
Security Fundamentals
Turtles, Clams, and Cyber Threat Actors: Shell Usage
The Socket Threat Research Team uncovers how threat actors weaponize shell techniques across npm, PyPI, and Go ecosystems to maintain persistence and exfiltrate data.
This repo aims to make grpc communication with (any version of) lnd trivial.
Currently, Go and Python are supported.
While lnd natively provides .go files for grpc communication, importing the entirety of lnd sometimes causes issues with dependencies (ex. the infamous btcd versioning), etc. We aim to solve it by having zero/minimal dependencies, and providing direct access to each version individually.
That snippet shows how to import grpc's from here, and use them to init authenticated lnd client.
package main
import (
"context"
"encoding/hex"
"fmt"
"io/ioutil"
"time"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
"google.golang.org/grpc/credentials"
"gopkg.in/macaroon.v2"
"github.com/lncm/lnd-rpc/v0.10.0/lnrpc"
)
type rpcCreds map[string]string
func (m rpcCreds) RequireTransportSecurity() bool { return true }
func (m rpcCreds) GetRequestMetadata(_ context.Context, _ ...string) (map[string]string, error) {
return m, nil
}
func newCreds(bytes []byte) rpcCreds {
creds := make(map[string]string)
creds["macaroon"] = hex.EncodeToString(bytes)
return creds
}
func getClient(hostname string, port int, tlsFile, macaroonFile string) lnrpc.LightningClient {
macaroonBytes, err := ioutil.ReadFile(macaroonFile)
if err != nil {
panic(fmt.Sprintln("Cannot read macaroon file", err))
}
mac := &macaroon.Macaroon{}
if err = mac.UnmarshalBinary(macaroonBytes); err != nil {
panic(fmt.Sprintln("Cannot unmarshal macaroon", err))
}
ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), 5*time.Second)
defer cancel()
transportCredentials, err := credentials.NewClientTLSFromFile(tlsFile, hostname)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
fullHostname:= fmt.Sprintf("%s:%d", hostname, port)
connection, err := grpc.DialContext(ctx, fullHostname, []grpc.DialOption{
grpc.WithBlock(),
grpc.WithTransportCredentials(transportCredentials),
grpc.WithPerRPCCredentials(newCreds(macaroonBytes)),
}...)
if err != nil {
panic(fmt.Errorf("unable to connect to %s: %w", fullHostname, err))
}
return lnrpc.NewLightningClient(connection)
}
func main() {
const (
hostname = "node's hostname"
port = 10009
tlsFile = "path/to/tls.cert"
macaroonFile = "path/to/macaroon/file.macaroon"
)
client := getClient(hostname, port, tlsFile, macaroonFile)
// Do stuff with the client…
}
This repo also holds the source (and scrips necessary to generate) the contents of lnd-rpc PyPI package. To use it, install the version of the version you want to use, and…
pip3 install lnd-rpc
TODO: Add an example usage here
This repo helps with:
lnd .proto's, and their dependencies.go sources for available .proto files.py sources for available .proto filesEach of these can be done in two ways:
docker run./script/download downloads all .proto files, and all their dependencies unless a specific version is provided.
./scripts/download --help
download v1.0.0
Download all .proto files necessary to build lnd's gRPC client libraries
Usage: ./scripts/download [options] LND_VERSION
Where LND_VERSION is in a form: [v]MAJOR.MINOR.PATCH (ex: v0.9.0), or "all" to download all versions
Options:
-h, --help, help Show this help message
-G, --no-google Skip download of google/api/* and google/protobuf/*
-S, --strip-version Don't include lnd version in the path (only works if LND_VERSION != "all")
-o, --output Download to a specified dir (will be created, if doesn't exist)
Examples:
./scripts/download all # Download all lnd versions, and all google/* protos
./scripts/download --no-google v0.4.2 # Only download protos for lnd v0.4.2, and no google/* protos
./scripts/download -G -S -o=~/last-lnd/ v0.9.0 # Only download protos for lnd v0.9.0, and save them to last-lnd/
# in user's HOME directory w/o the /LND_VERSION/ segment in path
github: github.com/lncm/lnd-rpc/
NOTE: this one requires DOCKER_BUILDKIT=1 due to usage of --target=
# Build with:
DOCKER_BUILDKIT=1 docker build . \
--target=protos-downloader \
--tag=lnd-rpc-downloader
# Run with:
docker run --rm -it \
--volume=$(pwd)/:/protos/ \
lnd-rpc-downloader # [VERSION|all]
./scripts/generate-go generates .go files for all available versions, unless a specific version is provided.
./scripts/generate-go --help
generate-go v1.0.0
Compile all .proto definitions into importable .go files
Usage: generate-go [options] LND_VERSION
Where LND_VERSION is in a form: [v]MAJOR.MINOR.PATCH (ex: v0.9.0), or "all" to generate for all versions
Options:
-h, --help, help Show this help message
-S, --strip-version Don't include lnd version in the path (only works if LND_VERSION != "all")
-o, --output Save generated files to a specified dir (created, if doesn't exist)
Examples:
./generate-go all
./generate-go -o /tmp/last/ v0.9.0
github: github.com/lncm/lnd-rpc/
docker build . \
--build-arg="LANG=go" \
--tag=lnd-rpc-go
docker run --rm -it \
--volume=$(pwd):/data/go/ \
lnd-rpc-go # [VERSION|all]
./scripts/generate-python generates .py files for all available versions, unless a specific version is provided.
NOTE: All generated versions are published to PyPi using this workflow
./scripts/generate-python --help
generate-python v1.0.0
Compile all .proto definitions into .py files
Usage: generate-python [options] LND_VERSION
Where LND_VERSION is in a form: [v]MAJOR.MINOR.PATCH (ex: v0.9.0), or "all" to generate for all versions
Options:
-h, --help, help Show this help message
-S, --strip-version Don't include lnd version in the path (only works if LND_VERSION != "all")
-o, --output Save generated files to a specified dir (created, if doesn't exist)
Examples:
./generate-python all
./generate-python -o /tmp/last/ v0.9.0
github: github.com/lncm/lnd-rpc/
docker build . \
--build-arg="LANG=python" \
--tag=lnd-rpc-python
docker run --rm -it \
--volume=$(pwd):/data/python/ \
lnd-rpc-python # [VERSION|all]
FAQs
gRPC bindings for various lnd versions
We found that lnd-rpc demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 2 open source maintainers collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security Fundamentals
The Socket Threat Research Team uncovers how threat actors weaponize shell techniques across npm, PyPI, and Go ecosystems to maintain persistence and exfiltrate data.

Security News
At VulnCon 2025, NIST scrapped its NVD consortium plans, admitted it can't keep up with CVEs, and outlined automation efforts amid a mounting backlog.
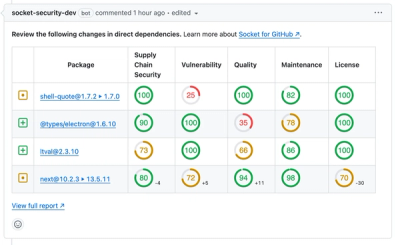
Product
We redesigned our GitHub PR comments to deliver clear, actionable security insights without adding noise to your workflow.