
Product
Introducing Webhook Events for Pull Request Scans
Add real-time Socket webhook events to your workflows to automatically receive pull request scan results and security alerts in real time.
.. image:: https://github.com/amol-/linetable/actions/workflows/run-tests.yml/badge.svg :target: https://github.com/amol-/linetable/actions/workflows/run-tests.yml
.. image:: https://coveralls.io/repos/amol-/linetable/badge.svg :target: https://coveralls.io/r/amol-/linetable
.. image:: https://img.shields.io/pypi/v/linetable.svg :target: https://pypi.python.org/pypi/linetable
.. image:: https://img.shields.io/pypi/pyversions/linetable.svg :target: https://pypi.python.org/pypi/linetable
.. image:: https://img.shields.io/pypi/l/linetable.svg :target: https://pypi.python.org/pypi/linetable
linetable is a library parse and generate co_linetable attributes in Python code objects.
Based on https://github.com/python/cpython/blob/main/Objects/locations.md
linetable can be installed from pypi::
pip install linetable
should just work for most of the users
Existing linetable can be parsed using linetable.parse_linetable::
>>> def testfunc():
... x = 3
... y = x + 1
... return y
>>> list(linetable.parse_linetable(testfunc.__code__.co_linetable))
[
(1, 1, 1, 0, 0),
(1, 2, 2, 6, 7),
(1, 2, 2, 2, 3),
(1, 3, 3, 6, 7),
(1, 3, 3, 10, 11),
(2, 3, 3, 6, 11),
(1, 3, 3, 2, 3),
(1, 4, 4, 9, 10),
(1, 4, 4, 2, 10),
]
If you prefer the output in the format of dis.Positions objects,
you can create them from the yielded values::
>>> [dis.Positions(*e[1:]) for e in linetable.parse_linetable(testfunc.__code__.co_linetable)]
[Positions(lineno=1, end_lineno=1, col_offset=0, end_col_offset=0), Positions(lineno=2, end_lineno=2, col_offset=8, end_col_offset=9), Positions(lineno=2, end_lineno=2, col_offset=4, end_col_offset=5), Positions(lineno=3, end_lineno=3, col_offset=8, end_col_offset=9), Positions(lineno=3, end_lineno=3, col_offset=12, end_col_offset=13), Positions(lineno=3, end_lineno=3, col_offset=8, end_col_offset=13), Positions(lineno=3, end_lineno=3, col_offset=4, end_col_offset=5), Positions(lineno=4, end_lineno=4, col_offset=11, end_col_offset=12), Positions(lineno=4, end_lineno=4, col_offset=4, end_col_offset=12)]
If you have the linetable, you can generate back the binary encoded version
using linetable.generate_linetable::
>>> lt = [
... (1, 1, 1, 0, 0),
... (1, 2, 2, 6, 7),
... (1, 2, 2, 2, 3),
... (1, 3, 3, 6, 7),
... (1, 3, 3, 10, 11),
... (2, 3, 3, 6, 11),
... (1, 3, 3, 2, 3),
... (1, 4, 4, 9, 10),
... (1, 4, 4, 2, 10),
... ]
>>> linetable.generate_linetable(lt)
b"\x80\x00\xd8\x06\x07\x80!\xd8\x06\x07\x88!\x81e\x80!\xd8\t\n\x80("
FAQs
library to manage Python Locations Table (co_linetable)
We found that linetable demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Product
Add real-time Socket webhook events to your workflows to automatically receive pull request scan results and security alerts in real time.

Research
The Socket Threat Research Team uncovered malicious NuGet packages typosquatting the popular Nethereum project to steal wallet keys.
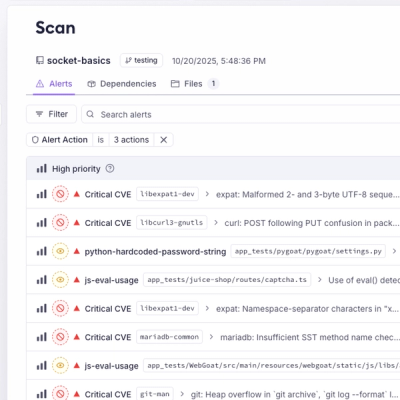
Product
A single platform for static analysis, secrets detection, container scanning, and CVE checks—built on trusted open source tools, ready to run out of the box.