
Product
Introducing Socket Fix for Safe, Automated Dependency Upgrades
Automatically fix and test dependency updates with socket fix—a new CLI tool that turns CVE alerts into safe, automated upgrades.
Lea is a Python module aiming at working with discrete probability distributions in an intuitive way.
It allows you modeling a broad range of random phenomena: gambling, weather, finance, etc. More generally, Lea may be used for any finite set of discrete values having known probability: numbers, booleans, date/times, symbols,... Each probability distribution is modeled as a plain object, which can be named, displayed, queried or processed to produce new probability distributions.
Lea also provides advanced functions and Probabilistic Programming (PP) features; these include conditional probabilities, joint probability distributions, Bayesian networks, Markov chains and symbolic computation.
All probability calculations in Lea are performed by a new exact algorithm, the Statues algorithm, which is based on variable binding and recursive generators. For problems intractable through exact methods, Lea provides on-demand approximate algorithms, namely MC rejection sampling and likelihood weighting.
Beside the above-cited functions, Lea provides some machine learning functions, including Maximum-Likelihood and Expectation-Maximization algorithms.
Lea can be used for AI, education (probability theory & PP), generation of random samples, etc.
Lea 4 requires Python 3.8+. For earlier Python versions (2.6+), Lea 3 can be used.
Please visit Lea project's wiki page for a comprehensive documentation.
FAQs
Discrete probability distributions in Python
We found that lea demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Product
Automatically fix and test dependency updates with socket fix—a new CLI tool that turns CVE alerts into safe, automated upgrades.

Security News
CISA denies CVE funding issues amid backlash over a new CVE foundation formed by board members, raising concerns about transparency and program governance.
Product
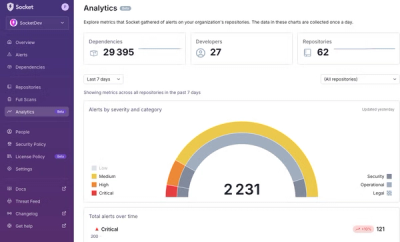
We’re excited to announce a powerful new capability in Socket: historical data and enhanced analytics.