homo_sapiens
# Get Ensembl IDs of human genes with "ace2" or "angiotensin converting enzyme 2" in their name/description
$ gget search -s homo_sapiens 'ace2' 'angiotensin converting enzyme 2'
# Look up gene ENSG00000130234 (ACE2) and its transcript ENST00000252519
$ gget info ENSG00000130234 ENST00000252519
# Fetch the amino acid sequence of the canonical transcript of gene ENSG00000130234
$ gget seq --translate ENSG00000130234
# Quickly find the genomic location of (the start of) that amino acid sequence
$ gget blat MSSSSWLLLSLVAVTAAQSTIEEQAKTFLDKFNHEAEDLFYQSSLAS
# BLAST (the start of) that amino acid sequence
$ gget blast MSSSSWLLLSLVAVTAAQSTIEEQAKTFLDKFNHEAEDLFYQSSLAS
# Align multiple nucleotide or amino acid sequences against each other (also accepts path to FASTA file)
$ gget muscle MSSSSWLLLSLVAVTAAQSTIEEQAKTFLDKFNHEAEDLFYQSSLAS MSSSSWLLLSLVEVTAAQSTIEQQAKTFLDKFHEAEDLFYQSLLAS
# Align one or more amino acid sequences against a reference (containing one or more sequences) (local BLAST) (also accepts paths to FASTA files)
$ gget diamond MSSSSWLLLSLVAVTAAQSTIEEQAKTFLDKFNHEAEDLFYQSSLAS -ref MSSSSWLLLSLVEVTAAQSTIEQQAKTFLDKFHEAEDLFYQSLLAS
# Use Enrichr for an ontology analysis of a list of genes
$ gget enrichr -db ontology ACE2 AGT AGTR1 ACE AGTRAP AGTR2 ACE3P
# Get the human tissue expression of gene ACE2
$ gget archs4 -w tissue ACE2
# Get the protein structure (in PDB format) of ACE2 as stored in the Protein Data Bank (PDB ID returned by gget info)
$ gget pdb 1R42 -o 1R42.pdb
# Find Eukaryotic Linear Motifs (ELMs) in a protein sequence
$ gget setup elm # setup only needs to be run once
$ gget elm -o results MSSSSWLLLSLVAVTAAQSTIEEQAKTFLDKFNHEAEDLFYQSSLAS
# Fetch a scRNAseq count matrix (AnnData format) based on specified gene(s), tissue(s), and cell type(s) (default species: human)
$ gget setup cellxgene # setup only needs to be run once
$ gget cellxgene --gene ACE2 SLC5A1 --tissue lung --cell_type 'mucus secreting cell' -o example_adata.h5ad
# Predict the protein structure of GFP from its amino acid sequence
$ gget setup alphafold # setup only needs to be run once
$ gget alphafold MSKGEELFTGVVPILVELDGDVNGHKFSVSGEGEGDATYGKLTLKFICTTGKLPVPWPTLVTTFSYGVQCFSRYPDHMKQHDFFKSAMPEGYVQERTIFFKDDGNYKTRAEVKFEGDTLVNRIELKGIDFKEDGNILGHKLEYNYNSHNVYIMADKQKNGIKVNFKIRHNIEDGSVQLADHYQQNTPIGDGPVLLPDNHYLSTQSALSKDPNEKRDHMVLLEFVTAAGITHGMDELYK
Python (Jupyter Lab / Google Colab):
import gget
gget.ref("homo_sapiens")
gget.search(["ace2", "angiotensin converting enzyme 2"], "homo_sapiens")
gget.info(["ENSG00000130234", "ENST00000252519"])
gget.seq("ENSG00000130234", translate=True)
gget.blat("MSSSSWLLLSLVAVTAAQSTIEEQAKTFLDKFNHEAEDLFYQSSLAS")
gget.blast("MSSSSWLLLSLVAVTAAQSTIEEQAKTFLDKFNHEAEDLFYQSSLAS")
gget.muscle(["MSSSSWLLLSLVAVTAAQSTIEEQAKTFLDKFNHEAEDLFYQSSLAS", "MSSSSWLLLSLVEVTAAQSTIEQQAKTFLDKFHEAEDLFYQSLLAS"])
gget.diamond("MSSSSWLLLSLVAVTAAQSTIEEQAKTFLDKFNHEAEDLFYQSSLAS", reference="MSSSSWLLLSLVEVTAAQSTIEQQAKTFLDKFHEAEDLFYQSLLAS")
gget.enrichr(["ACE2", "AGT", "AGTR1", "ACE", "AGTRAP", "AGTR2", "ACE3P"], database="ontology", plot=True)
gget.archs4("ACE2", which="tissue")
gget.pdb("1R42", save=True)
gget.setup("elm") # setup only needs to be run once
ortho_df, regex_df = gget.elm("MSSSSWLLLSLVAVTAAQSTIEEQAKTFLDKFNHEAEDLFYQSSLAS")
gget.setup("cellxgene") # setup only needs to be run once
gget.cellxgene(gene = ["ACE2", "SLC5A1"], tissue = "lung", cell_type = "mucus secreting cell")
gget.setup("alphafold") # setup only needs to be run once
gget.alphafold("MSKGEELFTGVVPILVELDGDVNGHKFSVSGEGEGDATYGKLTLKFICTTGKLPVPWPTLVTTFSYGVQCFSRYPDHMKQHDFFKSAMPEGYVQERTIFFKDDGNYKTRAEVKFEGDTLVNRIELKGIDFKEDGNILGHKLEYNYNSHNVYIMADKQKNGIKVNFKIRHNIEDGSVQLADHYQQNTPIGDGPVLLPDNHYLSTQSALSKDPNEKRDHMVLLEFVTAAGITHGMDELYK")
Call gget from R using reticulate:
system("pip install gget")
install.packages("reticulate")
library(reticulate)
gget <- import("gget")
gget$ref("homo_sapiens")
gget$search(list("ace2", "angiotensin converting enzyme 2"), "homo_sapiens")
gget$info(list("ENSG00000130234", "ENST00000252519"))
gget$seq("ENSG00000130234", translate=TRUE)
gget$blat("MSSSSWLLLSLVAVTAAQSTIEEQAKTFLDKFNHEAEDLFYQSSLAS")
gget$blast("MSSSSWLLLSLVAVTAAQSTIEEQAKTFLDKFNHEAEDLFYQSSLAS")
gget$muscle(list("MSSSSWLLLSLVAVTAAQSTIEEQAKTFLDKFNHEAEDLFYQSSLAS", "MSSSSWLLLSLVEVTAAQSTIEQQAKTFLDKFHEAEDLFYQSLLAS"), out="out.afa")
gget$diamond("MSSSSWLLLSLVAVTAAQSTIEEQAKTFLDKFNHEAEDLFYQSSLAS", reference="MSSSSWLLLSLVEVTAAQSTIEQQAKTFLDKFHEAEDLFYQSLLAS")
gget$enrichr(list("ACE2", "AGT", "AGTR1", "ACE", "AGTRAP", "AGTR2", "ACE3P"), database="ontology")
gget$archs4("ACE2", which="tissue")
gget$pdb("1R42", save=TRUE)
FAQs
Efficient querying of genomic databases.
We found that gget demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Research
/Security News
A flawed sandbox in @nestjs/devtools-integration lets attackers run code on your machine via CSRF, leading to full Remote Code Execution (RCE).

Product
Customize license detection with Socket’s new license overlays: gain control, reduce noise, and handle edge cases with precision.

Product
Socket now supports Rust and Cargo, offering package search for all users and experimental SBOM generation for enterprise projects.